Pathak and Simon studying airborne and vehicular millimeter-wave wireless networking
2023-02-21
(Press-News.org)
Parth Pathak, Associate Professor, Computer Science, and Robert Simon, Professor, Computer Science, received funding for the project: "Airborne and Vehicular Millimeter-wave Wireless Networking."
Pathak and Simon are developing a state-of-the-art unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) mmWave wireless networking and computing software/hardware platform at George Mason University. The platform will consist of battery-powered and gas-electric hybrid hexacopters, vehicular nodes, and ground robots that will be augmented with mmWave WiFi radios.
The researchers will leverage the commercial off-the-shelf mmWave WiFi radios with beamforming capabilities to support gigabit backhauling between UAVs and front hauling with terrestrial clients. The testbed will also include mmWave software radios with superior MAC and PHY reconfigurability and control for research and development of networking protocols. The UAVs and vehicles will also be equipped with LiDARs and mmWave ranging/imaging sensors to improve the beamforming performance in unknown terrains.
Regarding the importance of this project, Pathak said, "The research will enable high-speed wireless connectivity and robust sensing for drones and ground vehicles, fostering new applications in civilian and military domains."
Pathak and Simon received $260,260 from the U.S. Department of the Army for this project. Funding began in Feb. 2023 and will end in late Jan. 2024.
###
About George Mason University
George Mason University is Virginia's largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls 38,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the last half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity and commitment to accessibility. Learn more at http://www.gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-02-21
AMES, Iowa – Let’s see, thought James Vary, how can we have a little fun with the name of our $1 million nuclear physics project?
Hmm, can we work in the term hack?
So, it’s “Nuclei and Hadrons with Quantum Computers.” Or, “NuHaQ,” for short.
“It’s a takeoff on ‘hack,’” said Vary, an Iowa State University professor of physics and astronomy and leader of a new project supported by a three-year, $1 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy. In academic computing circles, “to be a good hacker is a positive compliment. Hackers ...
2023-02-21
INFORMS Journal Organization Science New Study Key Takeaways:
Choosing who to speak to greatly impacts how ideas are heard and implemented in the workplace.
Employees who speak to managers or bosses who have the authority and resources to address an issue, led to a 12%-15% increase in implementing ideas and subsequent sales performance.
Speaking to peers was associated with a 10% decrease in implemented ideas and subsequent sales performance.
BALTIMORE, MD, February 21, 2023 – Is speaking up at work worth it? New research in the INFORMS journal Organization Science finds that new ideas can be heard and implemented in the office, but it depends on who employees talk to.
“There ...
2023-02-21
Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have generated the first induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from bats, gaining valuable insights into the close relationship between bats and viruses. This research opens the door to studying how viruses like SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, survive, spread, and evade the immune system through molecular adaptations to new hosts.
The team’s findings, published February 21 in Cell, may also shed light on the unique properties of bats that underlie their remarkable defenses against aging and cancer.
“Our study suggests that bats have evolved mechanisms to tolerate a large ...
2023-02-21
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 – It is a cruel paradox that on a planet with a surface mostly covered by water, hundreds of millions of people don’t have access to clean drinking water. As for the pollution of potable and natural water sources, one of the main culprits is arsenic, an abundant and toxic element in the earth’s crust. Arsenic is currently known as the cause of groundwater contamination in more than 100 countries – and can produce life-threatening diseases, especially for populations in developing ...
2023-02-21
In 2015, scientists for the first time detected gravitational waves, ripples in space-time that occur when major cosmic events—like the collision and merging of two black holes—disrupt the cosmos. The observation of these waves confirmed Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which predicted such waves would occur if space-time worked as he believed it did. In the seven years since, nearly 100 merging black holes have been detected by observing the gravitational waves that these extraterrestrial events emit.
Now, thanks to new research from a team of 14 led by Caltech ...
2023-02-21
About The Study: Sustained low-wage earning in midlife may be associated with elevated mortality risk and excess deaths, especially when experienced alongside unstable employment, according to the results of this study including 4,000 workers. If causal, the findings suggest that social and economic policies that improve the financial standing of low-wage workers (e.g., minimum wage laws) could improve mortality outcomes.
Authors: Katrina L. Kezios, Ph.D., of Columbia University in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.0367)
Editor’s ...
2023-02-21
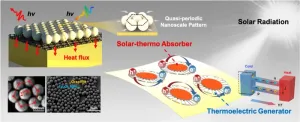
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 – Solar-thermal technology is a promising environmentally friendly energy harvesting method with a potential role to play in solving the fossil fuel energy crisis.
The technology transforms sunlight into thermal energy, but it’s challenging to suppress energy dissipation while maintaining high absorption. Existing solar energy harvesters that rely on micro- or nanoengineering don’t have sufficient scalability and flexibility, and will require a novel strategy for high-performance ...
2023-02-21
About The Study: This study found that COVID-19 treatment information on U.S. public health websites was poorly accessible, particularly for people with low literacy or limited English language proficiency, with worse accessibility for states and territories with Republican governors. The results suggest the need for national guidelines on accessibility and readability for public health websites.
Authors: Kevin A. Fiscella, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Rochester Medical Center in Rochester, New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2023-02-21
About The Study: The results of this neuroimaging study of 8,900 children ages 9 to 11 suggest that the observed sex differences in cognitive performance and brain connectivity likely reflect faster brain maturation in girls than boys. The findings are relevant to the future creation of brain developmental trajectory charts to monitor for deviations associated with impairments in cognition or behavior, including those due to psychiatric or neurological disorders.
Authors: Dardo Tomasi, Ph.D., of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism ...
2023-02-21
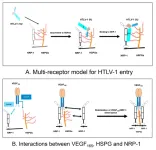
Tokyo, Japan – A retrovirus known as human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is known to cause a number of diseases, including inflammatory diseases of the eye. Recently, researchers in Japan have investigated an antibody treatment for inflammatory eye disease in ocular cells infected with HTLV-1.
In a new study published in Frontiers in Immunology, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) evaluated the safety of an anti-VEGF drug, Aflibercept, in a cell culture model exposed to HTLV-1. HTLV-1 infection can cause such diseases as adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-1 uveitis, an inflammatory eye condition.
Vascular ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pathak and Simon studying airborne and vehicular millimeter-wave wireless networking