(Press-News.org) Computer models are an important tool for studying how the brain makes and stores memories and other types of complex information. But creating such models is a tricky business. Somehow, a symphony of signals – both biochemical and electrical – and a tangle of connections between neurons and other cell types creates the hardware for memories to take hold. Yet because neuroscientists don’t fully understand the underlying biology of the brain, encoding the process into a computer model in order to study it further has been a challenge.
Now, researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have altered a commonly used computer model of memory called a Hopfield network in a way that improves performance by taking inspiration from biology . They found that not only does the new network better reflect how neurons and other cells wire up in the brain, it can also hold dramatically more memories.
The complexity added to the network is what makes it more realistic, says Thomas Burns, a PhD student in the group of Professor Tomoki Fukai, who heads OIST’s Neural Coding and Brain Computing Unit. “Why would biology have all this complexity? Memory capacity might be a reason,” Mr. Burns says.
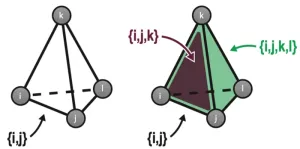
Hopfield networks store memories as patterns of weighted connections between different neurons in the system. The network is “trained” to encode these patterns, then researchers can test its memory of them by presenting a series of blurry or incomplete patterns and seeing if the network can recognize them as one it already knows. In classical Hopfield networks, however, neurons in the model reciprocally connect to other neurons in the network to form a series of what are called “pairwise” connections. Pairwise connections represent how two neurons connect at a synapse, a connection point between two neurons in the brain. But in reality, neurons have intricate branched structures called dendrites that provide multiple points for connection, so the brain relies on a much more complex arrangement of synapses to get its cognitive jobs done. Additionally, connections between neurons are modulated by other cell types called astrocytes.
“It’s simply not realistic that only pairwise connections between neurons exist in the brain,” explains Mr. Burns. He created a modified Hopfield network in which not just pairs of neurons but sets of three, four, or more neurons could link up too, such as might occur in the brain through astrocytes and dendritic trees. Although the new network allowed these so-called “set-wise” connections, over all it contained the same total number of connections as before. The researchers found that a network containing a mix of both pairwise and set-wise connections performed best and retained the highest number of memories. They estimate it works more than doubly as well as a traditional Hopfield network. “It turns out you actually need a combination of features in some balance,” says Mr. Burns. “You should have individual synapses, but you should also have some dendritic trees and some astrocytes.”
Hopfield networks are important for modeling brain processes, but they have powerful other uses too. For example, very similar types of networks called Transformers underlie AI-based language tools such as ChatGPT, so the improvements Mr. Burns and Professor Fukai have identified may also make such tools more robust.
Mr. Burns and his colleagues plan to continue working with their modified Hopfield networks to make them still more powerful . For example, in the brain the strengths of connections between neurons are not normally the same in both directions, so Mr. Burns wonders if this feature of asymmetry might also improve the network’s performance. Additionally, he would like to explore ways of making the network’s memories interact with each other, the way they do in the human brain. “Our memories are multifaceted and vast,” says Mr. Burns. “We still have a lot to uncover.”
The study is published as a conference paper, entitled, “Simplicial Hopfield networks,” in International Conference on Learning Representations.
END
What makes a neural network remember?
By modifying a classical neural network, researchers have introduced a new model inspired by recent biological findings which shows improved memory performance
2023-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How do microbes live off light?
2023-03-07
Plants convert light into a form of energy that they can use – a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – through photosynthesis. This is a complex process that also produces sugar, which the plant can use for energy later, and oxygen. Some bacteria that live in the light-exposed layers of water sources can also convert light to ATP, but the process they use is simpler and less efficient than photosynthesis. Nonetheless, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology researchers now find this process isn’t as straightforward and limited as was previously thought.
Rhodopsins are the light-driven proton pumps ...
Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
2023-03-07
1. Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3306
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of 4 cardiac surgery patients in one hospital found that they developed Mycobacterium abscessus infections, a multidrug-resistant nontuberculous mycobacteria, potentially due to a commercial water purifier. The water purifier had been installed in the hospital to improve water palatability but was inadvertently removing chlorine from the supply lines feeding ice and water machines in the affected area of ...
Dr. B. Hadley Wilson is new American College of Cardiology President
2023-03-07
B. Hadley Wilson, MD, FACC, is the new president of the American College of Cardiology. Today marks the first day of his one-year term leading the global cardiovascular organization in its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health.
“Some of the best qualities of the ACC and its members are the commitment to patient care and the shared vision of a world where science, innovation and knowledge optimize and transform cardiovascular care and outcomes for all,” Wilson said. “I believe we all really practice what we preach. I am honored to lead an organization dedicated to innovating ...
Dr. Nicole Lohr is new chair of ACC Board of Governors
2023-03-07
Beginning today, Nicole L. Lohr, MD, PhD, FACC, will serve as chair of the American College of Cardiology Board of Governors (BOG) and secretary of the Board of Trustees. Her term will run one year from 2023-2024.
Lohr will lead governors from chapters representing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico and representatives from the U.S. health services. The BOG is the grassroots governing body of the ACC, a nonprofit cardiovascular medical society representing over 56,000 cardiologists and cardiovascular care team members around the world.
“I have spent the last 11 years finding ways to get involved in my ACC state chapter and in various ACC councils, ...
Sexual minority families fare as well as, and in some ways better than, ‘traditional’ ones
2023-03-07
Sexual minority families—where parental sexual orientation or gender identity is considered outside cultural, societal, or physiological norms—fare as well as, or better than, ‘traditional’ families with parents of the opposite sex, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
Parental sexual orientation isn’t an important determinant of children’s development, the analysis shows.
The number of children in families with lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender ...
Frequent socialising linked to longer lifespan of older people
2023-03-07
Frequent socialising may extend the lifespan of older people, suggests a study of more than 28,000 Chinese people, published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Socialising nearly every day seems to be the most beneficial for a long life, the findings suggest.
In 2017, 962 million people around the globe were over 60, and their number is projected to double by 2050. Consequently, considerable attention has focused on the concept of ‘active’ or ‘successful’ ageing, an important component of which seems to be an active social life, note the researchers.
But most of the evidence for the health benefits of socialising ...
World first study into global daily air pollution shows almost nowhere on Earth is safe
2023-03-07
In a world first study of daily ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) across the globe, a Monash University study has found that only 0.18% of the global land area and 0.001% of the global population are exposed to levels of PM2.5 - the world’s leading environmental health risk factor – below levels of safety recommended by Word Health Organization (WHO). Importantly while daily levels have reduced in Europe and North America in the two decades to 2019, levels have increased Southern Asia, Australia, New Zealand, Latin America and the Caribbean, ...
Pioneering study shows flood risks can still be considerably reduced if all global promises to cut carbon emissions are kept
2023-03-07
Annual damage caused by flooding in the UK could increase by more than a fifth over the next century due to climate change unless all international pledges to reduce carbon emissions are met, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and global water risk modelling leader Fathom, reveals the first-ever dataset to assess flood hazard using the most recent Met Office climate projections which factor in the likely impact of climate change.
Its findings show the forecasted annual increase in national direct flood losses, defined as physical damage to property and businesses, due to climate change in the UK can be kept below 5% above recent historical levels. ...
Tracing 13 billion years of history by the light of ancient quasars
2023-03-07
Astrophysicists in Australia have shed new light on the state of the universe 13 billion years ago by measuring the density of carbon in the gases surrounding ancient galaxies.
The study adds another piece to the puzzle of the history of the universe.
“We found that the fraction of carbon in warm gas increased rapidly about 13 billion years ago, which may be linked to large-scale heating of gas associated with the phenomenon known as the ‘Epoch of Reionisation’,” says Dr Rebecca Davies, ASTRO 3D Postdoctoral ...
Wings, not webs: Certain bugs are the winners of urbanization, impacting cities’ insect diversity
2023-03-07
Cities are bursting with life, both human and animal. The smallest of them, insects, spiders, and ants are easily overseen, but their presence – or absence – in cities has wide-reaching effects. Scientists in Austria have published a study in Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, which found a correlation between the presence of arthropods – invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton; among them are bees, insects, and spiders – and level of urbanization.
“We show that richness and diversity of arthropods on trees and bushes decreases along the rural-urban gradient,” said first author Dr Marion Chatelain, a postdoctoral ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
The Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to Charles Manski for incorporating uncertainty into economic research and its application to public policy analysis
Walter Koroshetz joins Dana Foundation as senior advisor
Next-generation CAR-T designs that could transform cancer treatment
As health care goes digital, patients are being left behind
A clinicopathologic analysis of 740 endometrial polyps: risk of premalignant changes and malignancy
Gibson Oncology, NIH to begin Phase 2 trials of LMP744 for treatment of first-time recurrent glioblastoma
Researchers develop a high-efficiency photocatalyst using iron instead of rare metals
Study finds no evidence of persistent tick-borne infection in people who link chronic illness to ticks
New system tracks blockchain money laundering faster and more accurately
In vitro antibacterial activity of crude extracts from Tithonia diversifolia (asteraceae) and Solanum torvum (solanaceae) against selected shigella species
Qiliang (Andy) Ding, PhD, named recipient of the 2026 ACMG Foundation Rising Scholar Trainee Award
Heat-free gas sensing: LED-driven electronic nose technology enhances multi-gas detection
Women more likely to choose wine from female winemakers
E-waste chemicals are appearing in dolphins and porpoises
Researchers warn: opioids aren’t effective for many acute pain conditions
Largest image of its kind shows hidden chemistry at the heart of the Milky Way
JBNU researchers review advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
Novel cellular phenomenon reveals how immune cells extract nuclear DNA from dying cells
Printable enzyme ink powers next-generation wearable biosensors
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
[Press-News.org] What makes a neural network remember?By modifying a classical neural network, researchers have introduced a new model inspired by recent biological findings which shows improved memory performance