The anatomy of a planet
ETH researchers analyse marsquakes
2021-07-22
(Press-News.org) Since early 2019, researchers have been recording and analysing marsquakes as part of the InSight mission. This relies on a seismometer whose data acquisition and control electronics were developed at ETH Zurich. Using this data, the researchers have now measured the red planet's crust, mantle and core - data that will help determine the formation and evolution of Mars and, by extension, the entire solar system.
Mars once completely molten
We know that Earth is made up of shells: a thin crust of light, solid rock surrounds a thick mantle of heavy, viscous rock, which in turn envelopes a core consisting mainly of iron and nickel. Terrestrial planets, including Mars, have been assumed to have a similar structure. "Now seismic data has confirmed that Mars presumably was once completely molten before dividing into the crust, mantle and core we see today, but that these are different from Earth's," says Amir Khan, a scientist at the Institute of Geophysics at ETH Zurich and at the Physics Institute at the University of Zurich. Together with his ETH colleague Simon Stähler, he analysed data from NASA's InSight mission, in which ETH Zurich is participating under the leadership of Professor Domenico Giardini.
No plate tectonics on Mars
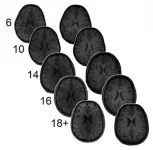
The researchers have discovered that the Martian crust under the probe's landing site near the Martian equator is between 15 and 47 kilometres thick. Such a thin crust must contain a relatively high proportion of radioactive elements, which calls into question previous models of the chemical composition of the entire crust.
Beneath the crust comes the mantle with the lithosphere of more solid rock reaching 400-600 kilometres down - twice as deep as on Earth. This could be because there is now only one continental plate on Mars, in contrast to Earth with its seven large mobile plates. "The thick lithosphere fits well with the model of Mars as a 'one-plate planet'," Khan concludes.
The measurements also show that the Martian mantle is mineralogically similar to Earth's upper mantle. "In that sense, the Martian mantle is a simpler version of Earth's mantle." But the seismology also reveals differences in chemical composition. The Martian mantle, for example, contains more iron than Earth's. However, theories as to the complexity of the layering of the Martian mantle also depend on the size of the underlying core - and here, too, the researchers have come to new conclusions.
The core is liquid and larger than expected
The Martian core has a radius of about 1,840 kilometres, making it a good 200 kilometres larger than had been assumed 15 years ago, when the InSight mission was planned. The researchers were now able to recalculate the size of the core using seismic waves. "Having determined the radius of the core, we can now calculate its density," Stähler says.
"If the core radius is large, the density of the core must be relatively low," he explains: "That means the core must contain a large proportion of lighter elements in addition to iron and nickel." These include sulphur, oxygen, carbon and hydrogen, and make up an unexpectedly large proportion. The researchers conclude that the composition of the entire planet is not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, the current investigations confirm that the core is liquid - as suspected - even if Mars no longer has a magnetic field.
Reaching the goal with different waveforms
The researchers obtained the new results by analysing various seismic waves generated by marsquakes. "We could already see different waves in the InSight data, so we knew how far away from the lander these quake epicentres were on Mars," Giardini says. To be able to say something about a planet's inner structure calls for quake waves that are reflected at or below the surface or at the core. Now, for the first time, researchers have succeeded in observing and analysing such waves on Mars.
"The InSight mission was a unique opportunity to capture this data," Giardini says. The data stream will end in a year when the lander's solar cells are no longer able to produce enough power. "But we're far from finished analysing all the data - Mars still presents us with many mysteries, most notably whether it formed at the same time and from the same material as our Earth." It is especially important to understand how the internal dynamics of Mars led it to lose its active magnetic field and all surface water. "This will give us an idea of whether and how these processes might be occurring on our planet," Giardini explains. "That's our reason why we are on Mars, to study its anatomy."
INFORMATION:
References
Khan A et al.: Upper mantle structure of Mars from InSight seismic data. Science, 373, (6553) p. 434-438. 10.1126/science.abf2966
Stähler S et al.: Seismic detection of the Martian core.
Science, 373, (6553) p. 443-448. doi:10.1126/science.abi7730
Knapmeyer-Endrun B et al.: Thickness and structure of the Martian crust from InSight seismic data. Science, 373, (6553) p. 438-443. doi:10.1126/science.abf8966
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-22
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are a renewable source of energy for electrical devices or electric vehicles, have attracted much attention as the next-generation energy solution. However, the anodes of LIBs in use today have multiple inadequacies, ranging from low ionic electronic conductivity and structural changes during the charge/discharge cycle to low specific capacity, which limits the battery's performance.
In search of a better anode material, Dr. Jun Kang of Korea Maritime and Ocean University, along with his colleagues from Pusan National University, Republic of Korea, END ...
2021-07-22
July 22, 2021 - Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, more than 40 percent of nurses and other health care workers had risks associated with an increased likelihood of burnout, reports a survey study in the August issue of the American Journal of Nursing (AJN). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The study identifies risk factors for poor well-being as well as factors associated with greater resilience - which may reduce the risk of burnout for hands-on care providers, according to the new research by Lindsay Thompson Munn, RN, PhD, and colleagues of a North Carolina healthcare system. They write, "The insights ...
2021-07-22
The University of Surrey has built an artificial intelligence (AI) model that identifies chemical compounds that promote healthy ageing - paving the way towards pharmaceutical innovations that extend a person's lifespan.
In a paper published by Nature Communication's Scientific Reports, a team of chemists from Surrey built a machine learning model based on the information from the DrugAge database to predict whether a compound can extend the life of Caenorhabditis elegans - a translucent worm that shares a similar metabolism to humans. The worm's shorter lifespan gave the researchers the opportunity to see the impact of the chemical compounds.
The AI singled ...
2021-07-22
Houston Methodist Neurological Institute researchers from the department of neurosurgery shrunk a deadly glioblastoma tumor by more than a third using a helmet generating a noninvasive oscillating magnetic field that the patient wore on his head while administering the therapy in his own home. The 53-year-old patient died from an unrelated injury about a month into the treatment, but during that short time, 31% of the tumor mass disappeared. The autopsy of his brain confirmed the rapid response to the treatment.
"Thanks to the courage of this patient and his family, we were able to test and verify the potential effectiveness of the first noninvasive therapy ...
2021-07-22
As a fourth-generation cattle farmer, Jared Decker knows that cattle suffer from health and productivity issues when they are taken from one environment -- which the herd has spent generations adapting to -- to a place with a different climate, a different elevation or even different grass. But as a researcher at the University of Missouri, Decker also sees an opportunity to use science to solve this problem, both to improve the welfare of cattle and to plug a leak in a nearly $50 billion industry in the U.S.
"When I joined MU in 2013, I moved cattle from a family farm in New Mexico to my farm here in Missouri," said Decker, an associate professor and Wurdack Chair in Animal Genetics at the College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources. "New Mexico is hot and dry, and Missouri is ...
2021-07-22
A computational analysis of COVID-19 tests suggests that, in order to minimize the number of infections in a population, the amount of testing matters more than the sensitivity of the tests that are used. Philip Cherian and Gautam Menon of Ashoka University in Sonipat, India, and Sandeep Krishna of the National Centre for Biological Sciences TIFR, Bangalore, India, present their findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
Different states in India use different mixes of two main tests for COVID-19: a very sensitive reverse-transcriptase polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) test and a less sensitive rapid antigen test. Traditional thinking holds that an all-RT-PCR approach ...
2021-07-22
The neurotransmitters GABA and glutamate have complementary roles -- GABA inhibits neurons, while glutamate makes them more active. Published 22nd July in PLOS Biology, researchers led by Roi Cohen Kadosh and George Zacharopoulos from the University of Oxford show that levels of these two neurotransmitters in the intraparietal sulcus of the brain can predict mathematics ability. The study also found that the relationships between the two neurotransmitters and arithmetic fluency switched as children developed into adults.
Levels of brain excitement/inhibition are thought to be related to learning, especially during critical periods. However, little is known about how they are related to complex learning that can take place over decades. To address this issue, the researchers ...
2021-07-22
For the first time, a team of international scientists have proven that cockatoos, an iconic Australian bird species, learn from each other a unique skill - lifting garbage bin lids to gather food. The world-first research published today in Science, confirms that cockatoos spread this novel behavior through social learning. Led by Barbara Klump and Lucy Aplin (Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior), along with John Martin (Taronga Conservation Society) and Richard Major (Australian Museum), the team have shown that this behavior by cockatoos is actually ...
2021-07-22
Based on a dozen earthquakes detected on Mars by the SEIS very broadband seismometer, developed in France, the international team of NASA's InSight mission reveals the internal structure of Mars. The three studies published July 23 in Science, involving many co-authors from French institutions and laboratories, including CNRS, the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Université de Paris, and supported by CNES and ANR, reveal, for the first time and thanks to the analysis of seismic waves, reflected and modified by these internal interfaces, an estimate of the size of the core, the thickness of the crust and the mantle structure. This is the first ...
2021-07-22
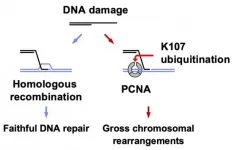
Osaka, Japan - Gross chromosomal rearrangements--where portions of the genome become moved, deleted, or inverted--can lead to cell death and diseases such as cancer in complex multicellular organisms. However, the details of how exactly these occur remain unknown. Now, studies in a single-celled organism called fission yeast have found evidence for the involvement of a protein called Rad8.
When DNA replicates or repairs itself, three copies of a protein called PCNA bind together and form a ring-like structure surrounding the DNA strand. This ring structure acts like a clamp and slides along the DNA strand. The team showed that Rad8 attaches ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The anatomy of a planet
ETH researchers analyse marsquakes