(Press-News.org) An international study led by the Molecular Physiology Laboratory at the UPF Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) identifies new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease. Combining molecular biology, genomics and bioinformatics techniques, 238 amyloid toxicity protective or activator genes have been identified. Among them, the gene Surf4 stands out. It is involved in the control of intracellular calcium and, by increasing the toxicity of the β-amyloid protein, contributes to the disease.
The research has been carried out thanks to the support of the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, the State Research Agency, ERDF grants, the Spanish Institute of Health Carlos III, ERANET and the QUAES Foundation through the QUAES-UPF Chair of Biomedicine and Biomedical Engineering.
Every year, 10 million new cases of dementia are diagnosed worldwide. Of these, 7 out of 10 are due to Alzheimer’s disease. This disease develops with age, when the β-amyloid protein - a small protein secreted by neurons - begins to misfold and aggregate within the brain, having a neurotoxic effect. For the time being, there is no effective treatment to prevent β-amyloid protein aggregation and neurotoxicity.
In the study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, researchers have identified, in yeast, 238 genes, similar to those of humans, that regulate Alzheimer’s disease. Of these, 81 increase the toxicity of the β-amyloid protein and 157 are protective against this cellular toxicity.
A bioinformatic analysis has shown that most of the 238 genes identified are involved in mitochondrial activity, protein translation and intracellular calcium regulation. In this latter process, in which a large part of the identified genes are involved, the Surf4 gene stands out, whose protein regulates the entry of calcium inside the cell and has been shown to increase the toxicity of the β-amyloid protein, contributing to Alzheimer’s disease.
According to the study coordinator, Francisco J. Muñoz, “calcium is one of the most important messengers that transfer information from the outside to within cells. It is involved in almost all cell functions. Hence, when the Surf4 protein is overexpressed, which decreases calcium entry and aborts the cellular processes dependent on it, neurons cannot function and they become very sensitive to amyloid toxicity”.
The identification of SURF4 as an accelerator of β-amyloid protein toxicity damage opens the door to identifying new therapeutic targets that regulate amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease.
To identify the genes that regulate Alzheimer’s disease, a collection of 5,154 mutants of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae -whose genome is greatly similar to the human genome - were analysed and the expression of a gene was eliminated. Each of these mutants was crossed with other yeasts of the same strain that overexpress the human β-amyloid protein and the viability of these cells was analysed over several days. In addition, a text mining analysis was performed to identify other genes related to the regulation of β-amyloid protein toxicity.
Also participating in this work were researchers from the UPF Department of Medicine and Life Sciences, Pol Picón-Pagès, Mònica Bosch-Morató, Laia Subirana, Francisca Rubio-Moscardó, Biuse Guivernau, Hugo Fanlo-Ucar, Víctor Herrera-Fernández, Rubén Vicente, José M. Fernández-Fernández, Jordi García-Ojalvo, Baldomero Oliva, Francesc Posas, and Eulàlia de Nadal.
Reference article:
Picón-Pagès, P.;Bosch-Morató, M.; Subirana, L.; Rubio-Moscardó, F.; Guivernau, B.; Fanlo-Ucar, H.; Zeylan, M.E.; Senyuz, S.; Herrera-Fernández, V.; Vicente, R.; et al. A Genome-Wide Functional Screen Identifies Enhancer and Protective Genes for Amyloid Beta-Peptide Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1278.
doi: https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/2/1278
END
Researchers identify new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease
In the study led by the UPF Molecular Physiology Laboratory, 238 genes have been identified that regulate Alzheimer’s disease, including Surf4, which contributes to the disease by altering the regulation of calcium within the cell
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smart light traps
2023-03-21
Plants use photosynthesis to harvest energy from sunlight. Now researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have applied this principle as the basis for developing new sustainable processes which in the future may produce syngas (synthetic gas) for the large-scale chemical industry and be able to charge batteries.
Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important intermediate product in the manufacture of many chemical starter materials such as ammonia, methanol and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels. "Syngas is currently made almost exclusively using fossil raw materials," ...
Visualization of electron dynamics on liquid helium for the first time
2023-03-21
An international team led by Lancaster University has discovered how electrons can slither rapidly to-and-fro across a quantum surface when driven by external forces.
The research, published in Physical Review B, has enabled the visualisation of the motion of electrons on liquid helium for the first time.
The experiments, carried out in Riken, Japan, by Kostyantyn Nasyedkin (now at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA) in the lab of Kimitoshi Kono (now in Taiwan at Yang Ming Chiao Tung University) detected unusual oscillations whose frequencies varied in time. Although it was unclear how ...
Argonne is helping U.S. companies advance battery recycling technology and strengthen the nation’s battery supply chain
2023-03-21
Argonne received $3.5 million in funding to help accelerate battery production in America, lower costs, provide a domestic source of materials and reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries.
Batteries are critical to powering a clean energy economy. This is especially true in the transportation sector, where electric vehicles (EVs) are on track to make up half of all new vehicle sales by 2030. In order to meet this rapidly increasing demand, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is distributing funding to advance domestic recycling and reuse of electric vehicle batteries. Managed by DOE’s Vehicle ...
Machine learning programs predict risk of death based on results from routine hospital tests
2023-03-21
If you’ve ever been admitted to hospital or visited an emergency department, you’ve likely had an electrocardiogram, or ECG, a standard test involving tiny electrodes taped to your chest that checks your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.
Hospital ECGs are usually read by a doctor or nurse at your bedside, but now researchers are using artificial intelligence to glean even more information from those results to improve your care and the health-care system all at once.
In recently published findings, the research team built and trained machine learning programs based on 1.6 ...
Imaging the proton with neutrinos
2023-03-21
The Science
Protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei, are themselves made up of strongly interacting quarks and gluons">quarks and gluons. Because the interactions are so strong, the structure of protons and neutrons is difficult to calculate from theory. Instead, scientists must measure it experimentally. Neutrino experiments use targets that are nuclei made of many protons and neutrons bound together. This complicates interpreting those measurements to infer proton structure. ...
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
2023-03-21
In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s ...
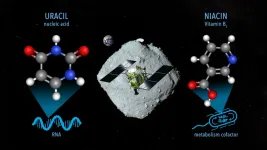
Uracil found in Ryugu samples
2023-03-21
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the informational units that make up RNA, the molecules that contain the instructions for how to build and operate living organisms. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, which is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms, was also detected in the same samples.
This discovery by an international team, led by Associate Professor ...
Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System awarded $30 million from NIH to support its Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
2023-03-21
March 21, 2023—BRONX, NY—Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System have received a seven-year, $30 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to continue support for the Harold and Muriel Block Institute for Clinical and Translational Research at Einstein and Montefiore (ICTR). The latest Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) will ensure the ICTR will further its vision to improve health in the Bronx, Westchester, and lower Hudson Valley by accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective and equitable prevention and treatment approaches.
“Since establishing ...
Diet and exercise programs alone won’t tackle childhood obesity
2023-03-21
Focusing on immediate fixes such as diet and exercise programs alone won’t curb the tide of childhood obesity, according to a new study that for the first time maps the complex pathways that lead to obesity in childhood.
Coordinated by the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre the study finds children whose parents did not complete high school and who live with social disadvantage, were more likely to be affected by overweight or obesity in mid-adolescence. High school completion is a strong indicator of socio-economic status.
These factors were ‘on ramps’ which flow down to influence the body ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s diseaseIn the study led by the UPF Molecular Physiology Laboratory, 238 genes have been identified that regulate Alzheimer’s disease, including Surf4, which contributes to the disease by altering the regulation of calcium within the cell