(Press-News.org) Reston, VA—A novel imaging modality that can visualize the distribution of medical radiopharmaceuticals with very fine resolution has been developed and successfully tested, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Known as the lensless radiomicroscope, the palm-sized instrument offers the same level of imaging performance as its closest imaging equivalent but comes with significantly larger field of view and costs less than $100.
“While many nuclear medicine imaging modalities can quantitively measure how radiopharmaceuticals interact with living tissues, few have the resolution necessary to zoom down to level of single cells,” said Guillem Pratx, PhD, associate professor of radiation oncology at Stanford University in Stanford, California. “This potentially hinders the development of effective radiopharmaceuticals for disease detection, staging, and treatment.”
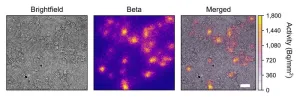
To address this issue, researchers constructed a compact instrument that images radiopharmaceuticals by direct detection of ionizing charged particles via a consumer-grade complementary metal-oxide semiconductor detector. It is made from off-the-shelf parts that cost less than $100, which is approximately 500 times less than the radioluminescence microscope, the closest imaging device to the lensless microscope.
Upon proof-of-concept testing, the lensless radiomicroscope produced high-resolution images of more than 5,000 cells within its 1 cm2 field of view, a hundredfold increase over current state-of-the-art technology. Static and dynamic images were successfully created for both beta- and alpha-emitting radionuclides with the lensless radiomicroscope.
“With these improvements, we expect that the new lensless radiomicroscope will be available for more labs to incorporate into their studies,” noted Pratx. “Researchers will be able to analyze the uptake of radiotracers by heterogeneous populations of cells, such as those extracted from tumors or the brain. This in turn, will provide an opportunity for researchers to incorporate cellular level data into the development pipeline of new radiopharmaceuticals.”
Currently the lensless radiomicroscope design is available to other researchers as open source. The instrument can be built using consumer grade components and 3-D printing.
This study was made available online in September 2022.
The authors of “Development of a lensless radiomicroscope for cellular-resolution radionuclide imaging” include Justin Shaun Klein, Tae Jin Kim, and Guillem Pratx, Department of Radiation Oncology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California.
Visit the JNM website for the latest research, and follow our new Twitter and Facebook pages @JournalofNucMed or follow us on LinkedIn.
###
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and precision imaging. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Rebecca Maxey at (703) 652-6772 or rmaxey@snmmi.org.
About JNM and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) is the world’s leading nuclear medicine, molecular imaging and theranostics journal, accessed 15 million times each year by practitioners around the globe, providing them with the information they need to advance this rapidly expanding field. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org.
JNM is published by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging—precision medicine that allows diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit www.snmmi.org.
END
New compact and low-cost lensless radiomicroscope developed for nuclear medicine imaging
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patients with baclofen pumps may safely undergo transcutaneous spinal stimulation
2023-03-21
East Hanover, NJ. March 21, 2023. Researchers from Kessler Foundation and Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation (collectively “Kessler”) conducted the first prospective study to assess whether transcutaneous spinal stimulation (TSS) interacts with implanted intrathecal baclofen (ITB) pump delivery systems for managing spasticity. The article, "Transcutaneous spinal stimulation in patients with intrathecal baclofen pump delivery system: A preliminary safety study," (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1075293), was published December 21, 2022, in Frontiers in Neuroscience. It is ...
Co-infection with ‘superbug’ bacteria increases SARS-CoV-2 replication up to 15 times, Western study finds
2023-03-21
Global data shows nearly 10 per cent of severe COVID-19 cases involve a secondary bacterial co-infection – with Staphylococcus aureus, also known as Staph A., being the most common organism responsible for co-existing infections with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers at Western have found if you add a ‘superbug’ – methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) – into the mix, the COVID-19 outcome could be even more deadly.
The mystery of how and why these two pathogens, when combined, ...
Advisory role: New research suggests peer-advisor relationship is key to success
2023-03-21
Collaborative research across the country has shown that strengthening the relationship between the student and advisor can increase retention rates in engineering doctoral studies.
Dr. Marissa Tsugawa, along with professors from Penn State, The University of Oregon, Indiana University Bloomington, University of Reno, Nevada and North Carolina State University, recently published a study with the Journal of Engineering Education on March 17. The study connects an engineering student’s identity and the intention to complete a Ph.D. in engineering. Identity is a role that students give themselves during their experiences in the lab and classroom. The authors argue ...
Researchers get to the “bottom” of how beetles use their butts to stay hydrated
2023-03-21
Beetles are champions at surviving in extremely dry environments. In part, this property is due to their ability to suck water from the air with their rear ends. A new collaborative study by researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the University of Edinburgh explains just how. Beyond helping to explain how beetles thrive in environments where few other animals can survive, the knowledge could eventually be used for more targeted and delicate control of global pests such as the grain weevil and red flour beetle.
Insect pests eat their way through thousands of tons of food around the world every year. Food security in developing ...
New MU study shapes understanding of adaptive clothing customer needs
2023-03-21
With the growth of the niche adaptive clothing market comes new challenges for retailers, including making the process of online shopping more inclusive for people with varying degrees of disability as well as expanding the functionality and aesthetic appeal of individual garments.
This study involved mining online reviews to understand the perspectives of adaptive clothing customers. University of Missouri researchers identified two main challenges for adaptive clothing consumers.
Customers said ...
Aging | Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome
2023-03-21
“[...] we identified > 1,000 candidate genes with genome-wide significant age-related methylation changes in sperm.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 21, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome.”
Advanced paternal age is associated with increased risks for reproductive and offspring medical problems. Accumulating evidence suggests age-related changes ...
Study finds similar association of progestogen-only and combined hormonal contraceptives with breast cancer risk
2023-03-21
There is a relative increase of 20% to 30% in breast cancer risk associated with both combined and progesterone-only contraceptives, whatever the mode of delivery, though with five years of use, the 15-year absolute excess incidence is at most 265 cases per 100,000 users. The results appear in a new study publishing March 21st in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Kirstin Pirie of University of Oxford, UK, and colleagues.
Use of combined oral contraceptives, containing both estrogen and progestogen, has previously been associated with a small increase in breast cancer risk but there is limited data about the ...
Exercise therapy is safe, may improve quality of life for many people with heart failure
2023-03-21
CONTENT UPDATED 3/17 - note new references to cardiac rehabilitation.
Statement Highlights:
A new scientific statement indicates supervised exercise therapy may help improve symptoms for people with one of the most common types of heart failure, known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), in which the heart muscle’s pumping strength is intact.
Exercise therapy had comparable or better results on improving exercise capacity for people with preserved EF compared to those who have heart failure with reduced ...
COVID-19 unemployment stigma is real and could threaten future job prospects: uOttawa study
2023-03-21
Regina Bateson, an Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Social Science’s Graduate School of Public and International Affairs, details the findings of her study, which shows the significant social and economic impacts to individuals who were out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Below she answers questions about her study.
Question: How was this research performed?
Regina Bateson: “In this study, I conducted a pre-registered survey experiment with a nationally representative sample of 974 U.S. adults. ...
Ultra-lightweight multifunctional space skin created to withstand extreme conditions in space
2023-03-21
A new nano-barrier coating could help protect ultra-lightweight carbon composite materials from extreme conditions in space, according to a study from the University of Surrey and Airbus Defence and Space.
The new functionality added to previously developed ‘space skin’ structures adds a layer of protection to help maintain space payloads while travelling in space, similar to having its very own robust ultralight protective jacket.
The research team has shown that their innovative nano-barrier would help drastically increase the stability of carbon fibre materials, while reducing radiation ...