(Press-News.org) A new study from researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, suggests that men who regularly lift heavy objects at work have higher sperm counts. The study, published in Human Reproduction, is part of the Environment and Reproductive Health (EARTH) cohort, a clinical study which aims to explore how exposure to environmental chemicals and lifestyle choices affect reproductive health.
“We already know that exercise is associated with multiple health benefits in humans, including those observed on reproductive health, but few studies have looked at how occupational factors can contribute to these benefits,” said first author Lidia Mínguez-Alarcón, a reproductive epidemiologist in Brigham’s Channing Division of Network Medicine and co-investigator of the EARTH study. “What these new findings suggest is that physical activity during work may also be associated with significant improvement in men’s reproductive potential.”
Infertility is a growing problem, and it can be caused by a wide variety of complex factors. However, about 40% of infertility cases can be traced to male factors, such as sperm count, semen quality and sexual function. In particular, sperm count and semen quality are thought to be the major drivers of growing infertility rates among males – a previous analysis led by the EARTH study team found that among men seeking fertility treatment, sperm count and quality declined by as much as 42% between 2000 and 2017.
“Further, there is increasing evidence that male infertility is associated with common chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and autoimmune disease, highlighting the broader importance of male reproductive health,” said Mínguez-Alarcón.
The EARTH study is a collaboration between the Harvard T. Chan School of Public Health and Mass General Brigham to evaluate the effect of environment and lifestyle factors on fertility. EARTH has collected samples and survey data from over 1,500 men and women, and the current study focused on a subset of these participants, including 377 male partners in couples seeking treatment at a fertility center.
The researchers found that men who reported often lifting or moving heavy objects at work had 46% higher sperm concentration and 44% higher total sperm count compared to those with less physical jobs. Men who reported more physical activity at work also had higher levels of the male sex hormone testosterone and, counterintuitively, the female hormone estrogen.
“Contrary to what some people remember from biology class, ‘male’ and ‘female’ hormones are found in both sexes, but in different amounts,” said Mínguez-Alarcón. “In this case, we hypothesize that excess testosterone is being converted into estrogen, which is a known way for the body to keep normal levels of both hormones.”
While the current study found a relationship between physical activity and fertility in men seeking fertility treatment, it will take further research to confirm if these findings hold true for men from the general population. The researchers also hope that future studies will reveal the underlying biological mechanisms at play.
“Reproductive health is important in its own right, but more and more evidence suggests that male infertility can give us insight into broader public health issues, including the most common chronic diseases,” said Mínguez-Alarcón. “Uncovering actionable steps people can take to improve their fertility stands to benefit all of us, not just couples trying to conceive.”
Disclosures: Co-author Ramy Abou Ghayda works part time for Legacy, Inc. There are no other conflicts of interest
Funding: Funding was provided by NIH grants R01ES022955, R01ES009718, R01ES033651, and R01ES000002 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and Legacy, Inc.
Paper cited: Mínguez-Alarcón. L et al. “Occupational factors and markers of testicular function among men attending a fertility center” Human Reproduction DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dead027
END
Physically demanding work tied to higher male fertility, study suggests
Occupational factors, such as physical demands and work schedules, were associated with higher sperm concentrations and serum testosterone among men in the EARTH study
2023-02-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
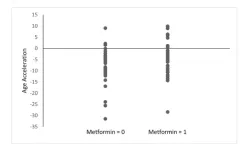
Aging | Metformin's impact on aging and longevity through DNA methylation
2023-02-22
“In this study, we compared genome-wide DNA methylation rates among metformin users and nonusers [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- February 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed as "Aging (Albany NY)" by MEDLINE/PubMed and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 3, entitled, “Metformin use history and genome-wide DNA methylation profile: potential molecular mechanism for aging and longevity.”
Metformin, a commonly prescribed anti-diabetic medication, has repeatedly been shown to hinder aging in pre-clinical ...
As sea ice declines in the Arctic, bowhead whales are adjusting their migration patterns
2023-02-22
NEWPORT, Ore. – As sea ice declines in the Arctic, bowhead whales are staying north of the Bering Strait more frequently, a shift that could affect the long-term health of the bowhead population and impact the Indigenous communities that rely on the whales, a new study by Oregon State University researchers shows.
Bowhead whales found in the Pacific Arctic, sometimes called Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort bowheads based on their migratory patterns, normally winter in the northern Bering Sea and migrate north in the spring through the Bering Strait to the Canadian Beaufort Sea, where they spend summer and fall. They then migrate ...
UBC's Daniel Pauly and Rashid Sumaila win Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement
2023-02-22
Two courageous UBC ocean fisheries experts - marine biologist Dr. Daniel Pauly and fisheries economist Dr. Rashid Sumaila — have been awarded the 2023 Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement.
The award, administered by the University of Southern California, has often been described as the ‘Nobel Prize for the Environment.’
Both are University Killam Professors at the University of British Columbia, and long-time colleagues at its Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries. They said that winning this ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for February 22, 2023
2023-02-22
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a new understanding of how HPV drives cancer development, a combination therapy to overcome treatment resistance in mantle cell lymphoma, novel ...
Early Cretaceous shift in the global carbon cycle affected both land and sea
2023-02-22
Scientists continue to refine techniques for understanding present-day changes in Earth’s environmental systems, but the planet’s distant past also offers crucial information to deepen that understanding. A geological study by University of Nebraska–Lincoln scientist Matt Joeckel and colleagues provides such information.
Scientific research in recent decades has confirmed that major changes in the global carbon cycle caused significant changes in the Earth’s atmosphere and oceans 135 million years ago, during the early Cretaceous Period. A range of questions remain about the ...
Discovery of massive early galaxies defies prior understanding of the universe
2023-02-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Six massive galaxies discovered in the early universe are upending what scientists previously understood about the origins of galaxies in the universe.
“These objects are way more massive than anyone expected,” said Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State, who modeled light from these galaxies. “We expected only to find tiny, young, baby galaxies at this point in time, but we’ve discovered galaxies as mature as our own in what was previously understood to be the dawn of the universe.”
Using the first dataset released from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, ...
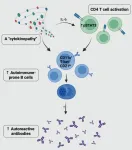
Mechanisms underlying autoimmunity in Down syndrome revealed
2023-02-22
New York, NY (February 22, 2023) – Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York have identified which parts of the immune system go awry and contribute to autoimmune diseases in individuals with Down syndrome. The findings published in the February 22 online issue of Nature [DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05736-y].
The work adds to the research team’s findings published in the journal Immunity in October 2022, showing that people with Down syndrome have less frequent but more severe viral infections.
Studying lab specimens from volunteers with Down syndrome, the investigators identified cytokines and a B cell subtype—key ...
Patients identified as frail before surgery less likely to die one year after
2023-02-22
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 22, 2023 – New research published today in JAMA Surgery shows that when frail patients are connected to resources, including conversations with a physician about possible outcomes and help preparing their body for surgery, they are less likely to die one year after surgery.
While age can be an important indicator of a patient’s likelihood of encountering adverse outcomes or complications of surgery, it does not provide a full picture of their health. Frailty considers the patient’s overall well-being, including their physical and cognitive abilities, as well as their body’s ability to recover from surgery.
“Frailty ...
Association of pandemic with unsafe living situations, intimate partner violence among pregnant individuals
2023-02-22
About The Study: This study found an overall increase in unstable and/or unsafe living situations and intimate partner violence (IPV) between January 2019 and December 2020, with a temporary increase associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. It may be useful for emergency response plans to include IPV safeguards for future pandemics. These findings suggest the need for prenatal screening for unsafe and/or unstable living situations and IPV coupled with referral to appropriate support services and preventive ...
Incidence of aggressive end-of-life care among older adults with metastatic cancer in nursing homes and community settings
2023-02-22
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that despite increased emphasis to reduce aggressive end-of-life care in the past several decades, such care remains common among older persons with metastatic cancer and is slightly more prevalent among nursing home residents than their community-dwelling counterparts. Multilevel interventions to decrease aggressive end-of-life care should target the main factors associated with its prevalence, including hospital admissions in the last 30 days of life and in-hospital death.
Authors: Siran M. Koroukian, Ph.D., of the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland, is the corresponding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Physically demanding work tied to higher male fertility, study suggestsOccupational factors, such as physical demands and work schedules, were associated with higher sperm concentrations and serum testosterone among men in the EARTH study