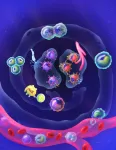
(Press-News.org) The ability of a cell to divide, to proliferate, is essential for life and gives rise to the formation of complex organisms from a single cell. It also allows the replacement of used cells from a limited number of “stem” cells, which then proliferate and specialize. In cancer, however, cell proliferation is no longer controlled and becomes chaotic. Researchers from the GIGA Institute at the University of Liège have discovered that, in a healthy individual, certain blood immune cells, the monocytes, also have this ability to proliferate, with the aim to replace tissue macrophages, which are essential for the proper functioning of our body. This study is published in Nature Immunology.
The formation of complex multicellular organisms, which human beings belong to, requires the generation of billions of cells from a limited number of progenitor cells that have first proliferated and then acquire particular morphologies and functions while assembling into tissues and organs. Our current knowledge indicates that most of the cells that constitute a living organism arise from so-called "stem" cells, which have divided by a process called mitosis in order to give rise to a greater number of cells. These cells then stop proliferating to specialize, differentiate and form muscles, brain, bones, immune cells, etc. When proliferation is no longer properly regulated, this can lead to the development of various diseases, among which cancers represent the most striking example. In a study published in Nature Immunology, Professor Thomas Marichal (Professor at ULiège, Welbio investigator at the WEL Research Institute) and his team from the GIGA Institute at ULiège discovered that this ability to proliferate is not merely restricted to stem cells, but is also an as-yet-unknown function of blood immune cells, the monocytes. Indeed, blood monocytes, previously considered as differentiated cells, are capable of proliferating and generating a pool of monocytes in the tissues in order to give rise to macrophages, which are important immune cells that protect us against microbes and support the proper functioning of our organs.
“This is a major fundamental discovery, which changes our conception of the involvement of cell proliferation in the constitution and maintenance of our immune system.” explains Thomas Marichal, director of the study. "Our finding also suggests that the information that can be drawn from an enumeration of blood monocytes, classically carried out during a blood test, would reflect only little of what is happening at the level of the tissues, during 'infection or inflammation, for example, since monocytes can proliferate when they enter tissues”. He also adds: “Fortunately, this proliferation is extremely well controlled and does not lead to a tumoral process. It has only one goal: to allow, as effectively as possible, the replacement of immune cells that populate our tissues: the macrophages”.
This discovery, funded by the WEL Research Institute (WELRI – Welbio) and by the European Research Council (see press release) was possible thanks to the development of new tools and the use of innovative technologies. “This study is a great example of how technological advances can drive breakthrough scientific discoveries. It would have been extremely difficult, if not impossible, to study with such a resolution this population of proliferating monocytes only 10 years ago. This required the use of state-of-the-art equipment recently acquired at the GIGA Institute, the generation of complex genomic data and very sophisticated bioinformatics analyses" explains Domien Vanneste, funded by a doctoral grant from the FNRS and first author of the study. This study paves the way for future investigations that will evaluate the possibility of manipulating or controlling monocyte proliferation for therapeutic purposes, at the benefit of an enhanced health.
END
Discovery of an unexpected function of blood immune cells : Their ability to proliferate !
Rearchers from the University of Liège publishe a fundamental discovery that suggests a greater involvement of cell proliferation in the functioning of our immune system
2023-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Women working rotating shifts especially likely to be frail, York study finds
2023-03-17
March 17, 2023, TORONTO — A new study led by researchers at York University has found a link between shift work and frailty among middle-aged and older workers in Canada, especially for women on rotating shifts.
While there is a large body of research suggesting the disruptions to circadian rhythms that shift workers experience are linked to various illnesses, this study was the first to take a comprehensive or “holistic” look at the connection between shift work and frailty.
“We cannot ignore the negative health outcomes related to shift work, including cardiovascular diseases, ...
Argonne hosts conference for undergraduate women in physics
2023-03-17
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory hosted an American Physical Society (APS) Conference for Undergraduate Women in Physics (CUWiP) on Jan. 20-22. The conference series, sponsored by DOE and the National Science Foundation, is designed to support undergraduate women and gender minorities in physics by connecting them with resources, community, information on graduate school and professionals in their field. It also provides students with access to other women in physics with whom they can share experiences, advice and ideas.
The January 2023 event is one of 14 APS CUWiP events hosted across the country and ...
How can we tackle the biggest challenges? Ask a plant
2023-03-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 16, 2023 — Without plants, we’d have no air to breathe or food to eat, yet plant science lingers in the shadowy wings while other fields take center stage. With the goal of shining the spotlight on plants, a new study presents the field’s top 100 most pressing questions for research to address the greatest challenges facing humanity.
“The study highlights the importance of plant science for society by laying out myriad questions and technical challenges ...
Genes shed light on why men and women experience different depression symptoms
2023-03-17
Depression is widely reported to be more common in women than in men, with women twice as likely to receive a diagnosis than men. A new sex-specific study from McGill University has found that there are differences between male and female genes and how they relate to depression. In a study of more than 270,000 individuals, the researchers found that sex-specific prediction methods were more accurate in forecasting an individual’s genetic risk of developing depression than prediction methods that did not specify sex. The researchers found ...
Breaking barriers in hepatitis C diagnosis and treatment for populations at risk
2023-03-17
A study with people who inject drugs evaluated a minimally invasive test based on dried blood spots (DBS) for the monitoring of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The use of DBS samples for HCV RNA detection and genotyping was shown to effectively assess cure after treatment and to differentiate between reinfection and treatment failure. The results support the viability of decentralizing treatment and post-treatment monitoring for people who inject drugs, who frequently face challenges accessing the healthcare system. The study, which has been published in the Journal of Medical Virology, was carried out as part of a project with support from the "Conquering ...
UMass Amherst providing 30 three-year scholarships to boost diversity in mathematics and statistics
2023-03-17
AMHERST, Mass. – University of Massachusetts Amherst’s Department of Mathematics and Statistics is offering 30 three-year scholarships to a diverse cohort of students majoring in mathematics and statistics, thanks to a $1.5 million dollar grant from the National Science Foundation (NSF).
The six-year project, called Enhancing Underrepresented Participation in Mathematics & Statistics: Mentoring from Junior to Master’s, will welcome its first cohort in the Fall of 2023, and will support each student for their junior and senior years, as well as through a one-year master’s program. The program will accept ...
Carbon nanotube films as ultrasensitive photodetectors: progress and challenges
2023-03-17
Semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes (s-SWCNTs) are being used to develop a third generation of optimized shortwave infrared photodetectors that will improve pixel size, weight, power consumption, performance and cost over photodetectors made from traditional materials.
Ultrasensitive shortwave infrared photodetectors, which detect a subset of shortwave infrared light wavelengths outside of the visual spectrum, have many potential applications, including night surveillance, navigation during poor weather conditions, fiber optic communications and semiconductor quality control. Shortwave ...
Mountain forests are being lost at an accelerating rate, putting biodiversity at risk
2023-03-17
More than 85% of the world’s bird, mammal, and amphibian species live in mountains, particularly in forest habitats, but researchers report in the journal One Earth on March 17 that these forests are disappearing at an accelerating rate. Globally, we have lost 78.1 million hectares (7.1%) of mountain forest since 2000—an area larger than the size of Texas. Much of the loss occurred in tropical biodiversity hotspots, putting increasing pressure on threatened species.
Though their rugged location once protected mountain forests from deforestation, they have been increasingly exploited since the turn of ...
River deltas: Valuable and under threat
2023-03-17
The livelihoods of millions of people who live in river deltas, among the world’s most productive lands, are at risk. Created where large rivers meet the ocean and deposit their natural sediment load, river deltas are often just a few meters above sea level. And while they make up less than 0.5 % of the world’s land area, river deltas contribute more than 4 % of the global GDP, 3% of global crop production, and are home to 5.5 % of the world’s population. All of these values are highly vulnerable to imminent global environmental change, according to a new Stanford University-led study.
“It is often not rising seas, but sinking land due to human activities that ...
Few Medicaid-participating primary care physicians providing longer-acting birth control methods
2023-03-17
WASHINGTON (March 17, 2023)— Medicaid beneficiaries face barriers in accessing medical care – and that includes contraceptive care. A new study finds that despite birth control being an essential health service, all primary care physicians that see them may not be offering Medicaid patients some of the most effective, longer-acting birth control methods. While nearly half (48%) of primary care physicians who treat Medicaid patients provided prescription contraception like the birth control pill, only 10% provided longer-acting methods like IUDs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
[Press-News.org] Discovery of an unexpected function of blood immune cells : Their ability to proliferate !Rearchers from the University of Liège publishe a fundamental discovery that suggests a greater involvement of cell proliferation in the functioning of our immune system