(Press-News.org) Plants use photosynthesis to harvest energy from sunlight. Now researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have applied this principle as the basis for developing new sustainable processes which in the future may produce syngas (synthetic gas) for the large-scale chemical industry and be able to charge batteries.
Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important intermediate product in the manufacture of many chemical starter materials such as ammonia, methanol and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels. "Syngas is currently made almost exclusively using fossil raw materials," says Prof. Roland Fischer from the Chair of Inorganic and Organometallic Chemistry.
A yellow powder, developed by a research team led by Fischer, is to change all that. The scientists were inspired by photosynthesis, the process plants use to produce chemical energy from light. "Nature needs carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis," says Fischer. The nanomaterial developed by the researchers imitates the properties of the enzymes involved in photosynthesis. The "nanozyme" produces syngas using carbon dioxide, water and light in a similar manner.
Record values for efficiency
Dr. Philip Stanley, who addressed the topic as part of his doctoral thesis, explains: "A molecule takes over the task of an energy antenna, analogous to a chlorophyll molecule in plants. Light is received and the electrons are passed on to a reaction center, the catalyst." The innovative aspect of the researchers' system: There are now two reaction centers which are linked to the antenna. One of these centers converts carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide, while the other turns water into hydrogen. The major design challenge was to arrange the antenna, the mechanism for passing on the electrons and the two catalysts, in such a way that the highest possible yield is achieved from the light.
And the team accomplished this. "At 36 percent, our energy yield from light is spectacularly high," says Stanley. "We succeed in converting as much as one third of the photons into chemical energy. Previous systems often attained every tenth photon at best. This result raises hopes that the technical realization could make industrial chemical processes more sustainable."
Photo accumulator to store charges
In a separate project the researchers are working on another material which uses light energy from the sun – but in this case stores it as electric energy. "One possible future application could be batteries which are charged by sunlight, without the detour through the wall socket," says Fischer.
The researchers used components similar to those in the nanozyme when developing these photo accumulators. Here too the material itself absorbs photons from the incident light. But instead of then serving as a catalyst for a chemical reaction, the energy receiver is so tightly integrated in the structure that it remains in this state, making storage of the electrons over a longer period of time possible. The researchers have demonstrated the feasibility of the system in the lab.
"There are two ways to make direct use of solar energy," summarizes Dr. Julien Warnan, group leader for photocatalysis. "Either we harvest electric energy from it or we use the energy to push chemical reactions. And these two systems, both based on the same principle, show that we've succeeded experimentally."
END
Smart light traps
Synthesis gas and battery power from sunlight energy
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Visualization of electron dynamics on liquid helium for the first time
2023-03-21
An international team led by Lancaster University has discovered how electrons can slither rapidly to-and-fro across a quantum surface when driven by external forces.
The research, published in Physical Review B, has enabled the visualisation of the motion of electrons on liquid helium for the first time.
The experiments, carried out in Riken, Japan, by Kostyantyn Nasyedkin (now at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA) in the lab of Kimitoshi Kono (now in Taiwan at Yang Ming Chiao Tung University) detected unusual oscillations whose frequencies varied in time. Although it was unclear how ...
Argonne is helping U.S. companies advance battery recycling technology and strengthen the nation’s battery supply chain
2023-03-21
Argonne received $3.5 million in funding to help accelerate battery production in America, lower costs, provide a domestic source of materials and reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries.
Batteries are critical to powering a clean energy economy. This is especially true in the transportation sector, where electric vehicles (EVs) are on track to make up half of all new vehicle sales by 2030. In order to meet this rapidly increasing demand, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is distributing funding to advance domestic recycling and reuse of electric vehicle batteries. Managed by DOE’s Vehicle ...
Machine learning programs predict risk of death based on results from routine hospital tests
2023-03-21
If you’ve ever been admitted to hospital or visited an emergency department, you’ve likely had an electrocardiogram, or ECG, a standard test involving tiny electrodes taped to your chest that checks your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.
Hospital ECGs are usually read by a doctor or nurse at your bedside, but now researchers are using artificial intelligence to glean even more information from those results to improve your care and the health-care system all at once.
In recently published findings, the research team built and trained machine learning programs based on 1.6 ...
Imaging the proton with neutrinos
2023-03-21
The Science
Protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei, are themselves made up of strongly interacting quarks and gluons">quarks and gluons. Because the interactions are so strong, the structure of protons and neutrons is difficult to calculate from theory. Instead, scientists must measure it experimentally. Neutrino experiments use targets that are nuclei made of many protons and neutrons bound together. This complicates interpreting those measurements to infer proton structure. ...
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
2023-03-21
In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s ...
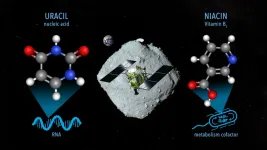
Uracil found in Ryugu samples
2023-03-21
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the informational units that make up RNA, the molecules that contain the instructions for how to build and operate living organisms. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, which is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms, was also detected in the same samples.
This discovery by an international team, led by Associate Professor ...
Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System awarded $30 million from NIH to support its Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
2023-03-21
March 21, 2023—BRONX, NY—Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System have received a seven-year, $30 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to continue support for the Harold and Muriel Block Institute for Clinical and Translational Research at Einstein and Montefiore (ICTR). The latest Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) will ensure the ICTR will further its vision to improve health in the Bronx, Westchester, and lower Hudson Valley by accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective and equitable prevention and treatment approaches.
“Since establishing ...
Diet and exercise programs alone won’t tackle childhood obesity
2023-03-21
Focusing on immediate fixes such as diet and exercise programs alone won’t curb the tide of childhood obesity, according to a new study that for the first time maps the complex pathways that lead to obesity in childhood.
Coordinated by the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre the study finds children whose parents did not complete high school and who live with social disadvantage, were more likely to be affected by overweight or obesity in mid-adolescence. High school completion is a strong indicator of socio-economic status.
These factors were ‘on ramps’ which flow down to influence the body ...
New Yale study evaluates PAXLOVID’s use in Long COVID recovery
2023-03-21
New Haven, Conn. — Yale School of Medicine announces the initiation of a novel, randomized trial that will test whether receiving PAXLOVIDTM (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets) for 15 days can improve the health of highly symptomatic adults with Long COVID.
The trial, led by Yale School of Medicine Professors Harlan Krumholz and Akiko Iwasaki, has a decentralized design, meaning that participants do not have to travel to study sites. It also uses a novel, participant-centric, digital approach to data collection.
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae SARS-CoV-2 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
[Press-News.org] Smart light trapsSynthesis gas and battery power from sunlight energy