(Press-News.org) Regina Bateson, an Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Social Science’s Graduate School of Public and International Affairs, details the findings of her study, which shows the significant social and economic impacts to individuals who were out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Below she answers questions about her study.
Question: How was this research performed?
Regina Bateson: “In this study, I conducted a pre-registered survey experiment with a nationally representative sample of 974 U.S. adults. I randomly assigned pandemic employment histories to fictional job applicants, then I asked the survey respondents to evaluate the job applicants.”
Q: What did you find?
RB: “The fictional applicants with pandemic gaps in employment were seen more negatively than identical applicants who worked continuously throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. This was true whether they were laid off and out of work for a long period of time, yo-yoed in and out of employment throughout lockdowns and re-openings, or stopped working to supervise virtual school for their children.
“Compared to identical people who remained employed throughout the pandemic, fictional job applicants with pandemic resume gaps are less likely to be seen as professional, qualified, hardworking, motivated, or dedicated. In addition, they are less likely to be selected for hypothetical job openings.
“Although pandemic job losses were widespread and beyond workers’ control, these findings suggest that there is stigma associated with pandemic gaps in employment. The public health emergency may now be winding down, but for people with pandemic resume gaps, the social and economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic could reverberate for years to come.”
Q: How can employers and public bodies assist those with COVID-19 employment gaps?
RB: “Throughout the pandemic, governments provided significant assistance to people who were out of work, and there was a widespread perception that pandemic gaps in employment would not be held against job seekers. This research suggests those assurances may have been overly optimistic. Even as the pandemic wanes, governments should remain attentive to the possibility that individuals who were out of work during the pandemic may face discrimination and stigma when they look for new jobs and seek to advance in their careers.
“In addition, hiring managers should be aware that negative stereotypes about those who were unemployed during the pandemic could inadvertently affect how they evaluate job applicants.”
Q: Any final thoughts?
RB: “It is important to note that this research measures perceptions of fictional job applicants, not actual outcomes in the real-world labour market. At present there is high demand for workers, and the hot labour market may be blunting any penalties associated with a pandemic resume gap. However, presumably the job market will cool again at some point--and when that happens, job seekers who were out of work during the pandemic may find themselves at a disadvantage.
“Stigma also has negative social and psychological consequences, creating additional burdens for the millions of people who found themselves out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
‘Perceptions of pandemic resume gaps: Survey experimental evidence from the United States’ by Regina Bateson, published in Plos One on March 16, 2023. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281449
END
COVID-19 unemployment stigma is real and could threaten future job prospects: uOttawa study
A survey experiment reveals people who were out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic are perceived more negatively than those who remained employed
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ultra-lightweight multifunctional space skin created to withstand extreme conditions in space
2023-03-21
A new nano-barrier coating could help protect ultra-lightweight carbon composite materials from extreme conditions in space, according to a study from the University of Surrey and Airbus Defence and Space.
The new functionality added to previously developed ‘space skin’ structures adds a layer of protection to help maintain space payloads while travelling in space, similar to having its very own robust ultralight protective jacket.
The research team has shown that their innovative nano-barrier would help drastically increase the stability of carbon fibre materials, while reducing radiation ...
Researchers identify new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-21
An international study led by the Molecular Physiology Laboratory at the UPF Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) identifies new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease. Combining molecular biology, genomics and bioinformatics techniques, 238 amyloid toxicity protective or activator genes have been identified. Among them, the gene Surf4 stands out. It is involved in the control of intracellular calcium and, by increasing the toxicity of the β-amyloid protein, contributes to the disease.
The research has been carried out thanks to the support ...
Smart light traps
2023-03-21
Plants use photosynthesis to harvest energy from sunlight. Now researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have applied this principle as the basis for developing new sustainable processes which in the future may produce syngas (synthetic gas) for the large-scale chemical industry and be able to charge batteries.
Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important intermediate product in the manufacture of many chemical starter materials such as ammonia, methanol and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels. "Syngas is currently made almost exclusively using fossil raw materials," ...
Visualization of electron dynamics on liquid helium for the first time
2023-03-21
An international team led by Lancaster University has discovered how electrons can slither rapidly to-and-fro across a quantum surface when driven by external forces.
The research, published in Physical Review B, has enabled the visualisation of the motion of electrons on liquid helium for the first time.
The experiments, carried out in Riken, Japan, by Kostyantyn Nasyedkin (now at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA) in the lab of Kimitoshi Kono (now in Taiwan at Yang Ming Chiao Tung University) detected unusual oscillations whose frequencies varied in time. Although it was unclear how ...
Argonne is helping U.S. companies advance battery recycling technology and strengthen the nation’s battery supply chain
2023-03-21
Argonne received $3.5 million in funding to help accelerate battery production in America, lower costs, provide a domestic source of materials and reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries.
Batteries are critical to powering a clean energy economy. This is especially true in the transportation sector, where electric vehicles (EVs) are on track to make up half of all new vehicle sales by 2030. In order to meet this rapidly increasing demand, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is distributing funding to advance domestic recycling and reuse of electric vehicle batteries. Managed by DOE’s Vehicle ...
Machine learning programs predict risk of death based on results from routine hospital tests
2023-03-21
If you’ve ever been admitted to hospital or visited an emergency department, you’ve likely had an electrocardiogram, or ECG, a standard test involving tiny electrodes taped to your chest that checks your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.
Hospital ECGs are usually read by a doctor or nurse at your bedside, but now researchers are using artificial intelligence to glean even more information from those results to improve your care and the health-care system all at once.
In recently published findings, the research team built and trained machine learning programs based on 1.6 ...
Imaging the proton with neutrinos
2023-03-21
The Science
Protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei, are themselves made up of strongly interacting quarks and gluons">quarks and gluons. Because the interactions are so strong, the structure of protons and neutrons is difficult to calculate from theory. Instead, scientists must measure it experimentally. Neutrino experiments use targets that are nuclei made of many protons and neutrons bound together. This complicates interpreting those measurements to infer proton structure. ...
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
2023-03-21
In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s ...
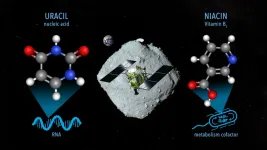
Uracil found in Ryugu samples
2023-03-21
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the informational units that make up RNA, the molecules that contain the instructions for how to build and operate living organisms. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, which is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms, was also detected in the same samples.
This discovery by an international team, led by Associate Professor ...
Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
A new method to steer AI output uncovers vulnerabilities and potential improvements
Why some objects in space look like snowmen
Flickering glacial climate may have shaped early human evolution
First AHA/ACC acute pulmonary embolism guideline: prompt diagnosis and treatment are key
Could “cyborg” transplants replace pancreatic tissue damaged by diabetes?
Hearing a molecule’s solo performance
Justice after trauma? Race, red tape keep sexual assault victims from compensation
Columbia researchers awarded ARPA-H funding to speed diagnosis of lymphatic disorders
James R. Downing, MD, to step down as president and CEO of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in late 2026
A remote-controlled CAR-T for safer immunotherapy
UT College of Veterinary Medicine dean elected Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology
AERA selects 34 exemplary scholars as 2026 Fellows
Similar kinases play distinct roles in the brain
New research takes first step toward advance warnings of space weather
Scientists unlock a massive new ‘color palette’ for biomedical research by synthesizing non-natural amino acids
Brain cells drive endurance gains after exercise
Same-day hospital discharge is safe in selected patients after TAVI
Why do people living at high altitudes have better glucose control? The answer was in plain sight
Red blood cells soak up sugar at high altitude, protecting against diabetes
A new electrolyte points to stronger, safer batteries
Environment: Atmospheric pollution directly linked to rocket re-entry
Targeted radiation therapy improves quality of life outcomes for patients with multiple brain metastases
Cardiovascular events in women with prior cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Transplantation and employment earnings in kidney transplant recipients
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 unemployment stigma is real and could threaten future job prospects: uOttawa studyA survey experiment reveals people who were out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic are perceived more negatively than those who remained employed