(Press-News.org)
On 14 March, the European Platform for Neurodegenerative Diseases (EPND) launched its Cohort Catalogue. Featuring an extensive list of international cohorts across the neurodegenerative disease spectrum, the Cohort Catalogue is a central, open, accessible repository for researchers to discover ongoing studies and search metadata by disease area, biosample availability, imaging and cognitive data, and more.
The EPND consortium brings together experts in neurodegeneration research, data science, diagnosis and treatment from 29 public and private organisations. Funded by the European Union’s Innovative Medicines Initiative, EPND aims to accelerate the identification, development, and validation of biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases, by establishing a data- and sample-sharing platform for collaborative, large-scale research. The Alzheimer’s Disease Data Initiative’s AD Workbench will power the EPND platform, connecting it to a global network of permissioned users and contributors.
According to Niranjan Bose of Gates Ventures, a member of EPND’s Project Management Team, “EPND is committed to revolutionising scientific breakthroughs in the effort to diagnose, treat, and prevent neurodegenerative diseases. The Cohort Catalogue is a first step towards data and sample sharing, by increasing visibility and awareness of neurodegeneration research studies, to maximise the benefit and impact of neurodegeneration research.”
Currently, 67 research cohorts are included in the Catalogue, with sites in 17 countries across Europe. In total, these neurodegenerative disease cohorts represent 159,675 research participants over 12 different disease areas, with a particular focus on Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies, but also including participants with rarer diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and multiple system atrophy (MSA).
"To ensure the Cohort Catalogue would be as useful as possible, we incorporated a vast array of metadata for each cohort, including whether plasma and cerebrospinal fluid samples are included, or MRI or amyloid PET scan images,” said EPND co-Coordinator and clinical epidemiologist, Pieter-Jelle Visser. “This way, researchers have a single location to easily search – and discover – the complete landscape of neurodegenerative disease cohorts across Europe, and beyond.”
Using the Catalogue, researchers can search and filter cohorts by metadata characteristics, to discover cohorts that could be useful in their own research. Through the Catalogue “contact cohort” feature, researchers can engage with cohorts of interest, to kick-start new collaborations, initiate the sharing of clinical data and biosamples, and partner on funding applications. The Catalogue also offers self-service tools for researchers to add and manage their cohort listings with ease. Additional features and benefits are currently under development to extend the size and scope of the catalogue, and support the research community with enhanced discovery and future request and analysis options.
“We’re proud to be part of the EPND Cohort Catalogue,” said Rejko Krüger from the University of Luxembourg, Principal Investigator of the NCER-PD cohort. “It is an important step to support our joint quest to develop new diagnostics and treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. And I strongly encourage other cohorts to join us in this effort, to synergise the missions of our cohort programmes.”
https://discover.epnd.org
For more information about EPND, please visit https://epnd.org/. Interested in adding your cohort to the Catalogue? Click here to register and take the first steps to joining the EPND community.
Acknowledgement
The EPND project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) 2 Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No. 101034344. The IMI JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and EFPIA.
END
Birmingham based charity, Help Harry Help Others and Aston University researchers, are working together to develop a pioneering pre-surgical diagnostic tool, which could see the eventual outcome of children with brain tumours drastically improve.
Help Harry Help Others, which became a registered charity in September 2012 and marked its 10th anniversary last year, was founded by Georgie Moseley, following the passing of her son Harry. Despite fighting an inoperable brain tumour, Harry raised over £750,000 for cancer research in the last two years of his life, before he passed away ...
Disposable plastics are everywhere: Food containers, coffee cups, plastic bags. Some of these plastics, called compostable plastics, can be engineered to biodegrade under controlled conditions. However, they often look identical to conventional plastics, get recycled incorrectly and, as a result, contaminate plastic waste streams and reduce recycling efficiency. Similarly, recyclable plastics are often mistaken for compostable ones, resulting in polluted compost.
Researchers at University College London (UCL) have published a paper in Frontiers ...
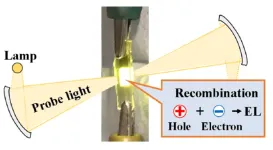
Electroluminescence is the production of light with an electrical current, without relying on heat or chemical reactions. This makes electroluminescent lights reliable and highly efficient: they are used as backlights in digital watches and in the displays of Apollo space shuttle guidance computers. Like OLEDs, light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs)—which emit light through electroluminescence—have undergone many technological advancements. Close examination of the processes that lead to luminescence is essential ...
HOUSTON – (March 13, 2023) – Synthetic biologists at Rice University are embarking on a three-year project to create “genetically encoded antibiotics,” strands of RNA that bacteria will readily copy and share that will selectively kill only disease-causing, pathogenic bacteria.
“Most bacteria pose no danger to human health,” said James Chappell, an assistant professor of biosciences and bioengineering at Rice. “The question for us as synthetic biologists is, ‘Can we create genetic programs that move through microbial communities and precisely remove only the bad actors from those communities?’”
Thanks ...
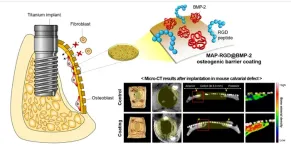
One of the key factors of success in a dental implant is the condition of the periodontium around the implant. A higher long-term success rate of dental implants requires sufficient and healthy alveolar bone. In those cases where lack of alveolar bone renders setting an implant difficult, the bone should be regenerated sufficiently to receive the implant, whether before or during the implant surgery. Development of osteogenic barrier coating material for implants by a Korean research team is expected to improve the success rate of alveolar bone grafting.
Three research teams led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha of the Chemical Engineering ...
Scientists have documented plant species for centuries to help us understand and protect the incredible diversity of flora in our world. But according to new research, many have never actually been photographed in their natural habitats – and that’s a problem.
Researchers from UNSW Sydney and the Australian Institute of Botanical Science, part of the Royal Botanic Gardens and Domain Trust, surveyed 33 major online databases of plant photographs to examine the photographic record of Australian plant species. The findings, published in New Phytologist, reveal out of 21,077 native Australian vascular plant species, almost 20 per cent lack a verifiable photograph.
Lead ...
Patients-turned-social-media-influencers routinely offer prescription drug advice to their followers and often have close ties with pharmaceutical companies, according to new University of Colorado Boulder research.
But they also tend to have good intentions, the study found.
The study, published this week in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, provides some of the first insights into the burgeoning, loosely regulated world of so-called “patient influencers,” sharing findings from 26 in-depth interviews about why and how they do it.
“The bottom line here is that patient influencers act as a form ...
A video game featuring a mystical character named Rumble has helped Griffith University researchers investigate how school kids fared following lockdown disruption.
Dr Jacqueline Allen from Griffith’s School of Criminology and Criminal Justice headed up the team looking at self-reported wellbeing in a sample of primary school-aged children in Queensland, Tasmania and Western Australia.
The team used an innovative video game called Rumble’s Quest, developed wholly within Griffith University, which measures the four key facets of wellbeing, as well as ...
Consumption of a traditional Mediterranean-type diet – rich in foods such as seafood, fruit, and nuts – is associated with a reduced risk of dementia, reports a study published in BMC Medicine. Individuals with a higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet had up to 23% lower risk for dementia compared with those who had lower adherence to a Mediterranean diet.
Diet may be an important modifiable risk factor for dementia that could be targeted for disease prevention and risk reduction but previous studies exploring the impact of a Mediterranean diet have typically been limited to small sample ...
Great apes spinning behaviours could provide clues about the role of altered states for the origins of the human mind.
Online videos observed great apes spin themselves to deliberately make themselves dizzy.
Researchers say these new findings suggest that the behaviour could be used to understand when humans evolved the desire to seek altered mental states and actively manipulate their mood and perception of reality.
Great apes deliberately spin themselves in order make themselves dizzy, academics at the University ...