(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study of survival outcomes for 1,618 U.S. counties suggest that greater representation of Black primary care physicians (PCPs) in the PCP workforce is associated with improved survival-related outcomes for Black individuals, although there was a dearth of U.S. counties with at least one Black PCP during each study time point. Investments to build a more representative PCP workforce nationally may be important for improving population health.
Authors: John E. Snyder, M.D., M.S., M.P.H., and Rachel D. Upton, Ph.D., of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services in Rockville, Maryland, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.6687)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.6687?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=041423
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancy
JAMA Network Open
2023-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Racial, ethnic differences in barriers faced by medical college admission test examinees
2023-04-14
About The Study: In this study of 81,755 Medical College Admission Test examinees, American Indian or Alaska Native, Black, and Hispanic students reported lower parental educational levels, greater educational and financial barriers, and greater discouragement from pre-health advisers than white students. These barriers may deter groups underrepresented in medicine from applying to and matriculating at medical school.
Authors: Jessica Faiz, M.D., M.S.H.P.M., of the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and UCLA in Los Angeles, is the corresponding ...
Calling AI experts! Join the hunt for exoplanets
2023-04-14
Artificial Intelligence (AI) experts have been challenged to help a new space mission to investigate Earth’s place in the universe.
The Ariel Data Challenge 2023, which launches on 14 April, is inviting AI and machine learning experts from industry and academia to help astronomers understand planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets.
Dr Ingo Waldmann, Associate Professor in Astrophysics, UCL (University College London) and Ariel Data Challenge lead said:
“AI has revolutionised many fields of science and industry in the past years. The field of exoplanets has fully arrived in the era of big-data and cutting edge AI is needed to break ...
Estonian researchers developed a method for instant energy-performance label
2023-04-14
The researchers of the FinEst Centre for Smart Cities of Tallinn University of Technology (Estonia, Europe) developed the DigiAudit platform to monitor and analyse energy use and indoor climate indicators of buildings and large real estate portfolios in real time. Thinnect, an Estonian IoT start-up company, will help sell the solution and market it worldwide.
We can only reach zero-emission buildings when we have reliable data
The European Union has set a target for all buildings to be zero-emission, or near-zero energy, by 2050. However, there is no reliable data on the energy consumption of many buildings, so it is not possible to monitor the condition ...
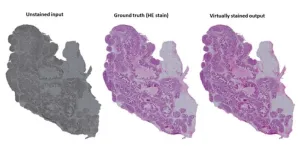
Researchers developed an AI-based method to replace chemical staining of tissue
2023-04-14
Researchers from the University of Eastern Finland, the University of Turku, and Tampere University have developed an artificial intelligence-based method for virtual staining of histopathological tissue samples as a part of the Nordic ABCAP consortium. Chemical staining has been the cornerstone of studying histopathology for more than a century and is widely applied in, for example, cancer diagnostics.
“Chemical staining makes the morphology of the almost transparent, low-contrast tissue sections visible. Without it, analysing tissue morphology is almost impossible for human vision. Chemical staining is irreversible, and in most ...
Rescuing corneal cells from death with the help of mitochondria
2023-04-14
Québec City, April 14, 2023 - Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy, a degenerative eye disease, causes progressive vision loss that can induce blindness. It is the leading cause of corneal transplantation, but the scarcity of grafts hinders its treatment. A research team from Université Laval and Université de Montréal has identified a way to slow the disease and even avoid transplantation if diagnosed at an early stage.
In people with the disease, the endothelial cells at the back of the cornea die more quickly than in healthy people. "Everyone loses them at a slow rate, slow enough to make it to the end of our lives ...
New specimens and species of the Oligocene toothed baleen whale Coronodon from South Carolina and the origin of Neoceti
2023-04-14
A new study published in the journal PeerJ by Robert W. Boessenecker (CofC), Brian L. Beatty (NYIT), and Jonathan H. Geisler (NYIT) reports a wealth of new fossils of the early toothed baleen whale Coronodon from Oligocene (23-30 million years old) rock layers near Charleston, South Carolina. These include five new skulls, representing two new species: Coronodon planifrons and Coronodon newtonorum, and young juveniles of Coronodon havensteini – first named from a single skull by this team in 2017. Coronodon is one of the most primitive members ...
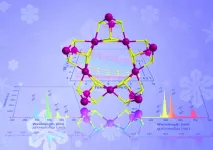
New family of wheel-like metallic clusters exhibit unique properties
2023-04-14
While the wheel does not need to be reinvented, there are benefits to the development of new nano-wheels, according to a multi-institute research team based in China. The group fabricated a novel family of metallic compounds, each of which exhibit unique properties desirable for next-generation technologies, such as advanced sensors.
Their findings were made available online on March 12 in Polyoxometalates.
“Polymetallic complexes are of great interest not only for their appealing molecular structure but also ...
How drugs get into the blood
2023-04-14
There is a need for new drugs. For example, many of the antibiotics that we have been using for a long time are becoming less effective. Chemists and pharmaceutical scientists are frantically searching for new active substances, especially those that can penetrate cell membranes, as these are the only ones that patients can take orally in the form of a tablet or syrup. Only these active ingredients pass through the intestinal wall in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream to reach the affected area in the body. For active ingredients that cannot penetrate the cell membrane, physicians have no choice but to inject them directly into ...
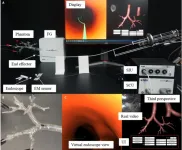
A novel robotic bronchoscope system for navigation and biopsy of pulmonary lesions
2023-04-14
Cancers are notoriously known for their high mortality rate and increasing incidence worldwide. Among them, lung cancer is arguably one of the most devastating ones. According to the World Cancer Research Fund International, lung cancer was the second most common cancer around the world in 2020, with more than 2.2 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths.
However, lung cancer, like other cancers, is easier to treat if caught earlier. “The reported 1-year survival rate for stage V is just 15% to 19% compared with 81% to 85% for stage I, which means that the early ...
Black cancer patients 71% more likely to experience heart damage following chemotherapy treatment
2023-04-14
Chemotherapy is associated with an increased risk of treatment-related heart damage, including heart failure and cerebrovascular disease, for many patients. But a new meta-analysis, presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient 2023 conference, finds that Black patients or patients of African ancestry have 71% higher odds of cardiotoxicity following cancer treatment compared to White patients.
Cardiotoxicity is any heart damage stemming from cancer treatment or drugs, including ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] Black representation in the primary care physician workforce and its association with population life expectancyJAMA Network Open