(Press-News.org) Sleeve gastrectomy (SG), where about 80% of the stomach is removed, is effective for treating obesity and its complications, but it has been associated with bone loss in adolescents. In a prospective study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, imaging tests revealed that SG decreases strength and bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in adolescents and young adults.
In the 12-month prospective nonrandomized study, 29 adolescents/young adults with obesity underwent SG and 30 were followed without surgery. At baseline and 12 months, participants underwent computed tomography of the lumbar spine for bone assessments and magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen and thigh for body composition assessments.
Participants in the SG group lost an average of 34.3 kg (75.6 lbs) 12 months after surgery, whereas weight was unchanged in controls. There were significant reductions in abdominal fat tissue and thigh muscle in the SG group compared with controls. Also, bone strength and bone mineral density decreased in the SG group compared with controls. Reductions in bone strength and bone mineral density were associated with reductions in body mass index, abdominal fat tissue, and muscle.
“Weight loss surgery is very effective in treating obesity and obesity-associated comorbidities in adolescents and young adults with obesity; however, it can cause loss of bone density and strength. We hope that our study raises awareness of the importance of bone health after weight loss surgery, so physicians can make sure that children eat a healthy diet with enough calcium and vitamin D and engage in weight-bearing activity to build up muscle mass, which is good for bones,” said corresponding author Miriam A. Bredella, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jbmr.4784
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research publishes highly impactful original manuscripts, reviews, and special articles on basic, translational and clinical investigations relevant to the musculoskeletal system and mineral metabolism.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in scientific research and career-connected education. Founded in 1807, Wiley enables discovery, powers education, and shapes workforces. Through its industry-leading content, digital platforms, and knowledge networks, the company delivers on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Does weight loss surgery harm adolescents’ bones?
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does higher education’s protection against cognitive decline differ by race and ethnicity?
2023-04-19
In a study of older adults, higher educational attainment seemed to protect adults from cognitive decline, but this protective effect differed by race and ethnicity. Higher-educated White adults received a greater benefit than higher-educated Black or Latinx adults.
The study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society involved telephone assessments of cognitive function among 20,311 Black, Latinx, and White US adults aged 51–100 years.
On average, Black and Latinx adults scored lower compared with White adults, regardless of educational attainment. Irrespective of race and ...
Does dim light at night impact the health of moths and other insects?
2023-04-19
Results from a new study published in the Journal of Applied Ecology indicate that dim light pollution may have detrimental effects on insect populations and may explain part of the ongoing, large-scale insect declines around the world.
During the study, investigators raised the offspring of moths from urban and rural populations from North- and Mid-European countries and treated them with and without dim light at night. The researchers assessed the induction of diapause, a dormant state that is critical for survival through the winter.
Light treatment affected diapause overall, but more so in Mid- than in North-European populations. ...
Can a healthy diet prevent prostate cancer?
2023-04-19
A study published in BJU International found that adhering to healthy diets seems to have no effect on prostate cancer risk, but following an unhealthy diet might increase the risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer.
The study assessed the diets of 15,296 men recruited in Spain in from 1992–1996. Among these men, 609 prostate cancer cases were identified during a median follow-up of 17 years. Diets were categorized as Western, Prudent, or Mediterranean. The Western dietary pattern consisted of a high intake of high-fat dairy products, processed meat, refined ...
Does taking traditional Chinese medicine during pregnancy increase the risk of birth defects?
2023-04-19
New research published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica has revealed a link between the use of traditional Chinese medicine during pregnancy and congenital malformations, including heart defects, in children.
In the prospective study, 16,751 women who received obstetrics care from hospitals in China completed a survey on their use of traditional Chinese medicine before and during pregnancy. Among fetuses, there were 273 congenital malformations.
Fetuses exposed to traditional Chinese medicine had 2.1-times higher odds of developing congenital malformations compared with those without exposure. There were significant associations with congenital malformations in women ...
Modulating a specific protein could lead to new liver disease treatments
2023-04-19
In research published in The FASEB Journal, scientists have discovered that a molecule called Yes-associated protein (YAP) plays a key role in the development of liver scarring, or fibrosis, by influencing the behavior of premature cells called liver progenitor cells.
By manipulating YAP expression in these cells, the investigators were able to improve the cells' ability to regenerate and repair liver tissue.
“Collectively, our findings indicate that liver progenitor cells’ expansion and differentiation during liver fibrosis could be modulated by YAP, further suggesting the possibility of manipulating YAP expression in these cells as a potential ...
Drones over Texas reveal agricultural damage caused by wild pigs
2023-04-19
There are an estimated 6.9 million wild pigs in the United States, and the population has been rising in recent decades. In research published in Wildlife Society Bulletin, investigators used drones to capture images of the agricultural damage caused by these animals.
Drones took pictures of corn fields at different growth stages during 36 missions over an agricultural region in Delta County, Texas in 2019–2020.
Most damage occurred in later growth stages, when corn ears were maturing, seed was most nutritious, and producers had already invested in the majority ...
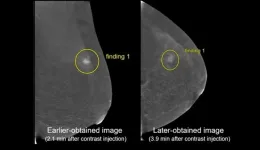
ARRS Annual Meeting: projection order, acquisition timing for contrast-enhanced mammography
2023-04-19
Honolulu, HI | April 19, 2023—Findings from a Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting at the Hawaiian Convention Center suggest there is institutional variability in both projection order and image acquisition timing for contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) protocol, with a previous systematic review revealing at least 7 different combinations in projection order.
“Our study demonstrates that earlier-obtained recombined imaging is significantly preferred in cancer lesion characterization, with a few instances demonstrating that biopsy-proven lesions may appear more conspicuously on earlier-obtained imaging (e.g., mass versus non-mass ...
Eating walnuts on a regular basis could benefit adolescents' cognitive development and contribute to their psychological maturation
2023-04-19
Eating walnuts on a regular basis could benefit the cognitive development of adolescents and contribute to their psychological maturation. These are some of the conclusions reached by a study led by the Institut d'Investigació Sanitària Pere Virgili (IISPV), in which ISGlobal (a centre promoted by "la Caixa" Foundation) and the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) have collaborated. This is unprecedented research; while there have been previous studies on ...
Concurrent vaping in early teen smokers linked to persistent and heavier smoking in late teens
2023-04-19
Young teen smokers who also vape may be at heightened risk of persistent and heavier smoking in their late teens, reveal the combined findings of two nationally representative UK and US studies, published online in the journal Tobacco Control.
Despite national differences in e-cigarette regulation and marketing between the two countries, the findings suggest that e-cigarettes may deepen early patterns of smoking, known as the ‘entrenchment hypothesis,’ conclude the researchers.
The prevalence of smoking among teens has fallen sharply over the past several decades. But it’s not clear what role ...
Previous cancer linked to long term heightened risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-04-19
Cancer survivors may be at long term heightened risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease, irrespective of traditional underlying risk factors, suggest the findings of a large UK Biobank study, published online in the journal Heart.
Those with previous breast or blood cancers may be at greatest risk, the findings indicate.
Shared vascular risk factors as well as the treatments and biological processes related to the cancer itself are all associated with a heightened risk of incident cardiovascular ...