(Press-News.org) A new study has found evidence of cheesemaking, using milk from multiple animals in Late Neolithic Poland.
The research suggests that early farmers reduced the lactose content in milk by making it into cheese or other dairy products like yoghurt, and used dairy products from a number of different animals, such as cows, sheep or goats.
Lactose intolerance was a common condition in almost everyone in Europe during the Neolithic and until the Late Bronze Age when the genetic mutation became widespread, enabling adults to produce lactase, the enzyme which breaks down lactose in the body.
Researchers looked at the practice of dairy processing in the Late Neolithic, identifying high curd-content residues in pottery indicating cheesemaking, and revealing that multiple dairy species were utilised.
Dr Harry Robson, from the Department of Archaeology at the University of York, said: “These results contribute significantly to our understanding of the use of dairy products by some of the earliest farmers of Central Europe.
“Whilst previous research has shown that dairy products were widely available in some European regions during this period, here, for the first time, we have clear evidence for a diversified dairy herd, including cattle, sheep and goats, from the analysis of ceramics.”
The scientists and archaeologists from the Universities of York, Cambridge, Toruń and Kraków used a multi-stranded proteomic and lipid-analysis approach to investigate ceramics and deposits on their surface, from the site of Sławęcinek in central Poland.
The new development provides evidence that cheesemaking (and other curd-enriching dairy processing) can be directly detected by scrutinising the proportion of curd proteins, by comparing proteomic data. The results are also the first of their kind in Europe.
Despite widespread lactose intolerance in the period, there is evidence of dairy being consumed during the Neolithic, such as animal bones with kill patterns expected for dairy herds, dairy lipids in ceramic vessels, and dairy proteins in ancient dental calculus or plaque.
Lead author, Miranda Evans, PhD student at Cambridge’s Department of Archaeology, said: “The proteomic results showed that the ancient residues closely resembled both the modern cheesemaking residues and cheese itself and not whole milk. This reveals that the people of Sławęcinek practised cheesemaking or another form of curd-enriching dairy processing.”
Evidence of multiple species used for cheesemaking was backed up by the presence of both cow and sheep or goat bones on the site.”
Dr Jasmine Lundy from the Department of Archaeology, said: “This study highlights how complementary lipid and proteomic analyses are, particularly in understanding the use of the ceramic vessel over time. From this, for example, we could see that not only did some techniques waterproof or seal the ceramics but also what foods were being produced in them.
The study is published in the Royal Society Open Science
END
Neolithic ceramics reveal dairy processing from milk of multiple species
2023-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Community health workers can help protect pregnant women and their babies from malaria
2023-03-15
Community health workers can make a great difference in increasing the number of pregnant women who receive life-saving preventive antimalarial treatment, according to a study conducted in four sub-Saharan African countries and led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The findings, published in The Lancet Global Health, will help to guide malaria control strategies in pregnant women and improve maternal and infant health in malaria-endemic ...
Robots can help improve mental wellbeing at work – as long as they look right
2023-03-15
Robots can be useful as mental wellbeing coaches in the workplace – but perception of their effectiveness depends in large part on what the robot looks like.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge carried out a study in a tech consultancy firm using two different robot wellbeing coaches, where 26 employees participated in weekly robot-led wellbeing sessions for four weeks. Although the robots had identical voices, facial expressions, and scripts for the sessions, the robots’ physical appearance affected how participants interacted with it.
Participants who did their wellbeing exercises with a toy-like robot said that they felt more of a connection ...
Knowing your ants from your anteaters: are wildlife documentaries showing us the ‘real’ natural world?
2023-03-15
Wildlife documentaries miss an opportunity to highlight the diversity of nature by focusing too much on mammals and birds, according to a new study.
In a new study published in People and Nature, researchers from the University of Cambridge have shown that while the production of wildlife documentaries has exploded over recent decades, they portray a biased view of the natural world around us.
Our natural world is under threat, from habitat and biodiversity loss, to high extinction rates. At the same time, there is a growing disconnect between people and nature, with children’s opportunities to experience the natural world diminishing.
Now more ...
Propeller advance paves way for quiet, efficient electric aviation
2023-03-15
Electrification is seen as having an important role to play in the fossil-free aviation of tomorrow. But electric aviation is battling a trade-off dilemma: the more energy-efficient an electric aircraft is, the noisier it gets. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a propeller design optimisation method that paves the way for quiet, efficient electric aviation.
In recent years, electrification has been described as having an important role in reducing emissions from future aviation. Due to the challenges posed by longer ranges, interest is chiefly focused on electric propeller planes covering shorter distances. Propellers connected to ...
People of color have been largely underrepresented among authors published in the American Journal of Archaeology
2023-03-14
A new demographic survey of authorship in the American Journal of Archaeology (AJA) reveals that people of color have been largely underrepresented among the scholars published in the journal. The results of the survey, which also found that authors who are the children of people without advanced degrees were also underrepresented in the journal’s pages, are published in the paper “Demographic Dynamics of Publishing in the American Journal of Archaeology.” The study was conducted ...
Common cold gives children immunity against COVID-19
2023-03-14
During the pandemic, medical doctors and researchers noticed that children and adolescents infected with COVID-19 became less ill than adults. A possible explanation for this is that children already had a prior level of immunity to COVID-19 provided by memory T cells generated by common colds.
After studying unique blood samples from children taken before the pandemic, researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now identified memory T cells that react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Four coronaviruses cause common colds
A possible explanation for this immunity in children is that they already had colds caused by one of the four coronaviruses ...
Researchers discover way to reverse infertility by reducing HDL cholesterol
2023-03-14
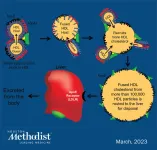
Houston Methodist scientists reversed infertility in sterile mice by reducing high-circulating cholesterol with a bacterial protein, showing further evidence that links high cholesterol to female infertility. This is a promising development, with one in every five women of childbearing age in the U.S. unable to get pregnant after trying for a year.
“We are working with a protein, called serum opacity factor, with unique characteristics,” said Corina Rosales, Ph.D., assistant research professor of molecular biology in medicine with the Houston Methodist ...
UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center celebrates 500th lung transplant
2023-03-14
LEXINGTON, Ky. (March 14, 2023) — The lung transplant team at UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center recently celebrated a major milestone, performing the 500th lung transplant since the lung transplant program was founded in 1991.
“This is an impressive milestone, and our whole staff — physicians, surgeons, nurse practitioners, nurse coordinators, pharmacists, nutritionists, social workers, therapists and support staff — should be very proud of their success,” said Sravanthi Nandavaram, M.D., medical director of the Lung Transplant Program. ...
How neuroimaging can be better utilized to yield diagnostic information about individuals
2023-03-14
Since the development of functional magnetic resonance imaging in the 1990s, the reliance on neuroimaging has skyrocketed as researchers investigate how fMRI data from the brain at rest, and anatomical brain structure itself, can be used to predict individual traits, such as depression, cognitive decline, and brain disorders.
Brain imaging has the potential to reveal the neural underpinnings of many traits, from disorders like depression and chronic widespread pain to why one person has a better memory than another, and why some people’s memories are resilient as they age. But how reliable brain imaging is for detecting traits has been a subject of wide debate.
Prior research ...
NASA’s Webb Telescope captures rarely seen prelude to supernova
2023-03-14
The rare sight of a Wolf-Rayet star – among the most luminous, most massive, and most briefly detectable stars known – was one of the first observations made by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in June 2022. Webb shows the star, WR 124, in unprecedented detail with its powerful infrared instruments. The star is 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
Massive stars race through their lifecycles, and only some of them go through a brief Wolf-Rayet phase before going supernova, making Webb’s detailed observations of this rare phase valuable to astronomers. Wolf-Rayet stars are in the process of casting off their outer layers, ...