Looking from different perspectives! Proper electronic structure of near-infrared absorbing functional dyes discovered
A big step toward the development of dyes with long-wavelength near-infrared absorption!
2023-03-27
(Press-News.org)
Near-infrared light, whose wavelength is longer than visible light, is invisible and can pass through many substances. Organic materials that efficiently absorb near-infrared light are essential for technological innovations that utilize near-infrared light, such as the dyes in the infrared blocking filters of smartphone cameras and security inks. These and many more technical applications make developing new dyes that can absorb longer wavelengths of near-infrared light desirable.
Previously, near-infrared absorbing organic materials were treated as closed-shell molecules without unpaired electrons. However, a joint research group led by Associate Professor Takeshi Maeda, Assistant Professor Daisuke Sakamaki, and Professor Hideki Fujiwara from Osaka Metropolitan University discovered that near-infrared absorbing oxocarbon-based dyes have an intermediate state between closed-shell and open-shell electronic configurations. They also found that as the wavelengths of near-infrared light absorbed increase, so does the contribution of open-shell forms in the dye.
"We have clarified the proper electronic structure of near-infrared absorbing oxocarbon-based dyes that are regarded as pure closed-shell molecules. We hope that this will lead to advances in the molecular design, properties, functions, and applications of near-infrared absorbing dyes and to the development of new near-infrared absorbing organic materials that be used in society,” Professor Takeshi Maeda concluded.
The results were published in Chemical Science on January 16, 2023, and was selected as 2023 Chemical Science HOT Article Collection.
Other authors on the paper include: graduate student Taishi Oka, Assistant Professor Naoya Suzuki, Professor Shigeyuki Yagi from Osaka Metropolitan University, Dr. Kenji Kamada from National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and Mr. Tatsuki Konishi.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-27
New research shows that people with a lifetime history of mental disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, or anxiety disorders have blood markers suggesting that they are older than their actual age. This may go some way to explaining why people with mental health problems tend to have shorter lifespans and more age-related diseases than the general population.
Dr Julian Mutz and Prof Cathryn Lewis, from King’s College London, looked at data on 168 different blood metabolites from 110,780 participants in the UK Biobank2. They linked these data to information on whether individuals had a history of mental illness and found that those with a mental illness ...
2023-03-27
NRG Oncology GOG-0240 is the phase 3 randomized trial which demonstrated that the incorporation of bevacizumab with chemotherapy resulted in a statistically significant and clinically meaningful survival benefit for women with recurrent and metastatic cervical carcinoma (NCT00803062). GOG-0240 was a proof of concept in anti-angiogenesis therapy and a proof of principle in supportive care and led directly to an indication for bevacizumab in this disease in over 60 countries. Whole genome sequencing and whole exome sequencing of tumor samples obtained in GOG-0240 suggest that ARID1A and PIK3CA could represent potential targets ...
2023-03-27
World-first ‘phase change inks’ that could transform how we heat and cool buildings, homes and cars – to achieve sophisticated ‘passive climate’ control – have been developed, with enormous potential to help reduce energy use and global greenhouse gas emissions.
New research published in The Royal Society of Chemistry’s Journal of Materials Chemistry A led by Dr Mohammad Taha, documents proof-of-concept ‘phase change inks’ that use nanotechnology to control temperature in everyday environments. They achieve this by adjusting the amount of radiation that can pass through ...
2023-03-27
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) shows that large infrastructure projects which are the focus of the UK government’s levelling up agenda and include support for business start-ups, must also offer sustainable, local investment in deprived communities.
Through place-based micro-enterprise training and employment support over a longer time frame, lasting local impact can be demonstrated, according to the study’s policy recommendations.
Supporting people to return to their communities, increasing social cohesion within them, boosting digital literacy and enabling net zero jobs are also likely to play a role.
These goals can be easily ...
2023-03-27
Embryos in pregnancies that end in miscarriage take longer to develop in the womb than those in pregnancies that result in live births, according to new research published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
For the first time, researchers in The Netherlands have been able to look at the way embryos develop while pregnancies are ongoing. They used state-of-the-art imaging technology, including 3D ultrasound with high resolution transvaginal probes and ...
2023-03-27
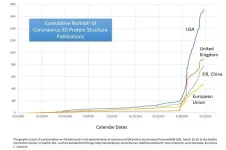
In a new study, researchers examined how a country’s number of published 3D protein structures for coronaviruses, including the one responsible for COVID-19, correlated with its economic output and population. The findings reveal important insights into how different countries' research establishments respond to disease outbreaks and could be useful for planning responses to future pandemics.
The study showed that countries with larger economies generated more 3D structure determinations for the protein components ...
2023-03-27
For vulnerable premature babies, an incubator in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is a lifesaver, but the consequences can last a lifetime. Many studies have shown that the NICU is a noisy environment and that babies who spend time there have higher rates of hearing impairment, which can lead to delays in language acquisition. Scientists from Vienna, Hamburg, Munich, and Osnabruck set out to investigate the role of the incubator, an underestimated element in the soundscape that surrounds babies during their time in the NICU.
“The ...
2023-03-27
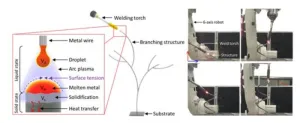
□ A research team led by Dr. Sang-woo Song, Dr. Chan-kyu Kim, Dr. Kang-myung Seo at the Department of Joining Technology of the Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, has developed a foundational technology for controlling the volume of molten metal in the process of 3D printing metal using welding techniques. They achieved this through collaborative research with a research team led by Professor Young-tae Cho and Professor ...
2023-03-27
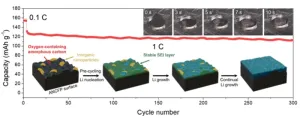
Owing to the worldwide trend of utilizing electric vehicles, there has been a rise in demand for next-generation secondary batteries with higher capacity and faster charging than the lithium-ion batteries currently in use. Lithium metal batteries have been recognized as promising rechargeable batteries because lithium metal anode exhibits theoretical capacity 10 times higher than commercial graphite anode. During charging-discharging processes, however, lithium dendrites grow on the anode, leading to poor battery performance and short-circuit.
Dr. Sungho Lee, Head of the ...
2023-03-27
The history of the Earth has been one of physical extremes—extreme atmospheric conditions, extreme chemical environments, and extreme temperatures. There was a time when the Earth was so hot all the water was vapor, and the first rain only fell once the planet cooled enough. Soon after, life emerged and through it all, life has found a way. Today life is found almost everywhere on Earth we have looked; it is difficult to find places where life does not exist. The remarkable ability of life to adapt to variable conditions is one of its defining characteristics. Of its many adaptations, the ability of life to adapt to varying temperatures ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Looking from different perspectives! Proper electronic structure of near-infrared absorbing functional dyes discovered
A big step toward the development of dyes with long-wavelength near-infrared absorption!