(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, Davis College of Engineering are using machine learning to identify new materials for high-efficiency solar cells. Using high-throughput experiments and machine learning-based algorithms, they have found it is possible to forecast the materials’ dynamic behavior with very high accuracy, without the need to perform as many experiments.
The work is featured on the cover of the April issue of ACS Energy Letters.
Hybrid perovskites are organic-inorganic molecules that have received a lot of attention over the past 10 years for their potential use in renewable energy, said Marina Leite, associate professor of materials science and engineering at UC Davis and senior author on the paper. Some are comparable in efficiency to silicon for making solar cells, but they are cheaper to make and lighter, potentially allowing a wide range of applications, including light-emitting devices.
A primary challenge in the field is that the perovskite devices tend to degrade way more readily than silicon when exposed to moisture, oxygen, light, heat, and voltage. The problem is to find which perovskites combine high-efficiency performance with resilience to environmental conditions.
Perovskites have a general structure of ABX3, where A is an organic (carbon-based) or inorganic group, B is lead or tin, and X is a halide (based on chlorine, iodine or fluorine or a combination). Therefore, “the number of possible chemical combinations alone is enormous”, Leite said. Further, they need to be assessed against multiple environmental conditions, alone and in combination, which results in a hyperparameter space that cannot be explored using conventional trial-and-error methods.
“The chemical parameter space is enormous,” Leite said. “To test them all would be very time consuming and tedious.”
High throughput experiments and machine learning
As a first and key step towards solving thesechallenges, Leite and graduate students Meghna Srivastava and Abigail Hering decide to test whether machine learning algorithms could be effective when testing and predicting the effects of moisture on material degradation.
Srivastava and Hering built an automated, high-throughput system to measure the photoluminescence efficiency of five different perovskite films against the conditions of summer days in Sacramento. They were able to collect over 7,000 measurements in a week, accumulating enough data for a reliable training set.
They used this data to train three different machine learning algorithms: a linear regression model, a neural network and a statistical model called SARIMAX. They compared the predictions of the models to physical results measured in the lab. The SARIMAX model showed best performance with a 90 percent match to observed results during a window of 50-plus hours.
“These results demonstrate that we can make use of machine learning in identifying candidate materials and suitable conditions to prevent degradation in perovskites,” Leite said. Next steps will be to expand the experiments to quantify combinations of multiple environmental factors.
The perovskite film itself is only a part of a complete photovoltaic cell, Leite said. The same machine learning approach could also be used to forecast the behavior of a complete device.
“Our paradigm is unique, and I am eager to see the upcoming measurements. Moreover, I am very proud of the students’ diligence during the pandemic” Leite said.
Srivastava is a 2021 National Science Foundation Fellow. Additional authors on the paper are Yu An and Juan-Pablo Correa-Baena, both from Georgia Tech. The work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation and Sandia National Laboratories.
END
Using machine learning to find reliable and low-cost solar cells
2023-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Resident T-cells key to salmonella immunity
2023-04-18
Salmonella infections cause about a million deaths a year worldwide, and there is an urgent need for better vaccines for both typhoid fever and non-typhoidal Salmonella disease. New work from researchers at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine shows how memory T cells, crucial for a vaccine that induces a powerful immune response, can be recruited into the liver in a mouse model of Salmonella.
The work was published April 11 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Understanding the immunology is key to developing a better vaccine,” said Professor Stephen McSorley, ...
Counting the cost of sunshine: Finding a better metric to measure human ecological footprints
2023-04-18
This planet of 8 billion people is bumping up against its ecological limits, and researchers are trying to quantify the effect of human activity on these finite resources. Some keep tallies of how much carbon they contribute to the atmosphere, others measure direct and indirect water consumption or keep tabs on the amount of land that our food habits demand.
Each of these “footprints” offers an estimate of the impacts individuals and institutions have on the wider world, and are useful — but are flawed, according to geographer Chris ...
School discipline can be predicted, new research says. Is it preventable?
2023-04-18
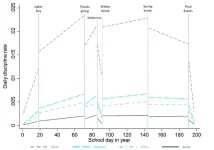
Berkeley — Rates of school discipline fluctuate widely and predictably throughout a school year and increase significantly faster for Black students than for their white counterparts, University of California, Berkeley, researchers have found.
A new study published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences documents for the first time the “dynamic” nature of student discipline during an academic year. Daily rates of punishment across all schools in the study ratchet up in the weeks before Thanksgiving break, decline immediately ...
How electricity can heal wounds three times as fast
2023-04-18
Chronic wounds are a major health problem for diabetic patients and the elderly – in extreme cases they can even lead to amputation. Using electric stimulation, researchers in a project at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Freiburg, Germany, have developed a method that speeds up the healing process, making wounds heal three times faster.
There is an old Swedish saying that one should never neglect a small wound or a friend in need. For most people, a small wound does not lead to any serious complications, but many common diagnoses ...
Orb weaver spider glue properties evolve faster than their glue genes, scientists find
2023-04-18
Spiders that don’t weave good silk don’t get to eat. The silk spiders produce which creates their webs is key to their survival – but spiders live in many different places which require webs fine-tuned for local success. Scientists studied the glue that makes orb weaver spiders’ webs sticky to understand how its material properties vary in different conditions.
“Discovering the sticky protein components of biological glues opens the doors to determining how material properties evolve,” said Dr Nadia Ayoub of Washington and Lee University, co-corresponding author of the study ...
Machine learning can help to flag risky messages on Instagram while preserving users’ privacy
2023-04-17
As regulators and providers grapple with the dual challenges of protecting younger social media users from harassment and bullying, while also taking steps to safeguard their privacy, a team of researchers from four leading universities has proposed a way to use machine learning technology to flag risky conversations on Instagram without having to eavesdrop on them. The discovery could open opportunities for platforms and parents to protect vulnerable, younger users, while preserving their privacy.
The team, led by researchers from Drexel University, Boston University, Georgia Institute of Technology ...
TOP advisory board welcomes new chair and members
2023-04-17
Charlottesville, VA – The Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines Advisory Board welcomes its new chair, Sean Grant, and board members to support its mission to promote transparency across the research lifecycle.
Grant is a Research Associate Professor at the HEDCO Institute for Evidence-Based Educational Practice at the University of Oregon with extensive experience researching TOP as Co-Principal Investigator for Transparency of Research Underpinning Social Intervention ...
UC Irvine physicists discover first transformable nano-scale electronic devices
2023-04-17
Irvine, Calif., April 17, 2023 — The nano-scale electronic parts in devices like smartphones are solid, static objects that once designed and built cannot transform into anything else. But University of California, Irvine physicists have reported the discovery of nano-scale devices that can transform into many different shapes and sizes even though they exist in solid states.
It’s a finding that could fundamentally change the nature of electronic devices, as well as the way scientists research atomic-scale quantum materials. The study is published ...
Dixit receives 2023 Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award
2023-04-17
Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was nominated for his work on imaging techniques for solid-state batteries.
Marm Dixit, a Weinberg Distinguished Staff Fellow at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was named the 2023 recipient of the Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award.
Since 2004, this biannual award has been given by the Advanced Photon Source (APS) user organization. It recognizes important scientific or technical accomplishments at (or beneficial to) the APS by a young investigator, typically a senior graduate student or early career researcher. The APS is a DOE Office ...
Medical dramas influence thoughts on dangers from vaping, new Twitter analysis reveals
2023-04-17
After three popular primetime medical dramas included storylines about health harms from using e-cigarettes, hundreds of people took to Twitter to comment – including some who said they planned to quit vaping because of what they saw on the shows. A new analysis led by University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health scientists and published in the Journal of Health Communication examines the tweets for insights into the use of television shows to share public health messaging.
Following the January 2020 episodes of New Amsterdam, Chicago Med and Grey’s Anatomy that each included plots involving adolescents with vaping-associated lung-injury, ...