(Press-News.org) AMES, Iowa - A new study led by an Iowa State University scientist sheds light on how organisms have evolved to address imbalances in sex chromosomes.
The study looks at a species of softshell turtle, but the results could help to illuminate an important evolutionary process in many species, said Nicole Valenzuela, professor of ecology, evolution and organismal biology and lead author of the study.
Many organisms determine their sex by a pair of specialized chromosomes that appear in virtually every cell of an organism's body. A matched pair of chromosomes results in one sex, while a mismatched pair results in another sex. For instance, in humans and many other species, sex chromosomes are referred to as X and Y. Typically, two X chromosomes result in a female while XY chromosomes result in males. These chromosomes also contain the genetic codes for the production of essential proteins, and the disproportion in chromosomes in XY individuals caused by them carrying only a single X for every pair of non-sex chromosomes (called autosomes) can lead to an imbalance in the production of proteins. The study sheds light on how organisms have evolved to address such imbalances through a process called sex chromosome dosage compensation, or SCDC.
The study focused on a species of softshell turtle known as Apalone spinifera, which are among the largest of freshwater turtles and inhabit a large portion of North America, including Iowa. But the research could help scientists understand the process in other organisms as well. The study also could generate better understanding of how disease can arise if the SCDC process doesn't function correctly.
"Understanding the diversity of SCDC mechanisms in nature, how they happen and evolve, informs more broadly on how animals and humans compensate for gene dose imbalance, and why the failure to properly compensate for these differences leads to disease states," Valenzuela said.
The study was published this week in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B.
What is sex chromosome dosage compensation?
Sex chromosome dosage compensation comes into play for individuals who have mismatched sex chromosomes. In the case of the softshell turtles included in the study, the sex chromosomes are referred to as Z and W, and it's the females of the species who have mismatched, or ZW, chromosomes. That mismatch means they lack a second copy of the Z chromosome, unlike their male counterparts who have two Z chromosomes.
The Z chromosomes contain instructions for some of the proteins normally functioning cells should produce, and having only a single copy of a chromosome can result in a reduced amount of proteins produced, because protein production is often affected by the number of gene copies. More copies means more protein production. Thus, unevenness in the number of copies of genes that work together can lead to developmental, physiological or other disorders. But SCDC mechanisms work to upregulate, or increase the level, of protein production from genes in the single Z (or X) chromosomes. The importance of maintaining a proper balance is made evident by diseases caused by abnormal numbers of sex chromosomes, including Klinefelter syndrome and Turner syndrome in humans, and Valenzuela said these processes have evolutionary and health implications in many other organisms as well.
Valenzuela and her co-authors sampled softshell turtles at various stages of development, including embryos, young hatchlings and adults, and analyzed various tissues to determine which genes were activated. The researchers then compared the activity of genes from sex chromosomes and from autosomes, broken down by male and female turtles.
The study represents not only the first such study to analyze sex chromosome dosage compensation in turtles, but the findings also show that remarkably, temperature appears to affect the SCDC process in the turtles. Valenzuela has studied temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD), or the way environmental temperatures influence whether a turtle embryo develops into a male or female in species that lack sex chromosomes, in previous research. But because softshell turtles lost this ancestral TSD system, this thermal sensitivity in the SCDC came as a surprise, she said. And the way in which softshell turtles carry out SCDC is also unusual and complex.
The study found that both sexes of softshell turtles double the activity of the Zs in early embryonic development, which fixes the expression imbalance in ZW females (twice Z expression now matches autosomal expression). But this same response creates an imbalance in males (Z expression now doubles autosomal expression). At later embryonic stages, male Z expression decreases, and this effect is more pronounced at cooler than at warmer incubation temperatures, according to the study. Valenzuela said the new study is likely the first to show that temperature can impact SCDC not just in turtles, or in animals, but as broadly as in eukaryotes, or organisms in which genetic material is contained in a cell nucleus. Eukaryotic species include a huge range of organisms, including animals, plants and fungi.
INFORMATION:
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new technology which allows non-contact manipulation of small objects using sound waves. They used a hemispherical array of ultrasound transducers to generate a 3D acoustic fields which stably trapped and lifted a small polystyrene ball from a reflective surface. Although their technique employs a method similar to laser trapping in biology, adaptable to a wider range of particle sizes and materials.
The ability to move objects without touching them might sound like magic, but in the world of ...
At a glance:
Researchers studied cells collected by nasal swabs at the moment of diagnosis for both mild and severe COVID-19 patients
Cells taken from patients who went on to develop severe disease had a muted antiviral response compared to those who went on to develop mild disease
This suggests that it may be possible to develop early interventions that prevent severe COVID-19 from developing
The team also identified infected host cells and pathways associated with protection against infection that may enable new therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections
CAMBRIDGE, MA (July 23, 2021) -- Over the past 18 ...
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators have demonstrated that comprehensive genomic sequencing of all pediatric cancer patients is feasible and essential to capitalize on the lifesaving potential of precision medicine. Results from the St. Jude Genomes for Kids study appear online today in the journal Cancer Discovery.
Whole genome and whole exome sequencing of germline DNA was offered to all 309 patients who enrolled in the study. Whole genome, whole exome and RNA sequencing of tumor DNA was carried out for the 253 patients for whom adequate tumor samples were available.
Overall, 86% of patients had at least one ...
MEADVILLE, PA - July 22, 2021 - Shark Week is many things. First and foremost, it's a week of shark-themed documentary programming on the Discovery Channel. Now in its 33rd year, it's the longest-running cable event in history. It's the biggest audience that marine biologists and ocean conservationists get, attracting millions of viewers who might otherwise not ever think about sharks at all. It's a stage that has launched careers of shark scientists and inspired many others to pursue jobs as ocean scientists.
However, a new analysis shows that Shark Week is also deeply flawed in ways that undermine its goals, potentially harming both sharks and shark scientists. To document just how pervasive ...
Toronto -- People post 500 million tweets and 4 billion pieces of content on Facebook a day. What makes them do it?
An urge to share and connect with others seems obvious. But, despite how toxic the social media sandbox can get, people more often share attitudes that are framed in terms of support instead of opposition, according to new research. That happens regardless of whether the opinion itself is positive or negative.
Take gun control. The research found that people were likelier to express themselves on that issue in terms of, "I support allowing guns," or, "I support banning guns," versus, "I oppose banning guns," or, "I oppose allowing guns."
"There are a lot of controversial issues where both sides talk about what they support - pro-life and pro-choice on abortion, for example," ...
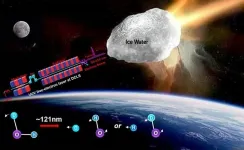
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YUAN Kaijun and Prof. YANG Xueming from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed strong isotope effects in photodissociation of the water isotopologue (HOD) using the Dalian Coherent Light Source.
Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 23.
"Our experimental results illustrate dramatically different quantum state population distributions of OH and OD fragments from HOD photodissociation. The branching ratios of the H+OD and D+OH channels display large wavelength-dependent isotopic fractionation," said Prof. YUAN.
Because ...
Research in mice, published today in Science Immunology by researchers at the Babraham Institute, UK and VIB-KU Leuven, Belgium, provides two solutions with potential to overcome a key clinical limitation of immune cell therapies. Regulatory T cells have potential in treating autoimmunity and inflammatory diseases yet they can switch from a protective to damaging function. By identifying the unstable regulatory T cells, and understanding how they can be purged from a cell population, the authors highlight a path forward for regulatory T cell transfer therapy.
Cell therapy is based on purifying cells from a patient, growing them up in cell culture to improve their properties, and then reinfusing them into the patient. Professor Adrian ...
In the evolving field of cancer biology and treatment, innovations in organ-on-a-chip microdevices allow researchers to discover more about the disease outside the human body. These organs-on-chips serve as a model of the state an actual cancer patient is in, thus allowing an opportunity to finding the correct treatment before administering it to the patient. At Texas A&M University, researchers are pushing these devices to new levels that could change the way clinicians approach cancer treatment, particularly ovarian cancer.
The team has recently submitted a patent disclosure with the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station.
"We claim several novelties in technological ...
A study by researchers at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health shows that inexpensive and convenient devices such as silicone wristbands can be used to yield quantitative air quality data, which is particularly appealing for periods of susceptibility such as pregnancy.
The research team found that the wristbands, when used as passive samplers, have the ability to bind smaller molecular weight semi-volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) -- a class of chemicals that occur naturally in coal, crude oil and gasoline and are produced when coal, oil, gas, wood, garbage and tobacco are burned -- in a similar pattern as active sampling.
Published recently in Nature's ...
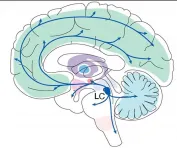
Small and seemingly specialized, the brain's locus coeruleus (LC) region has been stereotyped for its outsized export of the arousal-stimulating neuromodulator norepinephrine. In a new paper and with a new grant from the National Institutes of Health, an MIT neuroscience lab is making the case that the LC is not just an alarm button but has a more nuanced and multifaceted impact on learning, behavior and mental health than it has been given credit for.
With inputs from more than 100 other brain regions and sophisticated control of where and when it sends out norepinephrine (NE), the LC's tiny population of surprisingly diverse cells may represent an important regulator of learning from ...