(Press-News.org) For people with heart failure, restricting dietary sodium intake to levels below the standard recommended maximum of about 2.3 grams per day does not bring additional benefits and may increase the risk of death, according to findings from nine randomized controlled trials in a new meta-analysis presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session Together With the World Congress of Cardiology.
Heart failure, in which the heart muscle becomes too weak or stiff to pump blood effectively, is a chronic condition affecting over 6 million adults in the U.S. Physicians recommend a low-sodium diet to reduce blood pressure and avoid common symptoms such as fluid buildup and swelling. However, previous studies have reported mixed results regarding the optimal maximum daily sodium intake for people with heart failure.
“Our findings showed that restricting dietary sodium to less than the usual recommendation was counterproductive in the management of heart failure,” said Anirudh Palicherla, MD, an internal medicine resident at Creighton University School of Medicine in Omaha, Nebraska, and the study’s lead author. “This was in line with a recent randomized controlled trial suggesting that restricting sodium more than what we do now doesn’t necessarily lead to better outcomes.”
The U.S. Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that most adults limit dietary sodium intake to 2.3 grams per day or less, equivalent to about one teaspoon of table salt. The average American consumes over 3.4 grams of sodium per day.
In the study, researchers analyzed nine randomized controlled trials that assessed different levels of sodium restriction for people with heart failure and included data on rates of death and hospitalization. Most of the studies were conducted between 2008-2022, except for one earlier study published in 1991. Together the trials enrolled nearly 3,500 heart failure patients in total.
Analyzing outcomes across all studies, researchers found that patients following a diet with a sodium intake target below 2.5 grams per day were 80% more likely to die than those following a diet with a target of 2.5 grams per day or more. The sodium limits varied from about 1.2-1.8 grams per day in the more restrictive study arms. The analysis did not show a trend toward increased hospitalizations among patients following more restrictive diets.
“Limiting sodium is still the way to go to help manage heart failure, but the amount of restriction has been up for debate,” Palicherla said. “This study shows that the focus should be on establishing a safe level of sodium consumption instead of overly restricting sodium.”
The researchers said that there was significant variability in the study designs used in the clinical trials, including different participant baseline characteristics, different health care settings and different methods for tracking sodium intake and health outcomes. Some studies required participants to restrict their fluid intake in addition to their sodium intake, while other studies did not. However, Palicherla said that the number of studies and total number of participants gives the researchers a high level of confidence in the overall findings.
Future studies could help clarify the optimal targets for dietary sodium or identify subgroups of heart failure patients who might benefit from more or less restriction, researchers said. To limit sodium intake, experts recommend eating more fresh fruits and vegetables and cooking with basic ingredients rather than processed, boxed and canned foods and sauces that often contain high amounts of sodium. When eating out or buying prepared foods, ask for nutrition information or read the food labels and choose items with the lowest amounts of sodium.
For more information on how sodium impacts heart health, visit CardioSmart.org/sodium.
Palicherla will present the study, “Sodium Restriction in Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials,” on Sunday, March 5, at 11:15 a.m. CT / 17:15 UTC in Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies Moderated Poster Theater 11, Hall F.
ACC.23/WCC will take place March 4-6, 2023, in New Orleans, bringing together cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists from around the world to share the newest discoveries in treatment and prevention. Follow @ACCinTouch, @ACCMediaCenter and #ACC23/#WCCardio for the latest news from the meeting.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at ACC.org.
###
Media Contacts
Nicole Napoli
Thy-Ann Nguyen
202.669.1465
703.638.2938
nnapoli@acc.org
thyann.nguyen@curastrategies.com
END
Measuring a key blood molecule may help doctors diagnose whether or how much impaired blood flow to a patient’s brain is contributing to dementia or cognitive problems, according to a new study led by a UCLA Health researcher.
Cerebral small vessel disease, a common disease marked by damage to the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain, is a major driver of cognitive problems and dementia in older adults. However, it can be difficult for doctors to determine whether a patient’s cognitive impairments stem predominately from Alzheimer’s disease or vascular problems, the two most common causes of ...
The university world is international, but grapples with difficulties in integrating students from different countries. New research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, points to a method that both reduces academic and social gaps and increases well-being. The recipe for success is to work in pairs – as chosen by the teacher.
There is plenty of research indicating that integration is a decisive factor for a successful student life, both socially and academically, for the individual and for the university. Students who are involved in activities and feel connected to their fellow students can get higher grades and are more likely to continue ...
PULLMAN, Wash. -- An air filter made out of corn protein instead of petroleum products can concurrently capture small particulates as well as toxic chemicals like formaldehyde that current air filters can’t.
The research could lead to better air purifiers, particularly in regions of the world that suffer from very poor air quality. Washington State University engineers report on the design and tests of materials for this bio-based filter in the journal Separation and Purification Technology.
“Particulate matter is not that challenging to filter but to simultaneously capture various kinds of chemical ...
Patients with hypertension paired with a community health worker (CHW) through their primary care practice were more than three and a half times as likely to achieve blood pressure control within six months compared to patients who were not. New research, led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, suggest that similar CHW inventions could help other underserved, immigrant communities experiencing similar disparities.
Published online today in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, the findings focus on community health workers (CHWs), lay members of a community who usually share ethnicity, language, income level, and/or life experiences with the people ...
Dr. Omar Abdul-Rahman, a leading specialist in pediatric genetic medicine, has been named chief of the Division of Medical Genetics in the Department of Pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, effective March 1.
The Division of Medical Genetics provides inpatient and outpatient consultation and medical care for children and adolescents with common and rare genetic conditions, including screening and counseling for inherited disease risk during pregnancy. Dr. Abdul-Rahman, who was recruited ...
Bottom Line: Among cancer patients who developed cardiotoxicity after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy, those treated with abatacept (Orencia), ruxolitinib, and/or mechanical ventilation as needed had a significantly lower mortality rate than those treated with standard-of-care corticosteroids.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Joe-Elie Salem, MD, PhD, a professor at Sorbonne Université, and executive assistant director of one of France’s Clinical Investigation Centers focused on cardio-metabolism
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors comprise ...
WASHINGTON, D.C.—The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced awards totaling more than $68 million that will go to 53 small businesses that are solving scientific problems. Projects include developing tools for climate research and advanced materials and technologies for clean energy conversion. Understanding the climate and the ability to convert and store energy are instrumental to meeting President Biden’s goal of a completely clean electrical grid by 2035 and net-zero greenhouse-gas emissions ...
The ongoing opioid epidemic continues to take a heavy toll on American communities, with more than 80,000 opioid-related deaths reported in 2021, according to the National Institutes of Health. Despite the severity of this issue, the neurological mechanisms underlying opioid addiction, withdrawal and relapse are not fully understood.
A study recently published in Cell Reports sheds light on the subject. Jun Wang, associate professor in the Department of Neuroscience and Experimental Therapeutics at the Texas A&M University School of Medicine, and members ...
(SEATTLE, Wednesday 22 February 2023) Two newer simplified treatment options are at least as effective as current approaches, according to the results of a world-first international clinical trial into second-line HIV therapy led by the Kirby Institute at UNSW Sydney and presented today at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Seattle.
Second-line treatment is the name given to the range of treatment options available to a person for whom the first HIV treatment offered to them does not work. Worldwide, this is about 10% of people ...
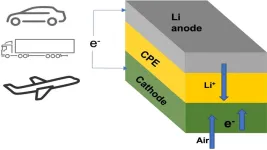
Many owners of electric cars have wished for a battery pack that could power their vehicle for more than a thousand miles on a single charge. Researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) and U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed a lithium-air battery that could make that dream a reality. The team’s new battery design could also one day power domestic airplanes and long-haul trucks.
The main new component in this lithium-air battery is a solid electrolyte instead of the usual liquid variety. Batteries with solid electrolytes ...