(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS – Studies have shown that Mexican Americans have worse outcomes after a stroke than non-Hispanic white Americans. A new study looks at whether the language Mexican American people speak is linked to how well they recover after a stroke. The study is published in the April 12, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our study found that Mexican American people who spoke only Spanish had worse neurologic outcomes three months after having a stroke than Mexican American people who spoke only English or were bilingual,” said study author Lewis B. Morgenstern, MD, of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor and a Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology. “More research is needed into what factors and barriers may influence these worse outcomes.”
The study involved 1,096 Mexican American people in Corpus Christi, Texas, who had a stroke over a 10-year period. Researchers looked at results three months after the stroke in three areas: neurologic, functional and thinking and memory skills. Neurologic results cover areas such as muscle strength and coordination and problems with speech or vision. Functional results look at how well people can complete their daily activities such as showering and preparing meals.
The 170 people who spoke Spanish only were compared to the 926 people who spoke English only or were bilingual. Those who spoke Spanish only were older, had received less education and had worse neurologic scores at the time of the stroke than those in the other group.
Three months after the stroke, the Spanish-only speakers had average neurologic scores of seven, where scores of five to 14 indicate moderate effects from a stroke. The English-only and bilingual speakers had average scores of four, where scores of one to four indicate mild effects. The results remained after researchers adjusted for the differences between the two groups and other factors that could affect stroke risk, such as high blood pressure and diabetes.
The study found no difference between the two groups in how well they recovered their ability to complete their daily activities or in their thinking and memory skills.
“We conducted an earlier study in this same community finding that the language people spoke was not associated with any delay in their getting to the hospital or using emergency medical services after an ischemic stroke, so we definitely need more information to determine what is driving the differences in outcomes between these two groups,” Morgenstern said.
A limitation of the study was that there was a low number of Spanish-only speakers. Also, the majority of Mexican Americans in Corpus Christi are born in the United States, so these results may not be applicable to areas with a larger population of people born outside the United States.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the TRANSCENDS (Training in Research for Academic Neurologists to Sustain Careers and Enhance the Numbers of Diverse Scholars) program funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Learn more about stroke at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Is the language you speak tied to outcome after stroke?
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Archaeological sites at risk from coastal erosion on the Cyrenaican coast, Libya
2023-04-12
Archaeological sites along the Libyan shoreline are at risk of being damaged or lost due to increasing coastal erosion, according to a study published April 12, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kieran Westley and Julia Nikolaus of Ulster University, UK and colleagues.
The Cyrenaican coast of Eastern Libya, stretching from the Gulf of Sirte to the current Egypt-Libya border, has a long history of human occupation back to the Palaeolithic era, and it therefore hosts numerous important and often ...
Poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological impacts in bereaved teenagers
2023-04-12
The death of a parent can affect the health and well-being of children and adolescents, including higher risk of depression. A study published in PLOS ONE by Dröfn Birgisdóttir at Lund University, Lund, Sweden and colleagues suggests poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological symptoms among bereaved youth.
Parentally bereaved children are at increased risk for mental illness including depression, anxiety, suicide attempts, and self-injurious behaviors. However, the relationship ...
The stripes of the Lesser Pacific Striped Octopus are as unique as our own fingerprints, enabling scientists to track individuals as they grow
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0265292
Article Title: Individually unique, fixed stripe configurations of Octopus chierchiae allow for photoidentification in long-term studies
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Most retail cannabis may be less potent than claimed, with THC being at least 15% less potent than reported on the label in around 70% of products sampled in Colorado
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282396
Article Title: Uncomfortably high: Testing reveals inflated THC potency on retail Cannabis labels
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Headspace Sensory LLC provided funding for purchase of 13 of the 23 Cannabis samples that were included as part of another study [47], but had no other involvement in this study. All other funding was provided by the McGlaughlin Lab at the University of Northern Colorado and by the first author. Mile High Labs provided support for this study in the form of salaries for VJ and JH. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ ...
New 52 million-year-old bat species discovered in Wyoming, US, is the oldest bat skeleton known
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283505
Article Title: The oldest known bat skeletons and their implications for Eocene chiropteran diversification
Author Countries: The Netherlands, USA
Funding: 1) Theodore Roosevelt Memorial Fund of the American Museum of Natural History (TBR) https://www.amnh.org/research/richard-gilder-graduate-school/academics-and-research/fellowship-and-grant-opportunities/research-grants-and-graduate-student-exchange-fellowships/roosevelt-memorial-fund 2) ...
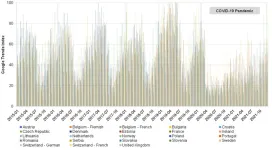
Google Trends reveal how the spread of chickenpox may have been suppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283465
Article Title: Impact assessment of immunization and the COVID-19 pandemic on varicella across Europe using digital epidemiology methods: A descriptive study
Author Countries: Sweden, Lithuania, Ireland, USA, Spain
Funding: Funding for this research was provided by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (MSD). We confirm that the funder provided support in the form of salaries for Ugne Sabale, Ligita Jarmale, Janice Murtagh, Manjiri Pawaskar, and Goran Bencina, but did not have any additional ...
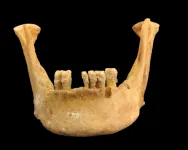
Got milk? The ancient Tibetans did, according to study
2023-04-12
New research into ancient populations that resided on the Tibetan Plateau has found that dairy pastoralism was being practiced far earlier than previously thought and may have been key to long-term settlement of the region’s extreme environment.
Professor Michael Petraglia, Director of Griffith’s Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, was part of the international research team that set out to understand how prehistoric populations adapted to the vast, agriculturally poor highlands of the Tibetan Plateau.
The research, ...
From tragedy, a new potential cancer treatment
2023-04-12
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a lethal pediatric brain cancer that often kills within a year of diagnosis. Surgery is almost impossible because of the tumors’ location. Chemotherapy has debilitating side effects. New treatment options are desperately needed.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Professor Adrian Krainer is best known for his groundbreaking research on antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)—molecules that can control protein levels in cells. His efforts led to Spinraza®, ...
Dairy foods helped ancient Tibetans thrive in one of Earth’s most inhospitable environments
2023-04-12
The Tibetan Plateau, known as the “third pole”, or “roof of the world”, is one of the most inhospitable environments on Earth. While positive natural selection at several genomic loci enabled early Tibetans to better adapt to high elevations, obtaining sufficient food from the resource-poor highlands would have remained a challenge.
Now, a new study in the journal Science Advances reveals that dairy was a key component of early human diets on the Tibetan Plateau. The study reports ancient ...
Multifunctional patch offers early detection of plant diseases, other crop threats
2023-04-12
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed an electronic patch that can be applied to the leaves of plants to monitor crops for different pathogens – such as viral and fungal infections – and stresses such as drought or salinity. In testing, the researchers found the patch was able to detect a viral infection in tomatoes more than a week before growers would be able to detect any visible symptoms of disease.
“This is important because the earlier growers can identify plant diseases or fungal infections, the ...