(Press-News.org) For nearly 50 years, a jawless fish called the lamprey has interested scientists because of its remarkable ability to recover from spinal cord injuries. A new study reveals a possible technique lampreys may use to swim again, despite sparse neural regeneration.
Christina Hamlet of Bucknell University and collaborators, including Jennifer R. Morgan of the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), used a mathematical model to demonstrate how lampreys may use body-sensing feedback to regain swimming abilities after spinal injury. The study could inspire new therapeutic approaches in humans or algorithms for locomotion in soft robots. The paper is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“The punchline of the paper is that even in the absence of descending command across that [spinal] lesion, you can boost the sensory feedback and restore locomotion,” said Morgan, MBL Senior Scientist and Director of the MBL’s Eugene Bell Center for Regenerative Biology and Tissue Engineering.
Unlike humans and other mammals, lampreys recover quickly and almost completely even after severe lesions high up in the spinal cord. Morgan previously discovered that although neural regeneration does aid recovery in lampreys, it doesn’t tell the full story. Only a small percentage of the neurons and neuronal connections are restored across a spinal injury, so they must use another mechanism.
“I had all of these questions about how that could possibly work. How could you get a functioning nervous system with a few small sparse connections?” Morgan asked.
Scientists had hypothesized that lampreys might use body-sensing feedback (called proprioception or kinesthesia) to guide their movements in addition to descending neural connections in the spinal cord. Morgan had reached out to discuss this with an old friend of hers from MBL, Eric Tytell, Associate Professor of Biology at Tufts University and former MBL Whitman Center Investigator. Eric was already collaborating with Lisa Fauci, a Professor of Mathematics at Tulane University, and Christina Hamlet, who was a co-mentored postdoc at Tulane.
Tytell, Fauci, and Hamlet were using mathematical models to mimic movement in lampreys. They teamed up to “see if we could model some of the effects of sensory feedback on swimming behavior in lampreys,” said Hamlet, who is currently an Assistant Professor of Mathematics at Bucknell University.
The team began playing around with different scenarios of spinal injured lampreys – including both biologically plausible and implausible ones – all of which assumed no neural regeneration across the spinal cord lesion. This is the utility of modeling, said Hamlet, “We can break things that you can't break in biology.” The model took into account the curves and stretch created in the body above the lesion and sent that information to the rest of the body through the muscles, not the spinal cord.
Even with a moderate amount of sensory feedback, the models showed a surprising recovery of swimming patterns in the biologically plausible models. Stronger sensory feedback led to even greater improvement.
Because lampreys do grow back some of their neurons after a lesion and therefore have descending command from the brain to drive movement, they may need even less sensory feedback than the model. The team hopes to add neuronal regeneration into the model and test how that affects movement and interacts with sensory feedback.
"If you have a good computational model, you can go through so many more scenarios of manipulations than is practical with experimentation,” said Morgan.
The team hopes that this study and future research will contribute to therapies for humans with spinal injuries and diseases that affect movement. Brain machine interfaces and stimulator devices are beginning to incorporate body sensing feedback to create smoother movements after injury, and this research could inform the amount and type of feedback that humans need.
“Whether you're an animal like a lamprey that [recovers] spontaneously or a human that needs to be given a drug or an electrical stimulator device, getting to the point where you have a few things in the right place and then reuse what's already there should be more achievable than trying to recapitulate the identical original pattern of synaptic connections and growth,” said Morgan.
—###—
The Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) is dedicated to scientific discovery – exploring fundamental biology, understanding marine biodiversity and the environment, and informing the human condition through research and education. Founded in Woods Hole, Massachusetts in 1888, the MBL is a private, nonprofit institution and an affiliate of the University of Chicago.
END
After spinal cord injury, kinesthetic sense helps restore movement, model suggests
2023-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cookin' with gas: UWO professor earns patent for flameless industrial oven
2023-04-01
Pawel Olszewski, a University of Wisconsin Oshkosh associate mechanical engineering technology professor, recently was granted a U.S. patent for his flameless impingement oven, designed and built in the Teaching and Energy Research Industrial Lab (TERIL) on the Oshkosh campus.
Olszewski began the patent process back in 2019 with WiSys, the Wisconsin-based nonprofit dedicated to helping inventors protect their intellectual property, and received the news of approval in February.
Titled “flameless impingement oven,” the invention is patent number US 11,585,601 ...
This is your brain on everyday life
2023-04-01
A new study from a Washington University researcher offers fresh insights into how the brain goes to great lengths to processes and remember everyday events.
Zachariah Reagh, an assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, and co-author Charan Ranganath of the University of California, Davis, used functional MRI scanners to monitor the brains of subjects watching short videos of scenes that could have come from real life. These included men and women working ...
Iguana stole my cake! and left behind a nasty surprise
2023-04-01
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Friday 31 March
**Note – the press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese, see links below**
A 3-year-old girl was infected with an unusual Mycobacterium marinum infection, that developed following an iguana bite while she was on holiday in Costa Rica, report the doctors who treated her ...
Combination therapy a promising option for advanced kidney cancer patients already treated with immunotherapy
2023-04-01
Study Title: Belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma previously treated with immunotherapy: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study
Publication: The Lancet Oncology, March 31, 2023, 6:30pm ET, https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00097-9/fulltext
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Toni K. Choueiri, MD
Summary:
Immunotherapies, such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1, have become standard first line therapies for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer). Most patients, however, eventually experience disease progression, with no consensus on what therapy to use next. In this ...
Final Human Brain Project Summit closes with a vision for the future of digital brain research
2023-04-01
The ten-year European Flagship Human Brain Project (HBP) links brain research with computing and technology in a large-scale, interdisciplinary approach. During the HBP Summit, researchers presented the abundant scientific achievements of the project and the legacy that it will leave for the research community. With the project approaching its conclusion in September 2023, a focal point of the final HBP Summit in Marseille was the discussion of the future of digital brain research.
One of the lasting contributions of the project is the research infrastructure EBRAINS, which provides open access to advanced technologies, tools, data and services for brain research and will ...
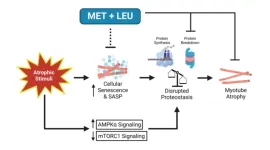
Metformin & leucine prevent cellular senescence & proteostasis disruption
2023-03-31
“Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
Aging coincides with the accumulation of senescent cells within skeletal muscle that produce inflammatory products, known as the senescence-associated secretory ...
Plastic transistor amplifies biochemical sensing signal
2023-03-31
Molecules in our body send faint biochemical signals when health issues arise
New technology boosts these signals by 1,000 times
New approach paves way for sensing signals in real-time in the body without sending blood or saliva samples to a lab
EVANSTON, Ill. — The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in ...
Childhood asthma declines during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-03-31
Half as many children in the United States were diagnosed with asthma in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous years, and Rutgers researchers think fewer colds may be part of the reason.
In a new Rutgers study, published in Respiratory Research, researchers examined the rates of new asthma diagnoses in a large commercial insurance claims database during the first year of the pandemic compared with rates of new diagnoses during the previous three years.
Using the Health Core Integrated Research ...
Study shows ketamine could be beneficial for treating brain injury in children
2023-03-31
A common anesthesia drug could be beneficial in reducing pressure inside the skull of children with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
Ketamine, a drug that has been used for anesthesia since the 1970s, has traditionally been avoided for patients with TBI due to early studies suggesting that it could raise the pressure inside of the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP).
More recent studies have suggested otherwise, said lead author Michael Wolf, MD, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Neurological ...
Yak milk consumption among Mongol Empire elites
2023-03-31
Photos
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed a date when elite Mongol Empire people were drinking yak milk, according to a study co-led by a University of Michigan researcher.
By analyzing proteins found within ancient dental calculus, an international team of researchers provides direct evidence for consumption of milk from multiple ruminants, including yak. In addition, they discovered milk and blood proteins associated with both horses and ruminants. The team's results are published in Communication Biology.
The study presents novel protein findings from an elite Mongol Era cemetery ...