New breakthrough to help immune systems in the fight against cancer
2021-07-26
(Press-News.org) New research has identified potential treatment that could improve the human immune system's ability to search out and destroy cancer cells within the body. Scientists have identified a way to restrict the activity of a group of cells which regulate the immune system, which in turn can unleash other immune cells to attack tumours in cancer patients.
"A patient's immune system is more than able to detect and remove cancer cells and immunotherapy has recently emerged as a novel therapy for many different types of cancers." Explained Nullin Divecha, Professor of Cell Signalling at the University of Southampton who led the study. "However, cancer cells can generate a microenvironment within the tumour that stops the immune system from working thereby limiting the general use and success of immunotherapy," he continued.
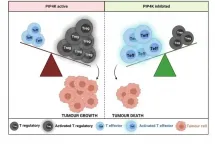
Detection and removal of cancer cells by the immune system is carried out in part by a group of cells called Teffector cells (Teffs). How well Teff cells work in detecting and removing cancer cells is in part dictated by other T cells called T-regulatory cells, or Tregs for short. Tregs physically interact with the Teff cells and produce molecules which reduce the ability of the Teff cells to work properly.
Prof Divecha added, "Tregs carry out an important function in the human body because without them, the immune system can run out of control and attack normal cells of the body. However, in cancer patients we need to give the Teff cells more freedom to carry out their job."
Molecules released by tumour cells compound the problem by attracting and accumulating Tregs, further reducing the activity and function of Teff cells. Mechanisms do exist to inhibit Treg cells, however as Treg and Teff cells are very similar, these generally also lead to inhibition of Teff cells.
In this new study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, scientists from the University of Southampton and the National Institute of Molecular Genetics in Milan showed that inhibition of a family of enzymes in cells called PIP4K could be the answer to how to restrict Tregs without affecting Teffs.
The research team isolated Tregs from healthy donors and used genetic technology to suppress the production of the PIP4K proteins. They observed that loss of PIP4Ks from Treg cells stopped them growing and responding to immune signals which would therefore stop them from blocking the growth and function of Teff cells.
Importantly, the loss of the same enzymes in Teff cells did not limit their activity.
"This was surprising because PIP4Ks are in both types of T cells in similar concentrations but our study shows that they seem to have a more important function for Tregs than Teffectors," said Dr. Alessandro Poli who carried out the experimental research.
Inhibition of PIP4K as a potential therapeutic for patients requires the development of inhibitory molecules. "Towards this end we show that treatment with a drug like inhibitor of PIP4K could enable the immune system to function more strongly and be better equipped to destroy tumour cells."
INFORMATION:
Notes to editors
The full study "PIP4Ks impact on PI3K, FOXP3 and UHRF1 signaling and modulate human regulatory T-cell proliferation and immunosuppressive activity." has been published in PNAS.
For further information and interview requests please contact Peter Franklin, Media Relations, University of Southampton, p.franklin@soton.ac.uk 07748 321087
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-26
Research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences describes a new type of liquid in thin films, which forms a high-density glass. Results generated in this study, conducted by researchers in Penn's Department of Chemistry, demonstrate how these glasses and other similar materials can be fabricated to be denser and more stable, providing a framework for developing new applications and devices through better design.
Glass is typically created through solidification, or falling out of equilibrium, of a liquid when it is cooled to a temperature where its motion arrests. The structure of a glass closely ...
2021-07-26
Mice exposed to the opioid oxycodone before birth experience permanent changes in behavior and gene expression. The new research published in eNeuro highlights a need to develop safer types of painkillers for pregnant women.
Opioids like oxycodone are prescribed to pregnant women to treat pain, but the drugs may affect the fetus, too. Opioids can pass through the placenta, binding to receptors in the fetal brain, which can lead to opioid withdrawal in newborn babies. The long-term consequences of prenatal opioid exposure haven't been fully studied, however.
To explore this, Martin et al. administered oxycodone to female mice every day for the two weeks prior ...
2021-07-26
A new MIT study of how a mammalian brain remembers what it sees shows that while individual images are stored in the visual cortex, the ability to recognize a sequence of sights critically depends on guidance from the hippocampus, a deeper structure strongly associated with memory but shrouded in mystery about exactly how.
By suggesting that the hippocampus isn't needed for basic storage of images so much as identifying the chronological relationship they may have, the new research published in Current Biology can bring neuroscientists closer to understanding how the brain coordinates long-term visual memory across key regions.
"This offers the ...
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the safety of the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccines in patients who experienced an allergic reaction to the first dose.
Authors: Kimberly G. Blumenthal, M.D., M.Sc., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3779)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. ...
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: The association between Medicare eligibility at age 65 and changes in racial and ethnic disparities in access to care and self-reported health was evaluated in this study.
Authors: Jacob Wallace, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3922)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and ...
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to investigate the relationship between loneliness and high-risk medication use in adults older than age 65.
Authors: Ashwin A. Kotwal, M.D., M.S., of the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3775)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-07-26
Lonely, older adults are nearly twice as likely to use opioids to ease pain and two-and-a-half times more likely to use sedatives and anti-anxiety medications, putting themselves at risk for drug dependency, impaired attention, falls and other accidents, and further cognitive impairment, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
The study found that just over half of 6,000 respondents in a nationally representative survey of seniors living independently were not lonely, while 40 percent were moderately lonely, and 7 percent were highly lonely.
The proportion of seniors ...
2021-07-26
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital and the University of Queensland have developed a new formulation based on regulatory T-cell exosomes (rEXS) to deliver vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibodies for choroidal neovascularization therapy.
The study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on July 26.
Ocular neovascularization is often associated with age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and other ocular diseases, which can cause severe vision loss.
The present treatment for ocular neovascular disease in clinic is intravitreal injection of VEGF antibodies (aV) to block the activity of VEGF ...
2021-07-26
BOSTON - In a multi-hospital analysis of individuals who experienced an allergic reaction to their first mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, all patients who went on to receive a second dose tolerated it without complications. The research, which was led by allergists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and is published in JAMA Internal Medicine, indicates that a first dose reaction to COVID-19 vaccination should not keep people from getting a second dose.
Allergic reactions after mRNA COVID-19 vaccinations have been reported to be as high as 2%, with anaphylaxis--a life-threatening whole-body allergic reaction--occurring in up to 2.5 per 10,000 people. ...
2021-07-26
Plants, including crops such as rice and wheat, obtain their essential mineral nutrients and water through their roots, making them an important interface between plants and the soil environment. The roots of land plants associate with a wide range of microbes - including bacteria - that are recruited from the surrounding soil and assemble into structured communities known as the root microbiota. These microbial communities are sustained by the plant host, which provides them with nutrients, primarily in the form of organic carbon compounds secreted by the root. In turn, these commensal bacteria mediate multiple processes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New breakthrough to help immune systems in the fight against cancer




