(Press-News.org) The earliest artificial neural network, the Perceptron, was introduced approximately 65 years ago and consisted of just one layer. However, to address solutions for more complex classification tasks, more advanced neural network architectures consisting of numerous feedforward (consecutive) layers were later introduced. This is the essential component of the current implementation of deep learning algorithms. It improves the performance of analytical and physical tasks without human intervention, and lies behind everyday automation products such as the emerging technologies for self-driving cars and autonomous chat bots.
The key question driving new research published today in Scientific Reports is whether efficient learning of non-trivial classification tasks can be achieved using brain-inspired shallow feedforward networks, while potentially requiring less computational complexity. “A positive answer questions the need for deep learning architectures, and might direct the development of unique hardware for the efficient and fast implementation of shallow learning,” said Prof. Ido Kanter, of Bar-Ilan's Department of Physics and Gonda (Goldschmied) Multidisciplinary Brain Research Center, who led the research. “Additionally, it would demonstrate how brain-inspired shallow learning has advanced computational capability with reduced complexity and energy consumption.”
"We've shown that efficient learning on an artificial shallow architecture can achieve the same classification success rates that previously were achieved by deep learning architectures consisting of many layers and filters, but with less computational complexity,” said Yarden Tzach, a PhD student and contributor to this work. “However, the efficient realization of shallow architectures requires a shift in the properties of advanced GPU technology, and future dedicated hardware developments,” he added.
The efficient learning on brain-inspired shallow architectures goes hand in hand with efficient dendritic tree learning which is based on previous experimental research by Prof. Kanter on sub-dendritic adaptation using neuronal cultures, together with other anisotropic properties of neurons, like different spike waveforms, refractory periods and maximal transmission rates (see also a video on dendritic learning: https://vimeo.com/702894966 ).
For years brain dynamics and machine learning development were researched independently, however recently brain dynamics has been revealed as a source for new types of efficient artificial intelligence.
END
Is Deep Learning a necessary ingredient for Artificial Intelligence?
Deep learning appears to be a key magical ingredient for the realization of many artificial intelligence tasks. However, these tasks can be efficiently realized by the use of simpler shallow architectures
2023-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study gives insight into cause of severe inflammatory bowel disease
2023-04-20
Cedars-Sinai investigators have identified a genetic variant that increases people’s risk of developing perianal Crohn’s disease, the most debilitating manifestation of Crohn’s disease.
The variant generates changes to DNA that lead to a loss of protein function, which in turn, alters how the body recognizes and handles bacteria, making it less effective at fighting infections.
The discovery is published in the peer-reviewed journal GUT.
“Fistulizing perianal Crohn’s disease ...
Gut bacteria could be behind weaker immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine
2023-04-20
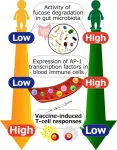
Gut bacteria that break down a sugar called fucose could be dampening our immune response to the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, according to a study led by researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST).
The scientists report that increased fucose digestion by bacteria in the gut before vaccination was associated with lower numbers of T-cells activated by vaccination. T-cells are an important type of blood immune cell that are activated by a specific strain of bacteria or virus, and then multiply to fight the infection.
The findings, published ...
Swedish quantum computer applied to chemistry for the first time
2023-04-20
There are high expectations that quantum computers may deliver revolutionary new possibilities for simulating chemical processes. This could have a major impact on everything from the development of new pharmaceuticals to new materials. Researchers at Chalmers University have now, for the first time in Sweden, used a quantum computer to undertake calculations within a real-life case in chemistry.
“Quantum computers could in theory be used to handle cases where electrons and atomic nuclei move in more complicated ways. If we can learn to utilise their full potential, we should be able to advance the boundaries of what is possible to calculate and understand,” says Martin Rahm, ...
Polar ice sheet melting records have toppled during the past decade
2023-04-20
The seven worst years for polar ice sheets melting and losing ice have occurred during the past decade, according to new research, with 2019 being the worst year on record.
The melting ice sheets now account for a quarter of all sea level rise – a fivefold increase since the 1990’s – according to IMBIE, an international team of researchers who have combined 50 satellite surveys of Antarctica and Greenland taken between 1992 and 2020.
Their findings are published today in the journal Earth System Science Data.
Global heating is melting ...
Companies’ zero-deforestation commitments have potential to halve cattle-driven deforestation in Brazilian Amazon
2023-04-20
Cattle-rearing is the biggest cause of tropical deforestation in the Amazon - and the world.
A study has found that some of the world’s largest slaughterhouses reduced cattle-driven deforestation in the Amazon by 15% - equivalent to sparing 7,000km2 of forest from clearance (4.5 times the size of London) - through their commitment to zero-deforestation policies between 2010 and 2018.
If these policies were fully implemented and adopted across all cattle companies operating in the Amazon, 24,000km2 of forest (an area larger than Wales) could have been spared over this time, effectively halving cattle-driven deforestation in Brazil.
Deforestation ...
Exposure to air pollution during pregnancy increases risk for flu
2023-04-20
During pregnancy, women are more susceptible to severe respiratory infections from multiple viruses, including influenza A virus (IAV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Additionally, pregnant women are disproportionately affected by influenza, resulting in a more than 10-fold increase in hospitalization risk.
A new study led by Dr. Natalie Johnson, associate professor in the Texas A&M University School of Public Health’s Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, shows that exposure to ultrafine particles (UFPs) during pregnancy enhances respiratory ...
Trim the sugar: New HIV vaccine design improves immune response
2023-04-20
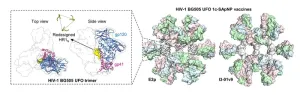
LA JOLLA, CA— A new HIV vaccine from Scripps Research has shown a significantly improved ability to neutralize the virus in preclinical tests, and it will soon be studied in healthy people who volunteer to participate in clinical trials.
The new and unique vaccine design, described in a paper in Nature Communications on April 9, 2023, uses tiny protein “nanoparticles” to display multiple copies of HIV’s surface protein Env, thus presenting itself to the immune system much as real HIV particles would ...
Immediate carbon cuts, common marine heatwave terminology urged
2023-04-20
Over the past two hundred years, the ocean and atmosphere have been accumulating massive amounts of carbon dioxide as factories, automobiles, airplanes, and more churn out the powerful greenhouse gas. Two articles published recently in Nature by University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa oceanographers provide a reality check on the limitations of carbon dioxide removal and a warning that marine heatwaves need clear definitions so communities can adapt.
Carbon dioxide removal is not the golden ticket
In all the scenarios assessed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, nations around the world must dramatically and rapidly reduce their dependence ...
Paul Hessburg receives Distinguished Landscape Ecologist Award
2023-04-20
Paul Hessburg received the International Association for Landscape Ecology-North America Chapter’s 2023 Distinguished Landscape Ecologist Award. The annual award recognizes major scientific contributions to landscape ecology, honors scientists who have played a pivotal role in shaping the field, and is the organization’s highest honor.
Hessburg is a senior research ecologist with the USDA Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Research Station based at the Wenatchee Forestry Sciences Laboratory. He was honored for a highly diverse career that has "greatly enhanced the capacity of landscape practitioners to develop strategies and ...
Cut council tax for green gardeners to help cities tackle climate change
2023-04-20
Homeowners should be rewarded to garden sustainably, new research by Professor of Environmental Horticulture at University of Sheffield, recommends
Rewards for sustainable gardening could include reductions to council tax, water bills or assistance with resources
Ensuring urban gardeners have the ability to have planted gardens will have numerous benefits for the environment and communities
Banning environmentally damaging materials, such as pesticides; or practices such as installing astroturf, could also benefit the environment
Research shows that some cities may have lost as much as 50 per cent of their green garden space over the last ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A genetic brake that forms our muscles
CHEST announces first class of certified critical care advanced practice providers awarded CCAPP Designation
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop an innovative prussian-blue based electrode for effective and efficient cesium removal
Self-organization of cell-sized chiral rotating actin rings driven by a chiral myosin
Report: US history polarizes generations, but has potential to unite
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
[Press-News.org] Is Deep Learning a necessary ingredient for Artificial Intelligence?Deep learning appears to be a key magical ingredient for the realization of many artificial intelligence tasks. However, these tasks can be efficiently realized by the use of simpler shallow architectures