(Press-News.org) Study’s findings suggest that maintaining normal vitamin D levels may benefit patients.
New research indicates that for patients with advanced skin cancer, it may be important to maintain normal vitamin D levels when receiving immunotherapy medications called immune checkpoint inhibitors. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Vitamin D has many effects on the body, including regulation of the immune system. To see whether levels of vitamin D might impact the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors, investigators analyzed the blood of 200 patients with advanced melanoma both before and every 12 weeks during immunotherapy treatment.
A favorable response rate to immune checkpoint inhibitors was observed in 56.0% of patients in the group with normal baseline vitamin D levels or normal levels obtained with vitamin D supplementation, compared with 36.2% in the group with low vitamin D levels without supplementation. Progression‐free survival—the time from treatment initiation until cancer progression—in these groups was 11.25 and 5.75 months, respectively.
“Of course, vitamin D is not itself an anti-cancer drug, but its normal serum level is needed for the proper functioning of the immune system, including the response that anti-cancer drugs like immune checkpoint inhibitors affect,” said lead author Łukasz Galus, MD, of Poznan University of Medical Sciences, in Poland. “In our opinion, after appropriately randomized confirmation of our results, the assessment of vitamin D levels and its supplementation could be considered in the management of melanoma.”
Additional information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. A free abstract of this article will be available via the CANCER Newsroom upon online publication. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com
Full Citation:
“Vitamin D supplementation increases objective response rate and prolongs progression‐free time in patients with advanced melanoma undergoing anti‐PD1 therapy.” Łukasz Galus, Michał Michalak, Mateusz Lorenz, Renata Stoińska‐Swiniarek, Daria Tusień Małecka,Agnieszka Galus, Tomasz Kolenda, and Jacek Mackiewicz. CANCER; Published Online: April 24, 2023 (DOI: 10.1002/cncr.34718).
URL Upon Publication: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/cncr.34718
Author Contact: Agnieszka Galus, co-author of the study, at galus.agnieszka@spsk2.pl or +48 609 766 781.
About the Journal
CANCER is a peer-reviewed publication of the American Cancer Society integrating scientific information from worldwide sources for all oncologic specialties. The objective of CANCER is to provide an interdisciplinary forum for the exchange of information among oncologic disciplines concerned with the etiology, course, and treatment of human cancer. CANCER is published on behalf of the American Cancer Society by Wiley and can be accessed online. Follow us on Twitter @JournalCancer.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in scientific research and career-connected education. Founded in 1807, Wiley enables discovery, powers education, and shapes workforces. Through its industry-leading content, digital platforms, and knowledge networks, the company delivers on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Do vitamin D levels affect the body’s response to anti-cancer immunotherapy?
2023-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug combination restores ability of leading treatment to signal for death of blood cancer cells
2023-04-24
Despite the promise of new medications that promote cancer cell death in people with acute myeloid leukemia, leukemic cells often adopt features that let them evade the drugs’ effects within a year.
Now, new research using human tissue samples and mouse models has found that resistance of leukemia cells to a widely prescribed drug called venetoclax occurs because of a rapid increase in the breakdown and turnover of mitochondria, structures inside the cell that help power its functions. In addition to their role in producing energy, mitochondria also tell cells to die under certain adverse conditions.
This process of “programmed cell ...
Increased risk of testicular cancer in people with neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-04-24
A new study by researchers at Uppsala University and Uppsala University Hospital shows that men who have a neurodevelopmental disorder, such as autism and ADHD, also have a slightly increased risk of testicular cancer, or seminoma. This is the first study to show such a link, with the results to be published in the British Journal of Cancer.
Testicular cancer is the most common form of cancer in young men, and its underlying causes are still largely unknown.
“As testicular cancer can be surgically removed, thus curing the disease, it is important to seek care in time if you feel a lump in your testicle,” notes Ingrid ...
Single CT scan in kids low risk for cancers, but 4 or more CTs increases risk
2023-04-24
For children under age 18 years, a single computed tomography (CT) scan is not associated with an increased risk of brain tumours, leukemia or lymphoma, but exposure to 4 or more scans before adulthood more than doubles the risk, according to new research https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221303 in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Computed tomography in children has increased worldwide in recent decades, but there is conflicting evidence about the risks of cancer from these ...
New programmable smart fabric responds to temperature and electricity
2023-04-24
A new smart material developed by researchers at the University of Waterloo is activated by both heat and electricity, making it the first ever to respond to two different stimuli.
The unique design paves the way for a wide variety of potential applications, including clothing that warms up while you walk from the car to the office in winter and vehicle bumpers that return to their original shape after a collision.
Inexpensively made with polymer nano-composite fibres from recycled plastic, the programmable fabric can change its colour and shape when stimuli are applied.
“As a wearable material alone, it has almost infinite potential ...
International study recommends replacing skull section after treatment for a brain bleed
2023-04-23
A major international trial has concluded that, where possible, surgeons should replace the removed section of the skull following surgery to treat a form of brain haemorrhage. This approach will save patients from having to undergo skull reconstruction further down the line.
The RESCUE-ASDH trial, funded by the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), involved 40 centres in 11 countries and involved 450 patients. The results of the trial are published today in the New England Journal of Medicine and are announced at the annual meeting of the American Association of Neurological ...
Achieving prevention and health, rather than more healthcare
2023-04-23
If more people have access to health insurance, we have to be sure the death rates of those with certain chronic conditions are decreasing.
This is one of the statements Gregory Peck, an acute care surgeon and associate professor at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, will be researching on behalf of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) at the National Institutes of Health.
Funded by NIH grants totaling more than $1 million through a recent two-year award from the New Jersey Alliance for Clinical and Translational Science (NJ ACTS), a Rutgers hub of the National Center for Advancing ...
Inflammation ‘brake’ gene may help reveal outcomes of kidney disease
2023-04-23
A discovery about gene variants of an inflammation ‘brake’ brings scientists a step closer to personalised treatment for patients at risk of kidney disease and kidney failure.
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research, University of New South Wales, Sydney and Westmead Hospital, found that common genetic variants of TNFAIP3, which increase inflammation in the body, can paradoxically protect the kidneys from damage in the short term.
“We wanted to investigate whether inherited differences in how people regulate inflammation could lead to better or worse kidney health outcomes,” says Professor Shane ...
Too much insulin can be as dangerous as too little
2023-04-22
Just over a century has passed since the discovery of insulin, a time period during which the therapeutic powers of the hormone have broadened and refined. Insulin is an essential treatment for type 1 diabetes and often for type 2 diabetes, as well. Roughly 8.4 million Americans use insulin, according to the American Diabetes Association.
One hundred years of research have greatly advanced medical and biochemical understanding of how insulin works and what happens when it is lacking, but the reverse, how potentially fatal insulin hyper-responsiveness is prevented, has remained a persistent mystery.
In a new study, published in the April 20, 2023 online edition ...
From sheets to stacks, new nanostructures promise leap for advanced electronics
2023-04-22
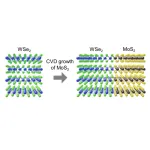
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have successfully engineered multi-layered nanostructures of transition metal dichalcogenides which meet in-plane to form junctions. They grew out layers of multi-layered structures of molybdenum disulfide from the edge of niobium doped molybdenum disulfide shards, creating a thick, bonded, planar heterostructure. They demonstrated that these may be used to make new tunnel field-effect transistors (TFET), components in integrated circuits with ultra-low power consumption.
Field-effect transistors ...
How alcohol consumption contributes to chronic pain
2023-04-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Chronic alcohol consumption may make people more sensitive to pain through two different molecular mechanisms—one driven by alcohol intake and one by alcohol withdrawal. That is one new conclusion by scientists at Scripps Research on the complex links between alcohol and pain.
The research, published in the British Journal of Pharmacology on April 12, 2023, also suggests potential new drug targets for treating alcohol-associated chronic pain and hypersensitivity.
“There is an urgent need to better ...