(Press-News.org) RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Until recently, psychologist Kalina Michalska had never used community-based participatory research, or CBPR, in her work, but now she can’t imagine not using it.
CBPR, which dates to the early 1930s, is an intensive research approach that involves partnerships between researchers and community members throughout the research process, giving communities a voice in how the research proceeds and allowing them to make use of the findings more effectually.
The study led by Michalska, an assistant professor of psychology at the University of California, Riverside, is published in the journal Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience and is part of a special issue on equity and diversity in neuroscience research. The study began with a focus on the neural bases of disruptive behavior disorder and conduct problems in Latina youth, based on Michalska’s prior work.
Through speaking with families, however, Michalska’s team found that the issues under study were more nuanced than behavioral disorders.
“We learned that what girls in our community were instead struggling with was elevated panic, and separation and social anxiety,” Michalska said. “We then re-evaluated the aims of our study to prioritize these concerns. An important aspect of community-engaged research is the condition that community members work with researchers as equal parties and shape the research of which they are a part.”
A $50,000 pilot grant Michalska and her graduate student Jordan Mullins received in July 2021 from the UCR School of Medicine’s Center for Health Disparities Research, or HDR@UCR, got her thinking about using CBPR, a method HDR@UCR encourages its members to consider.
“I am now such a believer in CBPR that I will not go back to not using it,” Michalska said. “When you listen to the community and give its members a voice about their own lived experiences, you prioritize the issues the community has, not the issues researchers think the community has. CBPR treats participating community members as experts, and it better reflects community needs and issues. And because CBPR doesn’t just advance science but also improves the community, it’s an opportunity for researchers like me to give back to society.”
According to Michalska, had her research team not incorporated a CBPR approach, many of the team’s ongoing research directions would not exist. Now, her team shares with participating families a biannual newsletter produced by the Kids Interaction and Neurodevelopment (KIND) Lab at UCR, which Michalska directs, as well as results, in lay language, on relevant published research papers and conference proceedings.
Michalska said CBPR asks: how will the lives of people in communities be impacted by a specific piece of research and do those people have a voice in whether and how the research will be conducted? She explained that psychology and neuroscience have not typically used CBPR.
“But as magnetic resonance imaging and other neuroscientific techniques get more incorporated into the mental health research agenda, it is incumbent on neuroscientists to pay close attention to diversity and representation in their work. Regrettably, in neuroscience, many discussions around these issues today do not involve the community under study.”
Neuroscientists’ research questions, hypotheses, and methods can have unacknowledged biases, Michalska said.
“We need to open communication channels and check in with our research participants to help minimize such biases,” she said. “Already, neuroscience research has a severe underrepresentation of marginalized groups as study participants; Black, Latina, and other women of color are conspicuously absent. Such exclusion directly harms communities and prevention and intervention approaches, such as medical protocols, mental health recommendations, and governmental policy creation, can get biased. CBPR can be a remedy and facilitate impactful change in neuroscience.”
Michalska believes community-engaged research can increase public trust in science and the scientific process.
“Including communities in the research design and interpretation can be a powerful learning opportunity for community members to experience first-hand how research is done,” she said. “This could especially empower young people.”
Next, Michalska’s team plans to incorporate youth voices in its research and interact more closely and strengthen partnerships with communities.
“Going forward, whenever possible, we plan to include measures in our research that are developed from the perspective of participating communities, including measures addressing systems of inequality,” she said.
Michalska and Mullins were joined in the study by graduate student Shayna La Scala of UCR, and Rengin Firat of the Korn Ferry Institute. Firat was an assistant professor of sociology at UCR when the study was done.
The title of the research paper is “Equity, diversity, and inclusion in developmental neuroscience: Practical lessons from community-based participatory research.”
The University of California, Riverside is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment is more than 26,000 students. The campus opened a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Center. The campus has an annual impact of more than $2.7 billion on the U.S. economy. To learn more, visit www.ucr.edu.
END
Researcher-community partnership uses collaborative process to yield novel insights
Community-engaged approach can help address bias and lack of diversity/inclusion in neuroscience research
2023-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Boosting survival of a beneficial bacterium in the human gut
2023-03-17
New Haven, Conn. — The microbes that inhabit the gut are critical for human health, and understanding the factors that encourage the growth of beneficial bacterial species — known as “good” bacteria — in the gut may enable medical interventions that promote gut and overall human health. In a new study, Yale researchers have uncovered a novel mechanism by which these bacteria colonize the gut.
Specifically, the Yale team discovered that one of the most abundant beneficial species found in the human gut showed an increase in colonization potential when experiencing carbon limitation — a finding that could yield novel clinical ...
International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) 22nd Annual Meeting to be held in Stockholm, Sweden May 3- 6, 2023
2023-03-17
The International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) will hold its 2023 Annual Meeting – the organization’s 22nd – from Wednesday, May 3 through Saturday, May 6, 2023, bringing together a global, multidisciplinary group of hundreds of autism researchers, clinicians, advocates, self-advocates, and students to exchange the latest scientific learnings and discoveries that are advancing the expanding understanding of autism and its complexities. This year’s meeting will be held in-person in Stockholm, Sweden at Stockholmsmässan, the largest exhibition facility in the Nordic region.
The INSAR ...
Genomic study of ancient humans sheds light on human evolution on the Tibetan Plateau
2023-03-17
The Tibetan Plateau, the highest and largest plateau above sea level, is one of the harshest environments settled by humans. It has a cold and arid environment and its elevation often surpasses 4000 meters above sea level (masl). The plateau covers a wide expanse of Asia—approximately 2.5 million square kilometers—and is home to over 7 million people, primarily belonging to the Tibetan and Sherpa ethnic groups.
However, our understanding of their origins and history on the plateau is patchy. Despite a rich archaeological context spanning the plateau, ...
Key role identified for nervous system in severe allergic shock
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C. – A key feature of the severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis is an abrupt drop in blood pressure and body temperature, causing people to faint and, if untreated, potentially die.
That response has long been attributed to a sudden dilation and leakage of blood vessels. But in a study using mice, Duke Health researchers have found that this response, especially body temperature drop, requires an additional mechanism – the nervous system.
Appearing online March 17 in the journal Science Immunology, the study could ...
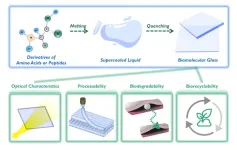
Researchers develop biodegradable, biorecyclable glass
2023-03-17
Everyone is familiar with glass—from putting on eyeglasses, pushing open the window, standing in front of a mirror, to holding a water glass. Glass is ubiquitous in nature and essential to human life.
But the widespread use of persistent, non-biodegradable glass that cannot be naturally eliminated causes long-term environmental hazards and social burdens.
To solve this problem, a research group led by Prof. YAN Xuehai from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a family of eco-friendly glass of biological origin fabricated from biologically derived amino acids or peptides. The ...
Qubits put new spin on magnetism: Boosting applications of quantum computers
2023-03-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 17, 2023 — Research using a quantum computer as the physical platform for quantum experiments has found a way to design and characterize tailor-made magnetic objects using quantum bits, or qubits. That opens up a new approach to develop new materials and robust quantum computing.
“With the help of a quantum annealer, we demonstrated a new way to pattern magnetic states,” said Alejandro Lopez-Bezanilla, a virtual experimentalist in the Theoretical Division at Los Alamos National Laboratory. ...
New combination of drugs works together to reduce lung tumors in mice
2023-03-17
LA JOLLA—(March 17, 2023) Cancer treatments have long been moving toward personalization—finding the right drugs that work for a patient’s unique tumor, based on specific genetic and molecular patterns. Many of these targeted therapies are highly effective, but aren’t available for all cancers, including non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that have an LKB1 genetic mutation. A new study led by Salk Institute Professor Reuben Shaw and former postdoctoral fellow Lillian Eichner, now an assistant professor ...
Biomarkers show promise for identifying early risk of pancreatic cancer
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C. – A research team at Duke Health has identified a set of biomarkers that could help distinguish whether cysts on the pancreas are likely to develop into cancer or remain benign.
Appearing online March 17 in the journal Science Advances, the finding marks an important first step toward a clinical approach for classifying lesions on the pancreas that are at highest risk of becoming cancerous, potentially enabling their removal before they begin to spread.
If successful, the biomarker-based approach could address the biggest impediment to decreasing the ...
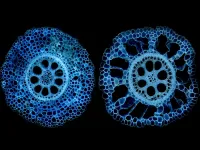
Discovery of root anatomy gene may lead to breeding more resilient corn crops
2023-03-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new discovery, reported in a global study that encompassed more than a decade of research, could lead to the breeding of corn crops that can withstand drought and low-nitrogen soil conditions and ultimately ease global food insecurity, according to a Penn State-led team of international researchers.
In findings published March 16 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, the researchers identified a gene encoding a transcription factor – a protein useful for converting DNA into RNA – that triggers a genetic sequence responsible for the development of an important trait enabling corn roots ...
New study shows social media content opens new frontiers for sustainability science researchers
2023-03-17
With more than half of the world’s population active on social media networks, user-generated data has proved to be fertile ground for social scientists who study attitudes about the environment and sustainability.
But several challenges threaten the success of what's known as social media data science. The primary concern, according to a new study from an international research team, is limited access to data resulting from restrictive terms of service, shutdown of platforms, data manipulation, censorship and regulations.
The study, published online March ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
[Press-News.org] Researcher-community partnership uses collaborative process to yield novel insightsCommunity-engaged approach can help address bias and lack of diversity/inclusion in neuroscience research