(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. – While listening to a favorite song is a known mood booster, researchers at Michigan State University have discovered that music-listening interventions also can make medicines more effective.
“Music-listening interventions are like over-the-counter medications,” said Jason Kiernan, an assistant professor in the College of Nursing. “You don’t need a doctor to prescribe them.”
While previous research studies have used music-listening interventions as a tool to treat pain and anxiety, Kiernan took a novel approach by studying the effects of music-listening interventions on chemotherapy-induced nausea.
“Pain and anxiety are both neurological phenomena and are interpreted in the brain as a state,” Kiernan said. “Chemotherapy-induced nausea is not a stomach condition; it is a neurological one.”
The small pilot study included 12 patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment who agreed to listen to their favorite music for 30 minutes each time they needed to take their as-needed anti-nausea medication. They repeated the music intervention anytime nausea occurred over the five days beyond their chemotherapy treatment. The patients in the study provided a total of 64 events.
"When we listen to music, our brains fire all kinds of neurons," Kiernan said.
While Kiernan did see a reduction in the ratings of patients’ nausea severity and their distress (how much it bothered them to be nauseous), he cautions that it is difficult to isolate whether it was the gradual release of the medication doing its job or the increased benefit of the music. For future studies, Kiernan is drawing inspiration from another previously published study that measured the amount of serotonin, a neurotransmitter, that was released by platelets in the blood after listening to unpleasant and pleasant music.
“Serotonin is the major neurotransmitter that causes chemotherapy-induced nausea,” Kiernan said. “Cancer patients take medications to block serotonin’s effects.”
During that previous study, researchers found that patients who listened to pleasant music experienced the lowest levels of serotonin release, indicating that the serotonin stayed in the blood platelets and was not released to circulate throughout the body. Results also showed that after listening to music they found unpleasant, patients experienced greater stress and increased levels of serotonin release.
“This was intriguing because it provides a neurochemical explanation and a possible way to measure serotonin and the blood platelet release of serotonin in my study,” Kiernan said. “In 10 to 20 years, wouldn’t it be neat if you could use a nonpharmacological intervention like listening to 10 minutes of your favorite music to complement a medicine?”
The research was published in the journal Clinical Nursing Research.
Read on MSUToday.
###
Michigan State University has been advancing the common good with uncommon will for more than 165 years. One of the world's leading research universities, MSU pushes the boundaries of discovery to make a better, safer, healthier world for all while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 400 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
END
Turn up your favorite song to improve medication efficacy
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Local manure regulations can help reduce water pollution from dairy farms
2023-03-21
URBANA, Ill. – Animal agriculture is a major source of water pollution in the United States, as manure runoff carries excess nutrients into rivers and lakes. Because of their non-point source nature, most farms are not regulated under the federal Clean Water Act. This leaves pollution control up to the states, resulting in a patchwork of different approaches that are difficult to evaluate.
A new study from the University of Illinois focuses on local manure management regulations in Wisconsin and how they affect water ...
Analysis by NYUAD researchers offers new insights into causes of persistent inequities affecting non-white scientists and their research
2023-03-21
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 21, 2023 – A team of NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) researchers, including data and computational social scientists, is reporting new findings that highlight previously unknown ways through which non-White scientists suffer from inequalities when it comes to the process of having their research considered, published, and cited, potentially hindering the advancement of their academic careers. Specifically, the NYUAD team’s analysis found fewer non-White editors than would be expected based on their share of authorship. In addition, non-White scientists endure longer waiting times between the submission ...
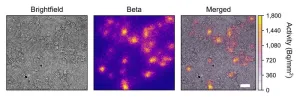
New compact and low-cost lensless radiomicroscope developed for nuclear medicine imaging
2023-03-21
Reston, VA—A novel imaging modality that can visualize the distribution of medical radiopharmaceuticals with very fine resolution has been developed and successfully tested, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Known as the lensless radiomicroscope, the palm-sized instrument offers the same level of imaging performance as its closest imaging equivalent but comes with significantly larger field of view and costs less than $100.
“While many nuclear medicine imaging modalities can quantitively measure ...
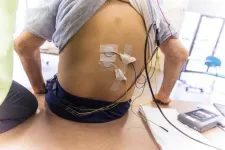
Patients with baclofen pumps may safely undergo transcutaneous spinal stimulation
2023-03-21
East Hanover, NJ. March 21, 2023. Researchers from Kessler Foundation and Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation (collectively “Kessler”) conducted the first prospective study to assess whether transcutaneous spinal stimulation (TSS) interacts with implanted intrathecal baclofen (ITB) pump delivery systems for managing spasticity. The article, "Transcutaneous spinal stimulation in patients with intrathecal baclofen pump delivery system: A preliminary safety study," (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1075293), was published December 21, 2022, in Frontiers in Neuroscience. It is ...
Co-infection with ‘superbug’ bacteria increases SARS-CoV-2 replication up to 15 times, Western study finds
2023-03-21
Global data shows nearly 10 per cent of severe COVID-19 cases involve a secondary bacterial co-infection – with Staphylococcus aureus, also known as Staph A., being the most common organism responsible for co-existing infections with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers at Western have found if you add a ‘superbug’ – methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) – into the mix, the COVID-19 outcome could be even more deadly.
The mystery of how and why these two pathogens, when combined, ...
Advisory role: New research suggests peer-advisor relationship is key to success
2023-03-21
Collaborative research across the country has shown that strengthening the relationship between the student and advisor can increase retention rates in engineering doctoral studies.
Dr. Marissa Tsugawa, along with professors from Penn State, The University of Oregon, Indiana University Bloomington, University of Reno, Nevada and North Carolina State University, recently published a study with the Journal of Engineering Education on March 17. The study connects an engineering student’s identity and the intention to complete a Ph.D. in engineering. Identity is a role that students give themselves during their experiences in the lab and classroom. The authors argue ...
Researchers get to the “bottom” of how beetles use their butts to stay hydrated
2023-03-21
Beetles are champions at surviving in extremely dry environments. In part, this property is due to their ability to suck water from the air with their rear ends. A new collaborative study by researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the University of Edinburgh explains just how. Beyond helping to explain how beetles thrive in environments where few other animals can survive, the knowledge could eventually be used for more targeted and delicate control of global pests such as the grain weevil and red flour beetle.
Insect pests eat their way through thousands of tons of food around the world every year. Food security in developing ...
New MU study shapes understanding of adaptive clothing customer needs
2023-03-21
With the growth of the niche adaptive clothing market comes new challenges for retailers, including making the process of online shopping more inclusive for people with varying degrees of disability as well as expanding the functionality and aesthetic appeal of individual garments.
This study involved mining online reviews to understand the perspectives of adaptive clothing customers. University of Missouri researchers identified two main challenges for adaptive clothing consumers.
Customers said ...
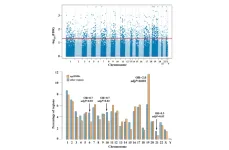
Aging | Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome
2023-03-21
“[...] we identified > 1,000 candidate genes with genome-wide significant age-related methylation changes in sperm.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 21, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome.”
Advanced paternal age is associated with increased risks for reproductive and offspring medical problems. Accumulating evidence suggests age-related changes ...
Study finds similar association of progestogen-only and combined hormonal contraceptives with breast cancer risk
2023-03-21
There is a relative increase of 20% to 30% in breast cancer risk associated with both combined and progesterone-only contraceptives, whatever the mode of delivery, though with five years of use, the 15-year absolute excess incidence is at most 265 cases per 100,000 users. The results appear in a new study publishing March 21st in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Kirstin Pirie of University of Oxford, UK, and colleagues.
Use of combined oral contraceptives, containing both estrogen and progestogen, has previously been associated with a small increase in breast cancer risk but there is limited data about the ...