(Press-News.org) Acute low back pain is a common cause of disability. An analysis in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research examined which non-opioid drugs are best for treating this condition.
The analysis, which included all randomized controlled trials published to date (18 studies with 3,478 patients), showed that muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) could effectively and rapidly reduce symptoms.
The combination of NSAIDs and paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen) was associated with a greater improvement than NSAIDs alone.
“This is a first step towards the optimization of the management of acute low back pain. However, specific patient characteristics such as having allergies and comorbidities must always be taken into consideration,” said lead author Alice Baroncini, MD, PhD, of RWTH University Hospital in Germany. “Further research will need to focus on the identification of the type of drugs that not only offer the best and quickest pain relief, but also show the lowest rate of symptom recurrence.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jor.25508
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Orthopaedic Research®, a publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, is the forum for the rapid publication of high quality reports of new information on the full spectrum of orthopaedic research, including life sciences, engineering, translational, and clinical studies.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in scientific research and career-connected education. Founded in 1807, Wiley enables discovery, powers education, and shapes workforces. Through its industry-leading content, digital platforms, and knowledge networks, the company delivers on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Which medications are best for treating acute low back pain?
2023-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How do companies’ climate change initiatives affect market value and greenhouse gas emissions?
2023-02-22
In an analysis published in the British Journal of Management that included 592 firms from 35 countries operating from 2002–2019, higher levels of greenhouse gas emissions were negatively associated with market value, whereas climate change initiatives were positively linked with market value.
Surprisingly, climate change initiatives were positively related to increased levels of greenhouse gas emissions. The presence of a board sustainability committee—which plays a crucial role in designing environmental initiatives and introducing best sustainability management practices—was also associated ...
Does a child’s mathematical ability have a genetic basis?
2023-02-22
A new study published in Genes, Brain and Behavior has identified several genetic variants that may be linked with mathematical abilities in children.
For the research, investigators performed genome-wide association studies on 11 mathematical ability categories in 1,146 students from Chinese elementary schools. They identified seven single nucleotide genetic variants in the genome that were strongly linked to mathematical and reasoning abilities.
Additional analyses revealed significant associations of three mathematical ...
Study supports previously identified links between bovine meat and milk factor protein expression and inflammation as possible cause of colorectal cancer
2023-02-22
Bovine meat and milk factors (BMMFs)—initially identified by de Villiers et al. in 2014—represent a class of infectious agents in beef and cow's milk that have been linked to the development of cancer. New research published in Molecular Oncology suggests that monitoring the presence and rate of expression of a BMMF-encoded replication protein (Rep) in inflammatory sites of the tissues may help identify individuals at risk for developing colorectal cancer subsequently after decades-long latency periods.
The study compared the presence of Rep and specific ...
Does electively induced labor in pregnancy affect a child’s future school performance?
2023-02-22
New research published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica found that in women with uncomplicated pregnancies, elective induction of labor at any point between 37 and 41 weeks was consistently associated with lower school performance in children at age 12.
The analysis included 266,684 children born between 37 and 42 weeks from uncomplicated pregnancies in white women in the Netherlands. School performance scores at age 12 years were lower in those from pregnancies with induced labor at 37–41 weeks compared with those with uninduced labor. At 42 weeks, there was no significant difference in school performance between these groups.
The proportion ...
Ageing with Grace: New Health and Social Care Model for Older People in Thailand
2023-02-22
In several poorer countries, ageing populations and a lack of universal access to long-term care place the burden of care for older adults on their family. To mitigate this, researchers have successfully implemented a community-integrated intermediary care model in Thailand. This care service has proven effective in reducing caregiver burden and improving the functional ability and independence of seniors. The multi-pronged model includes care prevention activities, capacity-building for family caregivers, and community respite services.
Rapidly ageing populations are a problem that many ...
Can smart watches and other fitness and wellness trackers do more harm than good for some people?
2023-02-22
Philadelphia, February 22, 2023 – In recent years, wearable devices such as smartwatches and rings, as well as smart scales, have become ubiquitous – “must-haves” for the health conscious to self-monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs. Despite the obvious benefits, certain fitness and wellness trackers could also pose serious risks for people with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) such as pacemakers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, reports a new study published in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm ...
Shock to the system
2023-02-22
Feb. 22, 2022 — In this high-tech era, wearable devices such as smartwatches have proven to be invaluable companions for the health conscious. But a new study from the University of Utah shows that for a small group of people, some of these electronic fitness gadgets could possibly be risky to their health — even potentially deadly.
University of Utah electrical and computer engineering assistant professor Benjamin Sanchez Terrones and U associate professor of medicine Benjamin Steinberg have published a new study that shows wearable devices such as ...
Promising new ENIGMA study launches to determine factors contributing to brain aging
2023-02-22
As part of an effort to address a diversity crisis in brain research, a USC-led brain research consortium is launching a massive data-gathering initiative in India. By 2050, 79% of the world's population over age 60 will live in developing countries, with 20% in India, according to the United Nations. Yet most brain research has been conducted in Caucasian populations from relatively wealthy backgrounds. This lack of ethnic diversity means that we do not know if predictors of health and disease generalize to other ethnic groups, and researchers struggle ...
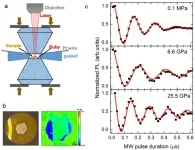
Novel quantum detection method developed to solve the problem of in-situ sensitive magnetic measurement under high pressure
2023-02-22
Substances exhibit many novel properties under high pressure, for example, pressure can induce insulator-metal or even superconductor transition. However, in-situ magnetic measurement is always a difficult problem in high pressure research and restricts the study of superconductor's Meissner effect and magnetic phase transition behavior of magnetic materials at high pressures.
A new high pressure in-situ magnetic detection method was developed recently by a collaborated research group of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, ...
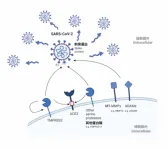
HKUMed identifies novel host protease determinants for SARS-CoV-2 infection
2023-02-22
Researchers from Department of Microbiology, School of Clinical Medicine, LKS Faculty of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), has identified novel host protease determinants, that facilitate the infection of SARS-CoV-2, including the Omicron variant, which provided new targets for combating the pandemic. In addition to the host protease determinants, members from the membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMP) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) families were found to be able to mediate SARS-CoV-2 entry, with an increase efficiency against Omicron BA.1. This finding suggests that a new treatment strategy at MMP inhibition should be explored to effectively combat ...