(Press-News.org) Cities are bursting with life, both human and animal. The smallest of them, insects, spiders, and ants are easily overseen, but their presence – or absence – in cities has wide-reaching effects. Scientists in Austria have published a study in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, which found a correlation between the presence of arthropods – invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton; among them are bees, insects, and spiders – and level of urbanization.
“We show that richness and diversity of arthropods on trees and bushes decreases along the rural-urban gradient,” said first author Dr Marion Chatelain, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Innsbruck, Austria. “More specifically, we show that urbanization disfavors wingless groups, particularly so on trees. Indeed, web spiders and springtails are less likely to be found in the city, where, on the contrary, aphids, woodlice and flies are common.”
From bush to treetop
“In this study, we compared how different indexes of urbanization shape arthropod communities,” explained Chatelain. To do so, they collected arthropod samples at 180 sites within an area covering 56.5 sq km in and around the Austrian city of Innsbruck.
At each site, samples were collected in three micro-habitats: the canopy, the tree bark, and the bush layer. By measuring the percentage of paved-over and built-up area, vegetation or trees, Chatelain and her colleagues estimated the level of urbanization within 100 meters, 500 meters and 1000 meters around each site. Then they tested the impact it had on the total number of arthropods (abundance), how many different taxonomic groups were present (richness), and what arthropods were present. The team also considered diversity, a metric taking both abundance and richness into account. Measuring the level of urbanization at different scales allowed to better explain the effects of urbanization on arthropod communities.
Urbanization bugs unwinged, carnivorous, web-building arthropods
Their findings showed a correlation between the level of urbanization and total arthropod numbers in the bush layer. The more urbanized the site was, the more bark lice and crab spiders dwelled on the shrubs – a pattern that may be due to more nutritious leaves in the bush layer in cities. In the canopy, certain species, like flies, increased in more urbanized areas, whereas certain groups of spiders were found less often. This may indicate an advantage of winged arthropods in cities, likely because of their increased ability to move between isolated green spaces.
Chatelain and her team also observed type-specific effects on bugs. For example, they found web-building spiders at consistently lower density than those that actively hunt, such as crab spiders. This suggests that the decline or increase of spider groups correlates with their hunting modes. The lower occurrence of four out of ten spider families examined in the study, suggests a direct impact on plant-eating bugs, which were found more often in urban settings.
Certain arthropod groups do well in cities while other don’t, the scientists said. This, however, offers no direct conclusion on total bug numbers: “Because some groups thrive while other are filtered from urban areas, there are at least as many arthropods in the city as in the rural surrounding,” Chatelain stated. “In fact, in bushes, arthropods, especially bark lice and crab spiders, are actually more abundant in the city.”
From bugs to birds
The researchers also pointed out possible bottom-up effects on insect-eating birds. “Our results suggest that urbanization affects the availability of arthropod prey, which is expected to have consequences on predator nutritional status, foraging behavior, reproduction success, survival and distribution within the urban landscape,” Chatelain said. “This study is part of a larger project aiming at understanding the effects of urbanization on food availability, diet and nutritional status of great tits and blue tits.”
END
Wings, not webs: Certain bugs are the winners of urbanization, impacting cities’ insect diversity
Scientists studying how urbanization impacts insects found that some bugs are better adapted to urban environments than others
2023-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
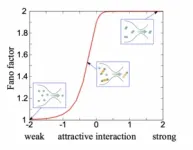
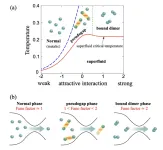
Quantum crossover: How to distinguish single-particle and pair currents
2023-03-07
If you cool down low-density atomic gas to ultralow temperatures (−273°C), you get a new state of matter called the Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC). A BEC has strongly coupled two-atom molecules behaving like a collective wave following quantum mechanics. Now if you reduce the pairing strength between them—for example, by increasing the magnetic field—the atoms form “Cooper-pairs” according to Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory—a Nobel Prize winner. The process is called BCS-BEC crossover. And the theory forms the basis ...
Females of all ages, sexes have more salt- sensitive hypertension than males
2023-03-07
There is increasing evidence that females of all ethnicities and ages are more salt sensitive than males, and that this propensity to hold onto more salt, which drives blood pressure up, increases after menopause.
Another important emerging bottom line is that healthy blood pressures might differ between the sexes, which means females might benefit from earlier and different intervention to avoid damage to their heart and vasculature.
“The realities are that women and men regulate our blood pressure differently and our blood pressures are different at baseline,” says Dr. Eric Belin de Chantemele, physiologist in the Vascular Biology Center at the Medical College of Georgia at ...
Mass General Brigham study finds virtual care team strategy improved treatment for heart failure patients
2023-03-06
Recent studies have provided strong evidence that patients with heart failure can benefit from medical therapies that can reduce risk of worsening symptoms and extend patients’ lives. But, despite new guidelines, adoption of these therapies has been slow, incomplete and inequitable. A prospective clinical study by investigators from Mass General Brigham evaluated a new approach to improve use of these therapies by putting in place a virtual care team, consisting of physicians and pharmacists, to help guide treatment strategies for patients seeking care at three Mass General Brigham hospitals: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital ...
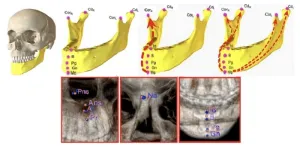
Deep-learning-based anatomical landmark identification in CT scans
2023-03-06
Millions of people around the world undergo some type of orthodontic treatment each year due largely to developmental deformities in the jaw, skull, or face. Computed tomography (CT) imaging is the go-to technique for surgeons when planning such treatments, especially surgeries. This is because CT provides 3D images of the bones and teeth, which helps the surgeon analyze complex cases in detail and determine the best treatment procedure based on that.
During the CT scan, surgeons typically try to pinpoint specific anatomical landmarks in the images. These are distinct points in the human body that can be used as a reference to make measurements and assess a condition ...
The challenges of mining for electric-vehicle batteries
2023-03-06
In August 2022, Congress passed the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). Signed by President Joe Biden, the legislation attempted to curb inflation, lower the deficit, and invest heavily into domestic clean energy.
One aspect of the bill was setting a market value-based target for battery-critical mineral content in electric vehicles (EVs). By 2027, for an EV to be tax-credit eligible, 80 percent of the market value of critical minerals in its battery must be extracted or processed domestically or by US free-trade partners (FTPs).
While this goal is well-intended, there are reasons to believe the mandate is unreachable and could create new problems.
In a commentary published ...
AI chatbot ChatGPT mirrors its users to appear intelligent
2023-03-06
LA JOLLA (March 6, 2023)—The artificial intelligence (AI) language model ChatGPT has captured the world’s attention in recent months. This trained computer chatbot can generate text, answer questions, provide translations, and learn based on the user’s feedback. Large language models like ChatGPT may have many applications in science and business, but how much do these tools understand what we say to them and how do they decide what to say back?
In new paper published in Neural Computation on February 17, 2023, Salk Professor Terrence Sejnowski, ...
Advancing engineering
2023-03-06
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — UC Santa Barbara professors Thuc-Quyen Nguyen and Carlos G. Levi are among 106 new members of the National Academy of Engineering. Academy membership honors those who have made outstanding contributions to “engineering research, practice or education, including, where appropriate, significant contributions to the engineering literature” and to “the pioneering of new and developing fields of technology, making major advancements in traditional fields of engineering, or developing/implementing innovative approaches to engineering education.”
“Our campus ...
Microscopic chalk discs in oceans play a key role in earth’s carbon cycle by propagating viruses
2023-03-06
A Rutgers-led team of scientists studying virus-host interactions of a globally abundant, armor-plated marine algae, Emiliania huxleyi, has found that the circular, chalk plates the algae produce can act as catalysts for viral infection, which has vast consequences for trillions of microscopic oceanic creatures and the global carbon cycle.
“In a drop of seawater, there will be about 1,000 to 10,000 E. huxleyi cells, and about 10 million viruses,” said Kay Bidle, a professor in the Department of ...
WVU water quality expert develops public tool for diagnosing health of America’s streams
2023-03-06
A model for predicting the levels of oxygen in water, developed by West Virginia Universityresearcher Omar Abdul-Aziz, gives citizen scientists nationwide a tool for taking action on stream pollution.
“I have been looking at water quality data for 20 years,” said Abdul-Aziz, an associate professor at the Benjamin M. Statler College of Engineering and Mineral Resources. “I can tell you that a big percentage of streams in the United States are polluted. Urban streams are getting dumpster runoff, stormwater ...
Iron & the brain: Where and when neurodevelopmental disabilities may begin during pregnancy
2023-03-06
The cells that make up the human brain begin developing long before the physical shape of the brain has formed. This early organizing of a network of cells plays a major role in brain health throughout the course of a lifetime. Numerous studies have found that mothers with low iron levels during pregnancy have a higher risk of giving birth to a child that develops cognitive impairments like autism, attention deficit syndrome, and learning disabilities. However, iron deficiency is still prevalent in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
[Press-News.org] Wings, not webs: Certain bugs are the winners of urbanization, impacting cities’ insect diversityScientists studying how urbanization impacts insects found that some bugs are better adapted to urban environments than others