Do your headaches happen at the same time of day?
Meta-analysis: Cluster headache, migraine have strong links to circadian system
2023-03-29
(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 29, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Both cluster headache and migraine have strong links to the circadian system, the internal clock that regulates body processes, according to a meta-analysis published in the March 29, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The meta-analysis included all available studies on cluster headache and migraine that included circadian features. This included information on the timing of headaches during the day and during the year as well as studies on whether genes associated with the circadian clock are more common in people with these headaches.
The researchers also looked at studies on cluster headache and migraine and hormones related to the circadian system, including cortisol and melatonin.
“The data suggest that both of these headache disorders are highly circadian at multiple levels, especially cluster headache,” said study author Mark Joseph Burish, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston in Texas and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. “This reinforces the importance of the hypothalamus—the area of the brain that houses the primary biological clock—and its role in cluster headache and migraine. It also raises the question of the genetics of triggers such as sleep changes that are known triggers for migraine and are cues for the body’s circadian rhythm.”
For cluster headache, the meta-analysis found a circadian pattern of headache attacks in 71% of people. Attacks peaked in the late hours of the night to early hours of the morning. During the year, people had more attacks in the spring and fall. On the genetic level, cluster headache was associated with two main circadian genes, and five of the nine genes that increase the likelihood of having cluster headache are genes with a circadian pattern of expression.
People with cluster headache also had higher cortisol levels and lower melatonin levels than people without cluster headache.
For migraine, the meta-analysis showed a circadian pattern of attacks in 50% of people. While the peak for attacks during the day was broad, ranging from late morning until early evening, there was a circadian low point during the night when few attacks happened. Migraine was also associated with two core circadian genes, and 110 of the 168 genes associated with migraine were genes with a circadian pattern of expression.
People with migraine had lower levels of melatonin in their urine than people without migraine. In addition, melatonin levels were lower during a migraine attack.
“These results raise the potential for using circadian-based treatments for headache disorders,” Burish said. “This could include both treatments based on the circadian rhythm - such as taking medications at certain times of the day - and treatments that cause circadian changes, which certain medications can do.”
A limitation of the study was that researchers did not have information on factors that could influence the circadian cycle, such as medications, other disorders such as bipolar disorder or circadian rhythm issues such as night shift work.
The study was supported by the Will Erwin Headache Research Foundation.
Learn more about headache at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 38,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-29
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a promising therapy for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). A first-of-its-kind collaborative study led by researchers at Texas Children’s Hospital, Baylor College of Medicine, and Brigham & Women’s Hospital has found that mapping neural connections in the brains of OCD patients offers key insights that explain the observed improvements in their clinical outcomes after DBS. The study was published in Biological Psychiatry.
Neuropsychiatric disorders such as obsessive-compulsive ...
2023-03-29
PORTLAND, Oregon -- New research from Oregon Health & Science University and collaborators indicates lab-made antibodies may be able to cure people infected with yellow fever, a virus for which there is no treatment.
The natural immune response to invading pathogens normally involves making protective proteins called antibodies. A study published today in Science Translational Medicine suggests that a single monoclonal antibody infusion can strengthen the body’s fight against yellow fever.
In the study, the yellow fever virus was undetectable in all animals that received monoclonal antibody infusions after being exposed to the virus.
“Two ...
2023-03-29
Evermed and the American College of Cardiology (ACC) have announced the launch of ACC Anywhere, a new content hub that provides cardiologists around the world with on-demand access to the latest clinical knowledge. The hub contains original content from five conferences including ACC’s 2022 and 2023 Annual Scientific Session, with additional conferences to be added in the future.
Evermed was selected to collaborate with ACC due to its advanced AI-powered recommender engine and its ability to effectively deliver medical education content 365 days per year. In addition, Evermed’s technology will help drive yearlong engagement to ensure that users are able ...
2023-03-29
A recent study from Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine has expanded the clinical spectrum of a new epileptic disorder called Intellectual Developmental Disorder with Macrocephaly, Seizures, and Speech Delay (IDDMSSD) with the identification of the first recurrently affected residue identified in the protein kinase domain of PAK1 protein. The study, published in the American Journal of Medical Genetics: Part A, found potential correlations between how and which organ ...
2023-03-29
“In the present study, we found that downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induced malignancy via upregulation of EGF-dependent CLDN-2 and TGF-β-dependent cell metabolism in human lung adenocarcinoma.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 29, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 24, 2023, entitled, “Downregulation of angulin-1/LSR induces malignancy via upregulation of EGF-dependent claudin-2 and TGF-β-dependent cell metabolism in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.”
Abnormal expression of bicellular tight junction claudins, including ...
2023-03-29
Nearly one in five American adults has diabetes. But that doesn’t mean the common condition is simple to treat or manage. Diabetes and its complications are the No. 1 cause of kidney failure, adult blindness, and lower-limb amputations. It’s also the seventh-leading cause of death in the U.S. As with so many chronic conditions, diabetes also disproportionately affects the most vulnerable in our communities, further exacerbating existing health disparities.
In a new supplemental issue of the ...
2023-03-29
(03/29/2023) — Resistance to Paxlovid is already evident among viral SARS-CoV-2 variants currently circulating globally, indicating that this stand-alone drug known as a protease inhibitor could soon become less effective in treating COVID-19 infections.
This conclusion was presented in a study published today online in the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances.
This study — conducted by the Midwest Antiviral Drug Discovery (AViDD) Center — shows that drug-resistant variants have appeared multiple times independently in different parts of the world, with regional clusters providing evidence for person-to-person transmission. In ...
2023-03-29
“[...] there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 29, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Senescence and extracellular vesicles: novel partners in vascular amyloidosis.”
In their editorial, researchers Meredith Whitehead, Marco Antonazzi and Catherine M. Shanahan from King’s College London discussed amyloidosis—a ...
2023-03-29
A new analysis shows that, compared to similarly high-income European countries, the US continues to have substantially higher death rates at all but the oldest ages, resulting in more “excess deaths,” and this gap widened during the Covid-19 pandemic. Patrick Heuveline, of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 29, 2023.
Calculating excess death rates can be useful for comparing mortality between different countries or sub-populations, as well as before and after the onset of a health crisis. Prior research has documented a substantial widening of ...
2023-03-29
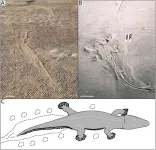
Ancient 2m-long amphibians swam like crocodiles long before true crocodiles existed, according to a study published March 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David P. Groenewald of the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa and colleagues.
During the Late Permian Period, just over 250 million years ago, South Africa was home to rhinesuchid temnospondyls, large predatory amphibians with bodies similar to crocodiles or big salamanders. These extinct animals are known mainly from skeletal remains, but in this study, researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Do your headaches happen at the same time of day?
Meta-analysis: Cluster headache, migraine have strong links to circadian system