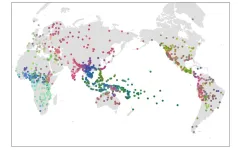
(Press-News.org) Linguists have long been interested in language variation. What are common or universal patterns across languages? What limits the possible variation between them? Grambank, the world's largest and most comprehensive database of language structure, enables researchers to answer some of these questions.
Grambank was constructed in an international collaboration between the Max Planck institutes in Leipzig and Nijmegen, the Australian National University, the University of Auckland, Harvard University, Yale University, the University of Turku, Kiel University, Uppsala University, SOAS, the Endangered Languages Documentation Programme, and over a hundred scholars from around the world. Grambank's coverage spans 215 different language families and 101 isolates from all inhabited continents. "The design of the feature questionnaire initially required numerous revisions in order to encompass many of the diverse solutions that languages have evolved to code grammatical properties", says Hedvig Skirgård, who coordinated much of the coding and is the lead author of the study.
Limits on variation
The team settled on 195 grammatical properties, ranging from word order to whether or not a language has gendered pronouns. For instance, many languages have separate pronouns for 'he' and 'she', but some also have male and female versions of 'I' or 'you'. The possible 'design space' would be enormous if grammatical properties were to vary freely. Limits on variation could be related to cognitive principles rooted in memory or learning, rendering some grammatical structures more likely than others. Limits could also be related to historical 'accidents', such as descent from a common language or contact with other languages.
The researchers discovered much greater flexibility in the combination of grammatical features than many theorists have assumed. "Languages are free to vary considerably in quantifiable ways, but not without limits", explains Stephen Levinson, Director emeritus of the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen and one of the founders of the Grambank project. "A sign of the extraordinary diversity of the 2400 languages in our sample is that only five of them occupy the same location in design space (share the same grammatical properties)."
Languages show much greater similarity to those with a common ancestor than those they are in contact with. "Genealogy generally trumps geography", says Russell Gray, Director of the Department of Linguistic and Cultural Evolution and senior author of the study. "Nevertheless, if processes of linguistic evolution and diversification were run again from the beginning, there would still be some resemblance to what we now have. The constraints of human cognition mean that, while there is a great deal of historical contingency in the organisation of grammatical structures, there are regular patterns as well".
Diversity under threat
"The extraordinary diversity of languages is one of humanity's greatest cultural endowments", concludes Levinson. "This endowment is under threat, especially in some areas such as Northern Australia, and parts of South and Northern America. Without sustained efforts to document and revitalise endangered languages, our linguistic window into human history, cognition and culture will be seriously fragmented."
The Grambank database is an open-access comprehensive resource maintained by the Max Planck Society. "It puts linguistics on an even footing with genetics, archaeology and anthropology in terms of quantitative, large scale, accessible data", says Gray. "I hope it will facilitate the exploration of links between linguistic diversity and a broad array of other cultural and biological traits, ranging from religious beliefs to economic behavior, musical traditions and genetic lineages. These links with other facets of human behavior will make Grambank a key resource not only in linguistics, but in the multidisciplinary endeavour of understanding human diversity."
END
Grambank shows the diversity of the world's languages
An international team has created a new database that documents patterns of grammatical variation in over 2400 of the world’s languages
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanoparticles provoke immune response against tumors but avoid side effects
2023-04-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Cancer drugs that stimulate the body’s immune system to attack tumors are a promising way to treat many types of cancer. However, some of these drugs produce too much systemic inflammation when delivered intravenously, making them harmful to use in patients.
MIT researchers have now come up with a possible way to get around that obstacle. In a new study, they showed that when immunostimulatory prodrugs — inactive drugs that require activation in the body — are tuned for optimal activation timing, the drugs provoke the immune system to attack tumors without the side effects that occur when the ...
Informed by mechanics and computation, flexible bioelectronics can better conform to a curvy body
2023-04-19
MADISON – Today, foldable phones are ubiquitous. Now, using models that predict how well a flexible electronic device will conform to spherical surfaces, University of Wisconsin–Madison and University of Texas at Austin engineers could usher in a new era in which these bendy devices can integrate seamlessly with parts of the human body.
In the future, for example, a flexible bioelectronic artificial retina implanted in a person’s eyeball could help restore vision, or a smart contact lens could continuously sense glucose levels in ...
Killer heatwaves endanger India’s development
2023-04-19
Deadly heatwaves fuelled by climate change in 2022 made almost 90 percent of Indians more vulnerable to public health issues, food shortages and increased risks of death, a new study from researchers at the University of Cambridge reported in PLOS Climate.
India currently uses a national Climate Vulnerability Indicator (CVI) to measure climate vulnerability and make plans for adaptation. The CVI includes many different socioeconomic, biophysical, institutional, and infrastructural factors. But it doesn't ...
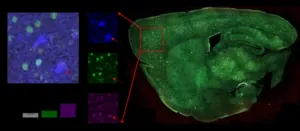
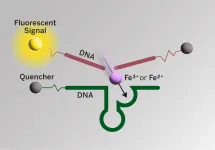
Newfound link between Alzheimer’s and iron could lead to new medical interventions
2023-04-19
There is a growing body of evidence that iron in the brain may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease. Lending weight to that idea, a new imaging probe has for the first time shown that in the same regions of the brain where the amyloid beta plaques associated with Alzheimer’s occur, there is also an increase in iron redox, meaning the iron in these regions is more reactive in the presence of oxygen. Their imaging probe could yield even more details about the causes of Alzheimer’s and help in the search for new drugs to treat it.
A ...
Scientists identify 2022 sea urchin killer
2023-04-19
TAMPA, Fla. (APRIL 19, 2023) – The search for the 2022 killer that decimated the long-spined sea urchin population in the Caribbean and along Florida’s east coast is over. A team of researchers organized by Mya Breitbart, Distinguished University Professor at the University of South Florida’s College of Marine Science, identified a single-celled organism called a ciliate as the cause of a massive die-off event to a marine animal vital to coral reef health.
Their findings were reported in Science Advances.
“We’re beyond ...
How the pandemic exacerbated racial inequalities in the US criminal legal system
2023-04-19
APRIL 19, 2023
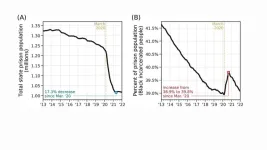
As Covid roared through prisons in 2020, the U.S. prison population fell by as much as 30 percent, creating the largest, fastest reduction in prison population in American history. But this decarceration disproportionately benefited white incarcerated people, sharply increasing the fraction of incarcerated Black and Latino people. A new study in Nature shows that this increased racial disparity in U.S. prisons stems in large part from a long-standing problem with the justice system: Non-white people tend ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for April 19, 2023
2023-04-19
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include effective combination therapies for patients with BRAFV600E mutations, an approach to identify cancer biomarkers in extracellular vesicles, therapeutic strategies for improving ...
A once-stable glacier in Greenland is now rapidly disappearing
2023-04-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – As climate change causes ocean temperatures to rise, one of Greenland’s previously most stable glaciers is now retreating at an unprecedented rate, according to a new study.
Led by researchers at The Ohio State University, a team found that between 2018 and 2021, Steenstrup Glacier in Greenland has retreated about 5 miles, thinned about 20%, doubled in the amount of ice it discharges into the ocean, and quadrupled in velocity. According to the study, such a rapid change is so extraordinary ...
The Container Store offers $10,000 in scholarships for Charisma Virtual Social Coaching
2023-04-19
The Container Store, the nation’s leading retailer of storage and organization solutions, custom spaces, and in-home organizing services, will fund $10,000 in scholarships for Charisma™ Virtual Social Coaching, a strengths-based social skills training developed by Center for BrainHealth.
Charisma is a personalized, avatar-driven program that provides real-time, unscripted social coaching in a safe, non-threatening virtual environment. Drawing on extensive cognitive neuroscience research, this program is demonstrated to help people with social challenges to ...
Study seeks to define quantum compression
2023-04-19
A study led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers identifies a new potential application in quantum computing that could be part of the next computational revolution.
The study surveys techniques for compressing data generated by sensors in edge computing — which processes data at or near sensors — and compares classical techniques with quantum approaches, which are mostly in development. Compressing data saves storage space and network bandwidth.
Classical computing stores information in bits equal to 0 or 1. Quantum computing stores information in qubits, which can exist ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Grambank shows the diversity of the world's languagesAn international team has created a new database that documents patterns of grammatical variation in over 2400 of the world’s languages