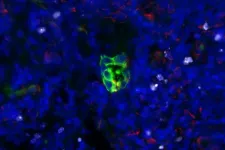
(Press-News.org) MSK researchers identified a key role for the STING signaling pathway in preventing dormant metastatic cancer cells from progressing to active metastases.
Treating laboratory mice with a STING activator helped eliminate lingering metastatic cells and stop the development of aggressive tumors.
The study suggests further investigation of STING activation as a new approach to prevent cancer from recurring or spreading to other organs after successful treatment of a primary tumor.
A team of scientists at the Sloan Kettering Institute have identified the STING cellular signaling pathway as a key player in keeping dormant cancer cells from progressing into aggressive tumors months, or even years, after they’ve escaped from a primary tumor.
The findings, which were published in Nature on March 29, suggest that drugs to activate STING could help prevent the spread of cancer to new sites throughout the body — a process known as metastasis.
In mouse models of lung cancer, treatment that stimulated the STING pathway helped eliminate lingering cancer cells and prevent them from progressing to aggressive metastases. Known as micrometastases, these cells, which can be found individually and in small clusters, are too small to be detected with standard imaging tests.
“The majority of cancer deaths are caused by metastasis,” says Joan Massagué, PhD, the study’s senior author and Director of the Sloan Kettering Institute — a hub for basic science and translational research within Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). “Anything we can do to keep these cells from waking up again or to help the immune system eliminate them could be of great benefit to many people. This research identified a previously unknown role for STING signaling in suppressing the development of aggressive metastasis.”
Along with heading a research lab that investigates cancer metastasis, Dr. Massagué also leads the Alan and Sandra Gerry Metastasis and Tumor Ecosystems Center at MSK, which supports efforts across the institution to better understand, prevent, and treat metastasis.
The Journey of a Metastatic Cell
Even when a primary tumor is successfully treated, cells that have broken away from the tumor often linger in the body in a dormant state that allows them to evade detection by the immune system for years at a time. Then, after the dormant cells have developed new traits to help them survive, they can wake up and start their runaway growth again.
Instead of focusing on late-stage disease, when large, aggressive metastases have already emerged, the researchers focused on earlier stages — after cancer has developed but before it has been able to successfully gain a foothold in new parts of the body, says Jing Hu, PhD, a senior research scientist in the Massagué Lab and the first author of the Nature study.
“For example, nearly half of patients diagnosed with stage 1 or stage 2 lung adenocarcinoma will develop metastases,” she says. “At the time of diagnosis, we believe many of those patients will already have had some cancer cells break away from their primary tumor and travel to other organs, where they will stay in a dormant state until they wake up and generate what we call spontaneous or breakthrough metastases.”
Many of these cancer cells that break away from a primary tumor will die during their journey through the bloodstream to far-flung organs. But those that survive learn to adjust to the assaults and stresses of the human body.
“The tumor cells are not in a supportive environment at the beginning,” Dr. Hu says. “So they have to adapt and develop their own self-supporting niche until they’re ready, eventually, to wake up and start a fast-growing metastasis. The interaction with the person’s immune system is very important to this process.”
Genetic Screen Identifies New Role for STING
Using mouse models of early-stage metastasis from lung cancer, the research team conducted a genetic screen to look at the activity of genes in the tumor cells that are important for interactions with the host’s immune system.
That’s how they identified the STING pathway — an acronym for stimulator of interferon genes — as a suppressor of metastatic outbreaks.
“This made a lot of sense to us because STING signaling is known to be important for triggering an immune response against cells made sick by viruses or by cancer mutations,” Dr. Hu adds.
STING Activity Changes Across Different Stages of Metastasis
Importantly, the researchers found that STING expression changes across different stages of metastasis.
In the dormant stage, STING activity is low — and the dormant cells excel at hiding out from immune defenders.
Moving out of the dormant stage and into an awakened, proliferative stage, the metastatic cells start to have increased STING activity. This makes them more vulnerable to attack by the immune system.
But cells that survive this bottleneck to generate larger clusters, called macrometastastes, again show reduced STING levels, which makes them more resistant to the immune system.
“This means that these tumor cells will be recognized differently by the immune system at different stages of metastasis development,” Dr. Massagué says. “Using STING activators in conjunction with that window of increased STING activity in the reawakened cancer cells could be an opportunity to help the body’s immune defenders destroy them.”
Indeed, when scientists artificially increased STING signaling in those aggressive metastatic cells, they attracted more immune defenders like natural killer cells and T cells, which swooped in to kill them off.
And when the scientists activated STING in mice lacking key immune cells, metastasis still developed — pointing to a critical role for STING in recruiting the immune cells to attack the cancer cells.
These tiny micrometastases are much easier to study in mice, however, than in people. So, to verify the applicability of their findings, the scientists compared their observations in the mouse models with small numbers of cancer cells found in the lymph nodes of patients with early-stage lung cancer. What they saw in patients supported what they were discovering in the lab.
The team also identified a new role for the signaling molecule TGF-beta in suppressing STING activity during the dormant stage of metastasis. Dr. Massagué is well known for his pioneering work elucidating TGF-beta signaling and has long studied its importance in cancer. “It’s our lab’s favorite molecule,” Dr. Hu jokes.
Moving Toward New Treatments for Metastasis
Drugs that increase STING activity, known as STING agonists, are already being evaluated in a few clinical trials, Dr. Hu notes. But those trials are for patients with advanced cancers, when aggressive metastases have already emerged. By then, the tumor cells have already reshaped their local environment to better protect themselves from the attacks of the host’s immune system.
“At the earlier stages of metastasis, STING agonists may be able to have a better effect,” Dr. Hu says. “At that point, the tumor has not yet fully established an immune-evading microenvironment for itself, and STING signaling within the tumor cells will be higher.”
Ultimately, the researchers hope to collaborate with clinicians to develop a clinical trial to target micrometastases’ newly discovered vulnerabilities in patients with early-stage disease. One approach would be to leverage STING to kill the cells off before they can start breakthrough metastases. Another possibility could be to try to keep the cells in a dormant state forever.
Meanwhile, the Massagué Lab is continuing to explore STING agonists’ ability to destroy lingering metastatic cells, as well as potential opportunities to harness TGF-beta against early-stage metastasis.
“There is a lot more work to be done before these new insights might be applied in the clinic,” Dr. Massagué says. “But we are encouraged that these efforts and others are bringing us closer to the day when we can prevent many more cancer deaths from metastasis.”
The research team also included Sloan Kettering Institute investigators Karuna Ganesh, MD, PhD; Scott Lowe, PhD; Dana Pe’er, PhD; and Joseph Sun, PhD; along with Christina Iacobuzio-Donahue, MD, PhD, from MSK’s Human Oncology and Pathogenesis Program.
Additional authors, all from MSK, include Rebecca Delconte, PhD; Siting Gan, PhD; Gabriela N. Johnson; Francisco J. Sánchez-Rivera, PhD (now at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology); Yu-Jui Ho, PhD; Jessica P. Hampton (now at Stanford Medical School); Sanjay Kottapalli; Adriana Mujal, PhD; Elisa de Stanchina, PhD; Huiyong Zhao, MD; and Zhenghan Wang, PhD.
The research was supported by National Institutes of Health grants (R35-CA252978, P01-CA129243, U54-CA209975, K08-CA230213, and P30 CA008748); the Alan and
Sandra Gerry Metastasis and Tumor Ecosystems Center at MSK; an Agilent Technologies Thought Leader Award; and postdoctoral fellowships from
the Terri Brodeur Breast Cancer Foundation, the Translational Research Oncology Training Program (5T32CA160001), and the Damon Runyon Quantitative Biology program. Additionally, Dr. Sánchez-Rivera is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Hanna H. Gray Fellow and Dr. Lowe is an HHMI Investigator.
Dr. Lowe received funding and research support from Agilent Technologies, used to generate sgRNA libraries described in the study.
END
Memorial Sloan Kettering scientists identify potential new strategy against metastasis
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
You can find the flow – and scientists can measure it
2023-03-29
You know when you’ve found the flow. You experience it when you are doing something that engages you so fully that time seems to fly by. Maybe it's a job, or something completely different, like chess or computer games or football or shovelling snow.
But flow is not just an expression that people use. It has been a concept used by psychologists for almost 50 years, because finding the flow can be useful for people.
“Finding the flow zone can be important when teachers have to adapt their instruction. If we find the flow, we’ve also found the right level for the students,” says Hermundur Sigmundsson, a professor in the Department of Psychology ...
Transportation noise increases risk for suicides
2023-03-29
Mental health disorders affect nearly one billion people worldwide and are a leading cause of suicide. In Switzerland, it is estimated that about 1.4 million people are affected by mental health issues and that approximately 1,000 people take their lives every year. Environmental factors such as air pollution or noise have been linked to adverse health effects such as cardiovascular diseases and general well-being. However, robust evidence on the effects of transportation noise on mental health disorders remains scarce.
For the first time, ...
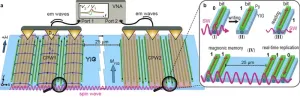
Magnon-based computation could signal computing paradigm shift
2023-03-29
Like electronics or photonics, magnonics is an engineering subfield that aims to advance information technologies when it comes to speed, device architecture, and energy consumption. A magnon corresponds to the specific amount of energy required to change the magnetization of a material via a collective excitation called a spin wave.
Because they interact with magnetic fields, magnons can be used to encode and transport data without electron flows, which involve energy loss through heating (known as Joule heating) of the conductor ...
New ways to protect food crops from climate change and other disruptions
2023-03-29
“There’s no doubt we can produce enough food for the world’s population - humanity is strategic enough to achieve that. The question is whether - because of war and conflict and corruption and destabilization - we do,” said World Food Programme leader David Beasley in an interview with Time magazine earlier this year.
Indeed, projections show that we are not on track to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 2 of Zero Hunger by 2030. As climate and security crises continue to destabilise our food sources, researchers are taking a critical look not just at how we produce food - but at the entire systems behind ...
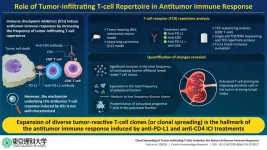
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Antitumor Response: Decoding Molecular Mechanisms
2023-03-29
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are widely sought after for the treatment of different types of cancers. Unfortunately, only 20–30% patients with cancer respond to ICI treatment. Although the factors that influence the positive or negative response to ICI treatment are poorly understood, the strength of the ICIs’ antitumor response by TILs is thought to play a key role. Hence, investigating the antitumor response induced by ICIs might provide insights into their underlying mechanism.
It is known that CD8+ tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TILs) are the primary effector cells that lead ...
Olivier Delattre, MD, Ph.D., honored with 2023 AACR-St. Baldrick’s Foundation Award for Outstanding Achievement in Pediatric Cancer Research
2023-03-29
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) will award Olivier Delattre, MD, PhD, with the 2023 AACR-St. Baldrick’s Foundation Award for Outstanding Achievement in Pediatric Cancer Research during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida.
Delattre is the director of the SIREDO Oncology Center and the research unit director of the Cancer, Heterogeneity, Instability and Plasticity (CHIP) unit at Inserm/Institut Curie. ...
SwRI’s NASGRO software selected for Space Technology Hall of Fame
2023-03-29
SAN ANTONIO — March 29, 2023 —The NASGRO® software suite will be inducted into the Space Technology Hall of Fame alongside the leaders of its development team, Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Craig McClung and Joe Cardinal, as well as Joachim Beek of NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC). The award ceremony will occur during the annual Space Symposium in Colorado Springs. NASGRO, originally developed by NASA and currently managed by SwRI, analyzes fatigue crack growth and fracture in structures and mechanical components. It is a key tool used to substantiate the structural integrity of aircraft, spacecraft, rotorcraft, gas turbine engines, pressure ...
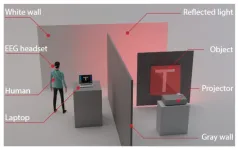
Study shows human brain can assist with computational ghost imaging
2023-03-29
Interacting with computers by brain activity seems less futuristic these days, thanks to researchers and entrepreneurs who have been attempting to tap the potential of brain-computer interfaces for augmented cognitive abilities. Recently, Gao Wang and Daniele Faccio at the University of Glasgow demonstrated that it is possible to connect a human brain and a computer to perform simple computational imaging tasks. Similar advances could someday extend the sensing range of human vision and provide new approaches to the neurophysics of human perception. This research was published Feb. 24 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner ...
COVID-19 during pregnancy may increase obesity risk in children
2023-03-29
WASHINGTON—Children born to mothers who had COVID-19 during pregnancy may be more likely to develop obesity, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
More than 100 million COVID-19 cases have been reported in the United States since 2019, and there is limited information on the long-term health effects of the infection. Pregnant women make up 9% of reproductive-aged women with COVID-19, and millions of babies will be exposed to maternal infection during ...
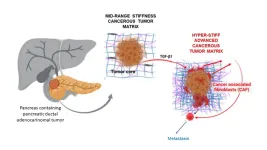
Advanced pancreatic cancer model for developing personalized therapies
2023-03-29
(LOS ANGELES) – March 28, 2023 - Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is highly aggressive and lethal. It is the most prevalent type of pancreatic cancer, making up 90% of cases; it also has a high rate of metastasis, with an average five-year survival rate of less than 10%.
It is thought that the dense, stiff matrix immediately surrounding its tumor cells plays a major role in PDAC disease progression. In addition to influencing pancreatic tissue fibrosis, it also limits accessibility and effectiveness of anticancer drugs against the tumor and enhances the promotion of surface ...