(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Cambridge have analysed more than 800,000 tweets and found that negative emotions expressed about geoengineering – the idea that the climate can be altered using technology – can easily fall into conspiracy.
The researchers analysed tweets 2009 and 2021 tagged with #geoengineering. They used a combination of natural language processing, deep learning and network analysis to explore how public emotions, perceptions and attitudes have changed over a 13-year period.
The researchers found that there is a large amount of ‘spillover’ between geoengineering and conspiracy theories, especially around ‘chemtrails’, a conspiracy theory dating back to the 1990s. The researchers suggest that negative emotions related to geoengineering have a contagion effect, transcending regional boundaries and engaging with wider conspiracies. Their results are reported in the journal iScience.
As the climate crisis worsens, the search for solutions has accelerated. Some potential, albeit untested and controversial, solutions involve geoengineering, where various technologies could be used to alter weather or climate. Solar radiation management (SRM) is one hypothetical geoengineering solution where temperature rise might be addressed by reflecting some sunlight back into space. Possible forms this technology could take include cirrus cloud thinning or spraying aerosols into the stratosphere. But there are few, if any, opportunities for researchers to test these potential solutions.
“The amount of funding that’s been made available for geoengineering research, and especially outdoor experiments, is tiny,” said first author Dr Ramit Debnath, Cambridge Zero Fellow at the University of Cambridge. “When you ask funders why this is, the reason often given is that the research is too controversial.”
“There are significant and well-founded concerns around geoengineering, but fundamentally we’re interested in furthering knowledge in this area,” said senior author Dr Shaun Fitzgerald, Director of the Centre for Climate Repair in Cambridge’s Department of Engineering. “In order to do that, we need to have more informed discussions. We don’t want to dismiss any concerns expressed on social media, but we do want to put them into context.”
“The views expressed on social media don’t necessarily translate directly into wider public views, but there is still a lot we can learn by studying conversations that are happening,” said Debnath. “We wanted to know whether people who were tweeting about geoengineering were in fact, a vocal minority, and if so, what else are these people talking about?”
The researchers analysed a large dataset of more than 800,000 English-language tweets sent in the 13-year period between 2009 and 2021. The researchers used natural language processing techniques to analyse the emotions expressed in the tweets and assigned each tweet a ‘toxicity score’. The researchers then conducted a network analysis to determine how tweets about geoengineering interact with other hashtag networks and conspiracy theories.
“The chemtrail conspiracy theory is particularly popular among conspiracy theorists based in the United States, and our analysis found that tweets about chemtrails are the common link between geoengineering and conspiracies,” said Debnath. “Most of these tweets are sent by American users, but they spill over across regional and national boundaries.”
The ‘chemtrail’ conspiracy theory dates back to the 1990s. Believers in this patently false conspiracy allege that condensational trails (contrails) from aircraft are intentionally seeded with various chemical or biological compounds for nefarious purposes including population control or military testing. Those who believe the chemtrails conspiracy theory also allege that aircraft could be used for intentional weather and climate modification.
The researchers say that the common link between the chemtrails conspiracy and conspiracy theories around geoengineering is the idea that bad actors are ‘weaponising’ the weather with chemicals.
Their analysis also showed that positive emotions rose on global and country scales following events related to SRM governance, and negative emotions increased following the announcement of SRM projects or experiments.
The researchers say their work could help inform future discussions around SRM and other forms of geoengineering by putting social media discussions in context. “It’s a small echo chamber, but it’s quite a noisy one,” said Debnath.
While the controversy around geoengineering will continue on social media, the team say what they really need is quality data and research. “There are risks associated with geoengineering, but how do these compare with the risks of letting climate change continue unabated?” said Fitzgerald. “I worry that knowledge hasn’t progressed in this area. What happens if some rogue entity decides to go for a huge deployment of SRM, and people end up suffering because of it? This is why it’s so important to have informed discussions backed up by quality research.”
The researchers say their study provides a data-driven glimpse into the structure of online climate misinformation that has a strong contagion effect, leading to strengthening of conspiracy theories in the public domain. Understanding such links with respect to climate action is critical for the design of counteraction strategies.
The research was supported in part by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the Cambridge Centre for Climate Repair, Cambridge Zero and Quadrature Climate Foundation, and the Google Cloud Climate Climate Innovation Challenge Award. This study is a part of an ongoing project co-lead by Dr Ramit Debnath with Cambridge Zero on improving public understand of climate change.
END
Social media posts around solar geoengineering ‘spill over’ into conspiracy theories
2023-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
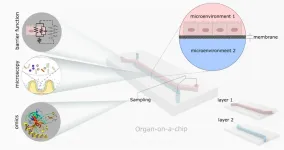
Your gut’s microbiome, on a chip
2023-02-28
WASHINGTON, Feb. 28, 2023 – The gut is one of the most complex organs in the body. Inside, it teems with a diverse microbial population that interacts and cooperates with intestinal cells to digest food and drugs. Disruptions in this microbiome have strong links to a wide spectrum of diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, asthma, and even psychological and behavioral disorders.
Valid models of the gut are therefore immensely useful for understanding its function and associated ailments. In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National ...
Portable breath-based volatile organic compound monitoring for detection of COVID-19
2023-02-28
About The Study: The findings of this diagnostic study with 167 participants suggest that breath analysis has promise for COVID-19 detection. However, similar to rapid antigen testing, the emergence of new variants poses diagnostic challenges. The results of this study warrant additional evaluation on how to overcome these challenges to use breath analysis to improve the diagnosis and care of patients.
Authors: Xudong Fan, Ph.D., and Kevin R. Ward, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Gender, racial, ethnic Inequities among recipients of multiple NIH research project grants
2023-02-28
About The Study: In this study of National Institutes of Health (NIH) investigators from 1991 to 2020, researchers found a growing gap among NIH investigators that created a cohort of highly funded NIH investigators. Importantly, there were persistent gender, ethnic, and racial inequities among this elite class of super principal investigators (investigators receiving three or more research project grants). As the NIH develops critical initiatives and reforms to promote equity among its investigators, consideration of the persistent gender and ethnic and racial gaps in this elite class ...
Study finds 1-in-5 patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease refuse statin therapy
2023-02-28
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, killing someone in the United States every 34 seconds, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, conducted the first population-based study on patients’ nonacceptance of statin therapy recommendations.
The study found that in patients at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease, over 20 percent refused to take statin medications. They were particularly ...
Digital twin opens way to effective treatment of inflammatory diseases
2023-02-28
Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis have complex disease mechanisms that can differ from patient to patient with the same diagnosis. This means that currently available drugs have little effect on many patients. Using so-called digital twins, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now obtained a deeper understanding of the “off and on” proteins that control these diseases. The study, which is published in Cell Reports Medicine, can lead to more personalised drug therapies.
Many patients with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, never feel fully healthy despite being on medication. ...
Super-fast insect urination powered by the physics of superpropulsion
2023-02-28
Saad Bhamla was in his backyard when he noticed something he had never seen before: an insect urinating. Although nearly impossible to see, the insect formed an almost perfectly round droplet on its tail and then launched it away so quickly that it seemed to disappear. The tiny insect relieved itself repeatedly for hours.
It’s generally taken for granted that what goes in must come out, so when it comes to fluid dynamics in animals, the research is largely focused on feeding rather than excretion. But Bhamla, an assistant professor in the School ...
Ultrasound device may offer new treatment option for hypertension
2023-02-28
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 28, 2023)—A device that uses ultrasound to calm overactive nerves in the kidneys may be able to help some people get their blood pressure under control.
A new study led by researchers at Columbia University and Université de Paris, France, has found that the device consistently reduced daytime ambulatory blood pressure by an average of 8.5 points among middle-aged people with hypertension.
Doctors usually prescribe lifestyle changes, such as reducing salt intake or losing weight, and medications to lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Yet about one-third of hypertensive ...
Identifying the inflammatory cells behind chemo brain
2023-02-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Immune cells that keep the brain free of debris but also contribute to inflammation are the likely culprits behind the concentration and memory problems that sometimes follow one type of chemotherapy, a new study in mice suggests.
Researchers previously showed that female mice given paclitaxel, a drug commonly used to treat breast, ovarian and other cancers, developed memory problems that were linked to inflammation in the brain. Mice receiving a placebo did not develop the “mental fog” phenomenon known as chemo brain.
In this study, the team used a technique to delete immune cells called microglia from the brains ...
Targeting wealth managers would cripple Russia's oligarchs
2023-02-28
From astronomical sums of money to opulent superyachts and lavish villas, the assets of the oligarchs providing the political and financial backing for Russian president Vladimir Putin's military ambitions have been publicly and fervently seized by Western nations since Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
Yet, the invasion—now in its second year—remains largely unabated as Russia's moneyed elite challenge sanctions in court or simply dodge them.
But a new study led by Dartmouth College researchers exposes a massive vulnerability for the Kremlin's critical cadre of billionaires—the small, secretive network of financial experts ...
The highlight advances in planetary science over the past 20 years
2023-02-28
With the development of human space technology, planetary exploration has become one of the most important space exploration activities of mankind. As of December 2021, a total of 252 planetary probes have been launched around the world. The missions reveal the deep space to humankind. In the new paper published in the journal Space: Science & Technology, Yixin Sun et al review some advances in planetary science made by these missions in the past years.
1.Research Advances in Terrestrial Planets
1. ...