(Press-News.org) Québec City, April 14, 2023 - Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy, a degenerative eye disease, causes progressive vision loss that can induce blindness. It is the leading cause of corneal transplantation, but the scarcity of grafts hinders its treatment. A research team from Université Laval and Université de Montréal has identified a way to slow the disease and even avoid transplantation if diagnosed at an early stage.
In people with the disease, the endothelial cells at the back of the cornea die more quickly than in healthy people. "Everyone loses them at a slow rate, slow enough to make it to the end of our lives without problems. For sick people, depletion is accelerated by factors not yet understood at the molecular level. Since the cells do not divide, they do not replace themselves," says Patrick J. Rochette, full professor at the Faculty of Medicine at Université Laval and a researcher at the CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Center, who conducted the study.
These endothelial cells play an essential role in vision. They ensure that the cornea remains transparent by keeping it partially dehydrated. When the cells die, the cornea becomes wet and cloudy, which can lead to complete blindness.
In a previous study, the research team showed that mitochondria, the energy factories of cells, were central to the disease. "In people with the disease, the mitochondria become depleted rapidly, leading to cell death. The more cells die, the more the mitochondria in other cells have to compensate, which accelerates their depletion. It's a vicious circle," explains Patrick J. Rochette.
Reduce Mortality Rate
The research team wondered whether injecting healthy mitochondria into cells could delay the progression of Fuchs' dystrophy. To test their hypothesis, the scientists used diseased endothelium removed during a corneal transplant. "We were able to save cells close to death, going from a 60% mortality rate to 10%," Rochette said. These results demonstrate a high therapeutic potential for the injection of mitochondria.
The strength of this approach lies in the automatic recycling of diseased mitochondria without injecting healthy ones directly into the cell. "Cells eat mitochondria as if their life depended on them. Any cell, even if it is dying, will take them up. The replacement happens by itself. After 24 hours, only healthy mitochondria remain," says the researcher.
In the study, the healthy mitochondria were grown under controlled conditions, but the research group is developing an approach to extract them from the patient's blood.
If Fuchs' dystrophy is diagnosed at an early stage, when most endothelial cells are still alive, the approach could maintain vision without a transplant. The injection of mitochondria would be a benign procedure, much less invasive than surgery.
This study was published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports. The authors are Sébastien Méthot, Stéphanie Proulx and Patrick J. Rochette, from Université Laval, and Isabelle Brunette, from Université de Montréal.
About Université Laval
Facebook | Twitter | LinkedIn
-30-
Source :
Public Affairs Team
Université Laval
418-656-3355
medias@ulaval.ca
Twitter feed
YouTube Press Room
END
A new study published in the journal PeerJ by Robert W. Boessenecker (CofC), Brian L. Beatty (NYIT), and Jonathan H. Geisler (NYIT) reports a wealth of new fossils of the early toothed baleen whale Coronodon from Oligocene (23-30 million years old) rock layers near Charleston, South Carolina. These include five new skulls, representing two new species: Coronodon planifrons and Coronodon newtonorum, and young juveniles of Coronodon havensteini – first named from a single skull by this team in 2017. Coronodon is one of the most primitive members ...
While the wheel does not need to be reinvented, there are benefits to the development of new nano-wheels, according to a multi-institute research team based in China. The group fabricated a novel family of metallic compounds, each of which exhibit unique properties desirable for next-generation technologies, such as advanced sensors.
Their findings were made available online on March 12 in Polyoxometalates.
“Polymetallic complexes are of great interest not only for their appealing molecular structure but also ...
There is a need for new drugs. For example, many of the antibiotics that we have been using for a long time are becoming less effective. Chemists and pharmaceutical scientists are frantically searching for new active substances, especially those that can penetrate cell membranes, as these are the only ones that patients can take orally in the form of a tablet or syrup. Only these active ingredients pass through the intestinal wall in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream to reach the affected area in the body. For active ingredients that cannot penetrate the cell membrane, physicians have no choice but to inject them directly into ...
Cancers are notoriously known for their high mortality rate and increasing incidence worldwide. Among them, lung cancer is arguably one of the most devastating ones. According to the World Cancer Research Fund International, lung cancer was the second most common cancer around the world in 2020, with more than 2.2 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths.
However, lung cancer, like other cancers, is easier to treat if caught earlier. “The reported 1-year survival rate for stage V is just 15% to 19% compared with 81% to 85% for stage I, which means that the early ...
Chemotherapy is associated with an increased risk of treatment-related heart damage, including heart failure and cerebrovascular disease, for many patients. But a new meta-analysis, presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient 2023 conference, finds that Black patients or patients of African ancestry have 71% higher odds of cardiotoxicity following cancer treatment compared to White patients.
Cardiotoxicity is any heart damage stemming from cancer treatment or drugs, including ...
WASHINGTON—On World Quantum Day, Optica Publishing Group announced it will begin publishing a new journal in September 2023 dedicated to highly selective results in quantum information science and technology (QIST). The new journal, Optica Quantum, joins the Society’s portfolio of the most-cited journals in optics and photonics and will provide the community with articles of the same exceptional standards for quality, novelty, and significance as its parent journal, Optica.
The concept of quantum light serves as a foundation for many quantum technologies and ongoing ...
The alnus ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus germanus, also known as the black stem borer, was accidentally introduced by humans from its native east Asia to North America and Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. X. germanus is a so-called ambrosia beetle, which means that it farms its own food: a specialized fungal symbiont which it ‘sows’ and tends inside the galleries that it digs inside wood. It is a destructive invasive pest, known to attack more than 200 species from 51 families of broadleaf and conifer trees. While it prefers to colonize dead ...
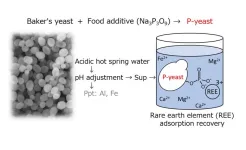
The demand for precious metals and rare earths is expected to continue increasing in the future. Due to limited production areas, recycling from precision equipment and recovering from seawater and hot spring water are needed to ensure a stable supply.
A research group led by Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering has successfully developed an adsorbent material that can selectively recover rare earth elements (REEs) using environmentally friendly and inexpensive baker’s yeast and trimetaphosphate, which is used as a food additive.
The research group conducted experiments using ...
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Did the recent mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) outbreak end because of “network immunity”? That’s the theory being put forward by Belgian researchers at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
2022 saw a global outbreak of mpox, a viral ...
Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
The Lancet Public Health: Hearing aids may protect against a higher risk of dementia associated with hearing loss, study suggests
Study of 437,704 people suggests those experiencing hearing loss and not using hearing aids may have a higher risk of dementia than people without hearing loss. Those using hearing aids did not appear to be at an increased risk of dementia.
After adjusting for other factors, study analysis suggests a 1.7% risk of dementia in people with hearing loss who are not using hearing aids, compared to 1.2% among those without hearing loss ...