(Press-News.org) Tallinn - APRIL 19TH, 2023 - Haut.AI, a SaaS company specializing in artificial intelligence for skin, hair, and wellness analytics, has just announced its new generative AI tech for modeling skin conditions - SkinGPT. This breakthrough in the beauty industry uses AI to create synthetic images and apply skin conditions to input image data. SkinGPT enables users to upload their photos and apply AI to simulate how their skin will change over time when using certain skincare products. SkinGPT enables the first-ever skincare virtual try-on with photorealistic simulations and scientific backing.
SkinGPT-generated content fills the gap between consumer expectations and product effects by visualizing long-term cosmetic benefits. The tool is intended for beauty brands and retailers, who can implement it into their e-commerce retail. They can educate consumers about the changes skin might undergo if using (or not using) certain products. Haut.AI’s product-specific technology uses simulations based on given products’ clinical claims to ensure accuracy.
Haut.AI's SkinGPT also raises awareness of the adverse effects of environmental factors such as allergens, solar insolation, and pollution on the skin. These factors can influence the skin long term, causing prolonged inflammation, but consumers are often unaware of the consequences - SkinGPT helps to visualize their effects over the months and years and show why it’s worth taking preventative measures.
Haut.AI aims to educate younger customers on the importance of skincare as well. Teenagers and people in their twenties tend to neglect adequate skincare, feeling they do not benefit from products as much as the mature group. SkinGPT simulation allows younger consumers to project different trajectories of their skin’s futures and realize the long-term benefits of personalized product usage.
It facilitates R&D and testing by generating synthetic images of aging effects, product effects, and environmental damage. It enables data augmentation and fills gaps in data, such as age and phenotype.
"Generative AI is omnipresent, and beauty shouldn’t lag. I am proud that Haut.AI is the first to introduce generative skincare AI. Our technology educates consumers and allows them to get transparency on the effects promised by beauty brands. SkinGPT is just beginning, further facilitating R&D through synthetic images and unlocking new heights in the beauty industry. We're committed to pushing the boundaries of AI in skin care, and SkinGPT is proof of our ongoing research," commented Anastasia Georgievskaya, the Co-Founder and CEO of Haut.AI.
Haut.AI's SkinGPT combines generative pre-trained transformers, diffusion models, GANs, and classical computer vision models, enabling the creation of photorealistic images. Image-to-image and noise-to-image conversion techniques are used, utilizing computer vision models for a skin assessment and image generation.
Knowing the current generative AI has its limitations, Haut.AI is determined to push the boundaries of AI in skincare continuously. Following the launch of SkinGPT, Haut.AI plans to expand its AI offerings, currently working with DALL-E for skin - a text-to-image tool for beauty-specific fields. Haut.AI aims to become a toolbox for AI-powered beauty industry solutions, pioneering personalization and beauty intelligence.
SkinGPT is a game-changer in the skincare industry, providing a fun and engaging way to gamify technology while providing tangible benefits. Haut.AI facilitates R&D, educates consumers, and elevates customer experiences. Following its launch in 2018, the company again proves they are the key player to watch at the forefront of beauty tech research and innovation.
About Haut.AI
Haut.AI is a European AI startup pioneering next-gen self-care. No more guesswork or one-size-fits-all solutions: with a selfie snap, our “beauty intelligence” AI creates routines exclusive to you. Built on best-in-class R&D and trained on over 3 million images, Haut.AI’s proprietary software analyzes image, lifestyle, and environmental data to develop precise reports and personalized recommendations for skin and hair with enamel and acne analysis coming. More than 80 companies, including Ulta, have used our SaaS toolkit to launch B2C applications, create personalized product journeys, and deliver on their sustainability commitments. As a proudly women-led company, our mission is to help you know your body and see your beauty. Start by visiting us at www.haut.ai.
END
Haut.AI becomes the first company to incorporate generative AI for skin simulations
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diet high in fruit and vegetables linked to lower miscarriage risk
2023-04-19
A preconception and early-pregnancy diet that contains lots of fruit, vegetables, seafood, dairy, eggs and grain may be associated with reducing risk of miscarriage, a new review of research suggests.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham, funded by Tommy’s, analysed 20 studies which explored women and birthing people’s eating habits in the months before and shortly after conceiving a baby to see whether these studies showed evidence of association with a lower or higher chance of miscarriage.
Writing in the journal Fertility and Sterility the Tommy’s National Centre for Miscarriage Research team conclude that there is evidence to ...
Does weight loss surgery harm adolescents’ bones?
2023-04-19
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG), where about 80% of the stomach is removed, is effective for treating obesity and its complications, but it has been associated with bone loss in adolescents. In a prospective study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, imaging tests revealed that SG decreases strength and bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in adolescents and young adults.
In the 12-month prospective nonrandomized study, 29 adolescents/young adults with obesity underwent SG and 30 were followed without surgery. At baseline and 12 months, participants underwent computed tomography of ...
Does higher education’s protection against cognitive decline differ by race and ethnicity?
2023-04-19
In a study of older adults, higher educational attainment seemed to protect adults from cognitive decline, but this protective effect differed by race and ethnicity. Higher-educated White adults received a greater benefit than higher-educated Black or Latinx adults.
The study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society involved telephone assessments of cognitive function among 20,311 Black, Latinx, and White US adults aged 51–100 years.
On average, Black and Latinx adults scored lower compared with White adults, regardless of educational attainment. Irrespective of race and ...
Does dim light at night impact the health of moths and other insects?
2023-04-19
Results from a new study published in the Journal of Applied Ecology indicate that dim light pollution may have detrimental effects on insect populations and may explain part of the ongoing, large-scale insect declines around the world.
During the study, investigators raised the offspring of moths from urban and rural populations from North- and Mid-European countries and treated them with and without dim light at night. The researchers assessed the induction of diapause, a dormant state that is critical for survival through the winter.
Light treatment affected diapause overall, but more so in Mid- than in North-European populations. ...
Can a healthy diet prevent prostate cancer?
2023-04-19
A study published in BJU International found that adhering to healthy diets seems to have no effect on prostate cancer risk, but following an unhealthy diet might increase the risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer.
The study assessed the diets of 15,296 men recruited in Spain in from 1992–1996. Among these men, 609 prostate cancer cases were identified during a median follow-up of 17 years. Diets were categorized as Western, Prudent, or Mediterranean. The Western dietary pattern consisted of a high intake of high-fat dairy products, processed meat, refined ...
Does taking traditional Chinese medicine during pregnancy increase the risk of birth defects?
2023-04-19
New research published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica has revealed a link between the use of traditional Chinese medicine during pregnancy and congenital malformations, including heart defects, in children.
In the prospective study, 16,751 women who received obstetrics care from hospitals in China completed a survey on their use of traditional Chinese medicine before and during pregnancy. Among fetuses, there were 273 congenital malformations.
Fetuses exposed to traditional Chinese medicine had 2.1-times higher odds of developing congenital malformations compared with those without exposure. There were significant associations with congenital malformations in women ...
Modulating a specific protein could lead to new liver disease treatments
2023-04-19
In research published in The FASEB Journal, scientists have discovered that a molecule called Yes-associated protein (YAP) plays a key role in the development of liver scarring, or fibrosis, by influencing the behavior of premature cells called liver progenitor cells.
By manipulating YAP expression in these cells, the investigators were able to improve the cells' ability to regenerate and repair liver tissue.
“Collectively, our findings indicate that liver progenitor cells’ expansion and differentiation during liver fibrosis could be modulated by YAP, further suggesting the possibility of manipulating YAP expression in these cells as a potential ...
Drones over Texas reveal agricultural damage caused by wild pigs
2023-04-19
There are an estimated 6.9 million wild pigs in the United States, and the population has been rising in recent decades. In research published in Wildlife Society Bulletin, investigators used drones to capture images of the agricultural damage caused by these animals.
Drones took pictures of corn fields at different growth stages during 36 missions over an agricultural region in Delta County, Texas in 2019–2020.
Most damage occurred in later growth stages, when corn ears were maturing, seed was most nutritious, and producers had already invested in the majority ...
ARRS Annual Meeting: projection order, acquisition timing for contrast-enhanced mammography
2023-04-19
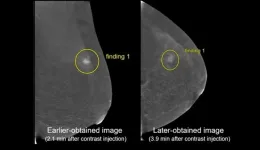
Honolulu, HI | April 19, 2023—Findings from a Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting at the Hawaiian Convention Center suggest there is institutional variability in both projection order and image acquisition timing for contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) protocol, with a previous systematic review revealing at least 7 different combinations in projection order.
“Our study demonstrates that earlier-obtained recombined imaging is significantly preferred in cancer lesion characterization, with a few instances demonstrating that biopsy-proven lesions may appear more conspicuously on earlier-obtained imaging (e.g., mass versus non-mass ...
Eating walnuts on a regular basis could benefit adolescents' cognitive development and contribute to their psychological maturation
2023-04-19
Eating walnuts on a regular basis could benefit the cognitive development of adolescents and contribute to their psychological maturation. These are some of the conclusions reached by a study led by the Institut d'Investigació Sanitària Pere Virgili (IISPV), in which ISGlobal (a centre promoted by "la Caixa" Foundation) and the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) have collaborated. This is unprecedented research; while there have been previous studies on ...