(Press-News.org) A terrestrial planet hovering between Mars and Jupiter would be able to push Earth out of the solar system and wipe out life on this planet, according to a UC Riverside experiment.
UCR astrophysicist Stephen Kane explained that his experiment was meant to address two notable gaps in planetary science.
The first is the gap in our solar system between the size of terrestrial and giant gas planets. The largest terrestrial planet is Earth, and the smallest gas giant is Neptune, which is four times wider and 17 times more massive than Earth. There is nothing in between.
“In other star systems there are many planets with masses in that gap. We call them super-Earths,” Kane said.
The other gap is in location, relative to the sun, between Mars and Jupiter. “Planetary scientists often wish there was something in between those two planets. It seems like wasted real estate,” he said.
These gaps could offer important insights into the architecture of our solar system, and into Earth’s evolution. To fill them in, Kane ran dynamic computer simulations of a planet between Mars and Jupiter with a range of different masses, and then observed the effects on the orbits of all other planets.
The results, published in the Planetary Science Journal, were mostly disastrous for the solar system. “This fictional planet gives a nudge to Jupiter that is just enough to destabilize everything else,” Kane said. “Despite many astronomers having wished for this extra planet, it’s a good thing we don’t have it.”
Jupiter is much larger than all the other planets combined; its mass is 318 times that of Earth, so its gravitational influence is profound. If a super-Earth in our solar system, a passing star, or any other celestial object disturbed Jupiter even slightly, all other planets would be profoundly affected.
Depending on the mass and exact location of a super-Earth, its presence could ultimately eject Mercury and Venus as well as Earth from the solar system. It could also destabilize the orbits of Uranus and Neptune, tossing them into outer space as well.
The super-Earth would change the shape of this Earth’s orbit, making it far less habitable than it is today, if not ending life entirely.
If Kane made the planet’s mass smaller and put it directly in between Mars and Jupiter, he saw it was possible for the planet to remain stable for a long period of time. But small moves in any direction and, “things would go poorly,” he said.
The study has implications for the ability of planets in other solar systems to host life. Though Jupiter-like planets, gas giants far from their stars, are only found in about 10% of the time, their presence could decide whether neighboring Earths or super-Earths have stable orbits.
These results gave Kane a renewed respect for the delicate order that holds the planets together around the sun. “Our solar system is more finely tuned than I appreciated before. It all works like intricate clock gears. Throw more gears into the mix and it all breaks,” Kane said.
END
The planet that could end life on Earth
Experiment demonstrates solar system’s fragility
2023-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
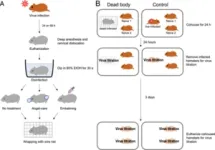
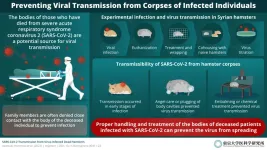
Scientists suggest guidelines to prevent SARS-CoV-2 transmission from deceased individuals
2023-03-07
Their findings highlight that embalming or "angel care" can effectively prevent virus transmission, to allow family members to say goodbye
During the pandemic, COVID-19 control measures in several countries prevented family members from coming into contact with loved ones who died from the infection. This had an impact on cremation practices and caused emotional distress. Researchers from Japan have now shown that, while deceased SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals may be a potential source of the ...
An internal thermometer tells the seeds when to germinate
2023-03-07
Germination is a crucial stage in the life of a plant as it will leave the stage of seed resistant to various environmental constraints (climatic conditions, absence of nutritive elements, etc.) to become a seedling much more vulnerable. The survival of the young plant depends on the timing of this transition. It is therefore essential that this stage be finely controlled. A Swiss team, led by scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), has discovered the internal thermometer of seeds that can delay or even block germination if temperatures are too high for the future seedling. This work could help optimize plant growth in a context of global warming. These results can be ...
Study reveals limitations in evaluating gene editing technology in human embryos
2023-03-07
A commonly used scientific method to analyze a tiny amount of DNA in early human embryos fails to accurately reflect gene edits, according to new research led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University.
The study, published today in the journal Nature Communications, involved sequencing the genomes of early human embryos that had undergone genome editing using the gene-editing tool CRISPR. The work calls into question the accuracy of a DNA-reading procedure that relies on amplifying a small amount of DNA for purposes of genetic testing.
In addition, the study reveals that gene editing to correct disease-causing mutations in early human embryos can also lead to unintended ...
Keck Medicine of USC names Ikenna (Ike) Mmeje president and CEO of USC Arcadia Hospital
2023-03-07
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has named Ikenna (Ike) Mmeje president and CEO of USC Arcadia Hospital (USC-AH), effective March 13.
In this position, Mmeje will further the health system’s mission to expand access to specialized health care and research to the San Gabriel Valley and beyond. He will oversee all management and operations of the hospital, including corporate compliance, strategic plan implementation and fundraising.
“Mmeje will utilize his wealth of knowledge and experience running complex, high-performing hospitals in his new role leading USC Arcadia Hospital,” said Rod Hanners, CEO of Keck Medicine.
Mmeje replaces current ...
What makes a neural network remember?
2023-03-07
Computer models are an important tool for studying how the brain makes and stores memories and other types of complex information. But creating such models is a tricky business. Somehow, a symphony of signals – both biochemical and electrical – and a tangle of connections between neurons and other cell types creates the hardware for memories to take hold. Yet because neuroscientists don’t fully understand the underlying biology of the brain, encoding the process into a computer model in order to study it further has been a challenge.
Now, ...
How do microbes live off light?
2023-03-07
Plants convert light into a form of energy that they can use – a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – through photosynthesis. This is a complex process that also produces sugar, which the plant can use for energy later, and oxygen. Some bacteria that live in the light-exposed layers of water sources can also convert light to ATP, but the process they use is simpler and less efficient than photosynthesis. Nonetheless, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology researchers now find this process isn’t as straightforward and limited as was previously thought.
Rhodopsins are the light-driven proton pumps ...
Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
2023-03-07
1. Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3306
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of 4 cardiac surgery patients in one hospital found that they developed Mycobacterium abscessus infections, a multidrug-resistant nontuberculous mycobacteria, potentially due to a commercial water purifier. The water purifier had been installed in the hospital to improve water palatability but was inadvertently removing chlorine from the supply lines feeding ice and water machines in the affected area of ...
Dr. B. Hadley Wilson is new American College of Cardiology President
2023-03-07
B. Hadley Wilson, MD, FACC, is the new president of the American College of Cardiology. Today marks the first day of his one-year term leading the global cardiovascular organization in its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health.
“Some of the best qualities of the ACC and its members are the commitment to patient care and the shared vision of a world where science, innovation and knowledge optimize and transform cardiovascular care and outcomes for all,” Wilson said. “I believe we all really practice what we preach. I am honored to lead an organization dedicated to innovating ...
Dr. Nicole Lohr is new chair of ACC Board of Governors
2023-03-07
Beginning today, Nicole L. Lohr, MD, PhD, FACC, will serve as chair of the American College of Cardiology Board of Governors (BOG) and secretary of the Board of Trustees. Her term will run one year from 2023-2024.
Lohr will lead governors from chapters representing all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico and representatives from the U.S. health services. The BOG is the grassroots governing body of the ACC, a nonprofit cardiovascular medical society representing over 56,000 cardiologists and cardiovascular care team members around the world.
“I have spent the last 11 years finding ways to get involved in my ACC state chapter and in various ACC councils, ...
Sexual minority families fare as well as, and in some ways better than, ‘traditional’ ones
2023-03-07
Sexual minority families—where parental sexual orientation or gender identity is considered outside cultural, societal, or physiological norms—fare as well as, or better than, ‘traditional’ families with parents of the opposite sex, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.
Parental sexual orientation isn’t an important determinant of children’s development, the analysis shows.
The number of children in families with lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] The planet that could end life on EarthExperiment demonstrates solar system’s fragility