Dr. B. Hadley Wilson is new American College of Cardiology President
2023-03-07
(Press-News.org) B. Hadley Wilson, MD, FACC, is the new president of the American College of Cardiology. Today marks the first day of his one-year term leading the global cardiovascular organization in its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health.
“Some of the best qualities of the ACC and its members are the commitment to patient care and the shared vision of a world where science, innovation and knowledge optimize and transform cardiovascular care and outcomes for all,” Wilson said. “I believe we all really practice what we preach. I am honored to lead an organization dedicated to innovating best practices for a growing number of patients with cardiovascular disease, combating clinician burnout and supporting the cardiovascular workforce, and expanding and diversifying our cardiovascular team.”
Wilson is an interventional cardiologist and executive vice chair at Sanger Heart and Vascular Institute/Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina, and Clinical Professor of Medicine, Wake Forest University School of Medicine. He graduated with honors from Davidson College and subsequently from Duke University School of Medicine. He trained in internal medicine at Vanderbilt University, where he served as chief resident. After completing his cardiology fellowship, Wilson joined Sanger Heart and Vascular Institute as an interventional cardiologist and served as director of the catheterization laboratory and chief of cardiology for 15 years.
Throughout his almost 25 years of ACC membership, Wilson has held numerous leadership positions, including governor of ACC's North Carolina Chapter, chair of the Board of Governors, secretary of the Board of Trustees, and chair-elect of the Governance Committee. He also was chair of the Membership Committee and served on the NCDR Management Board.
Wilson has been extensively involved in international service through the ACC. Since 2019, he has been a senior adviser to the steering committee for the ACC Global Heart Attack Treatment Initiative, a program launched by ACC to improve heart attack outcomes in low- and middle-income countries by encouraging adherence to guideline-directed medical therapy. He has also led numerous cardiology medical missions to other countries, including Haiti, Panama, Nicaragua and Honduras. Wilson is a past co-chair of ACC Latin America and is a past ACC ambassador to Mexico.
“I have been fortunate to observe and learn a tremendous amount about the importance of the ACC around the world for education, leadership, and transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all,” he said.
Other new officers for 2023-24 are Vice President Cathleen Biga, MSN, RN, FACC; Board of Trustees Member Sandra J. Lewis, MD, FACC; Finance Committee Chair-Elect Akshay K. Khandelwal, MD, FACC; Board of Governors Chair Nicole Lohr, MD, PhD, FACC; and Board of Governors Chair-Elect Himabindu Vidula, MD, MS, FACC.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org or follow @ACCinTouch.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-07
Beginning today, Nicole L. Lohr, MD, PhD, FACC, will serve as chair of the American College of Cardiology Board of Governors (BOG) and secretary of the Board of Trustees. Her term will run one year from 2023-2024.
Lohr will lead governors from chapters representing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico and representatives from the U.S. health services. The BOG is the grassroots governing body of the ACC, a nonprofit cardiovascular medical society representing over 56,000 cardiologists and cardiovascular care team members around the world.
“I have spent the last 11 years finding ways to get involved in my ACC state chapter and in various ACC councils, ...
2023-03-07
Sexual minority families—where parental sexual orientation or gender identity is considered outside cultural, societal, or physiological norms—fare as well as, or better than, ‘traditional’ families with parents of the opposite sex, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
Parental sexual orientation isn’t an important determinant of children’s development, the analysis shows.
The number of children in families with lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender ...
2023-03-07
Frequent socialising may extend the lifespan of older people, suggests a study of more than 28,000 Chinese people, published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Socialising nearly every day seems to be the most beneficial for a long life, the findings suggest.
In 2017, 962 million people around the globe were over 60, and their number is projected to double by 2050. Consequently, considerable attention has focused on the concept of ‘active’ or ‘successful’ ageing, an important component of which seems to be an active social life, note the researchers.
But most of the evidence for the health benefits of socialising ...
2023-03-07
In a world first study of daily ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) across the globe, a Monash University study has found that only 0.18% of the global land area and 0.001% of the global population are exposed to levels of PM2.5 - the world’s leading environmental health risk factor – below levels of safety recommended by Word Health Organization (WHO). Importantly while daily levels have reduced in Europe and North America in the two decades to 2019, levels have increased Southern Asia, Australia, New Zealand, Latin America and the Caribbean, ...
2023-03-07
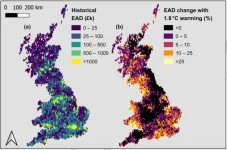
Annual damage caused by flooding in the UK could increase by more than a fifth over the next century due to climate change unless all international pledges to reduce carbon emissions are met, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and global water risk modelling leader Fathom, reveals the first-ever dataset to assess flood hazard using the most recent Met Office climate projections which factor in the likely impact of climate change.
Its findings show the forecasted annual increase in national direct flood losses, defined as physical damage to property and businesses, due to climate change in the UK can be kept below 5% above recent historical levels. ...
2023-03-07
Astrophysicists in Australia have shed new light on the state of the universe 13 billion years ago by measuring the density of carbon in the gases surrounding ancient galaxies.
The study adds another piece to the puzzle of the history of the universe.
“We found that the fraction of carbon in warm gas increased rapidly about 13 billion years ago, which may be linked to large-scale heating of gas associated with the phenomenon known as the ‘Epoch of Reionisation’,” says Dr Rebecca Davies, ASTRO 3D Postdoctoral ...
2023-03-07
Cities are bursting with life, both human and animal. The smallest of them, insects, spiders, and ants are easily overseen, but their presence – or absence – in cities has wide-reaching effects. Scientists in Austria have published a study in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, which found a correlation between the presence of arthropods – invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton; among them are bees, insects, and spiders – and level of urbanization.
“We show that richness and diversity of arthropods on trees and bushes decreases along the rural-urban gradient,” said first author Dr Marion Chatelain, a postdoctoral ...
2023-03-07
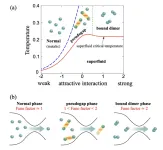
If you cool down low-density atomic gas to ultralow temperatures (−273°C), you get a new state of matter called the Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC). A BEC has strongly coupled two-atom molecules behaving like a collective wave following quantum mechanics. Now if you reduce the pairing strength between them—for example, by increasing the magnetic field—the atoms form “Cooper-pairs” according to Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory—a Nobel Prize winner. The process is called BCS-BEC crossover. And the theory forms the basis ...
2023-03-07
There is increasing evidence that females of all ethnicities and ages are more salt sensitive than males, and that this propensity to hold onto more salt, which drives blood pressure up, increases after menopause.
Another important emerging bottom line is that healthy blood pressures might differ between the sexes, which means females might benefit from earlier and different intervention to avoid damage to their heart and vasculature.
“The realities are that women and men regulate our blood pressure differently and our blood pressures are different at baseline,” says Dr. Eric Belin de Chantemele, physiologist in the Vascular Biology Center at the Medical College of Georgia at ...
2023-03-06
Recent studies have provided strong evidence that patients with heart failure can benefit from medical therapies that can reduce risk of worsening symptoms and extend patients’ lives. But, despite new guidelines, adoption of these therapies has been slow, incomplete and inequitable. A prospective clinical study by investigators from Mass General Brigham evaluated a new approach to improve use of these therapies by putting in place a virtual care team, consisting of physicians and pharmacists, to help guide treatment strategies for patients seeking care at three Mass General Brigham hospitals: Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), Brigham and Women’s Faulkner Hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Dr. B. Hadley Wilson is new American College of Cardiology President