Maternal and early-life high-fat diets result in a taste for salty food
2023-04-24
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan – We are all aware of the importance of eating healthy food, especially during pregnancy. A high-fat diet has dramatic consequences on the metabolism. It can lead to obesity, diabetes, chronic liver disease, and possibly cancer. Previous works have demonstrated that eating high amounts of fat during pregnancy affects the taste preference and metabolism in offspring. In most households, children and parents eat the same food. In other words, mums eating a high-fat diet will likely feed their children fatty foods. What are the consequences of maternal and early-life exposure to high amounts of fat on the offspring? This is what researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have explored in a study published in Scientific Reports.
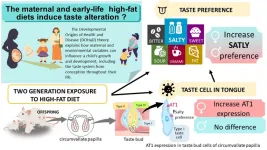
The researchers used a rat model to investigate the effect on taste preference of a two-generational (i.e., pregnant mother and young newborns) exposure to a high-fat diet. Pregnant and lactating females were fed a high-fat diet, while a control group received a standard diet. After weaning, the offspring from each group received the same diet – babies from mothers fed a high-fat diet during pregnancy and those fed a standard diet continued receiving a high-fat diet and a standard diet, respectively.
Young rats from the high-fat diet groups gained more weight and consumed more energy than their counterparts from the standard diet groups. “We wondered if the different diets had affected the taste preferences of the rats,” explains Takashi Ono, senior author. “It is well established that taste impacts food intake. If something tastes good, the brain reward circuits are activated, and you will likely eat more of it.” The researchers tested the animal preference for the five basic tastes: bitter, sour, salty, sweet, and umami, using a two-bottle challenge, in which two bottles – one containing water and the other one water with taste – were added to the rat cage. Offspring exposed to a high-fat diet during gestation and early life preferred salty water. In contrast, they showed no specific preference for the other tastes when compared with the standard-diet group.
What mechanisms underlie this preference? The researchers investigated the levels of proteins involved in perceiving the salty taste. “The protein and gene expression of AT1 increased in the taste buds of female offspring exposed to a high-fat diet. This happened as early as three weeks after birth,” explains Saranya Serirukchutarungsee, lead author of the study. “AT1 is known to be associated with a preference for salty taste and evidence suggests that it is likely that AT1 affects the salty taste preference by increasing sodium intake in taste bud cells.”
Better understanding of the programming of offspring’s eating behavior and taste preferences is vital when considering the strong links between poor diet and poor health. These findings provide a crucial first step that can lead to further studies aimed at reducing the risk of developing obesity and diet-linked diseases, such as cardiovascular disease in offspring and subsequent generations.
###
The article, “Two-generation exposure to a high-fat diet induces the change of salty taste preference in rats,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31662-0.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-24
DALLAS, April 24, 2023 — The American Heart Association and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with its 32 NFL clubs, are challenging kids to move more with an NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break for the NFL Draft happening later this week. The free program on Wednesday, April 26 at 1 p.m. ET/ 12 p.m. CT/ 10 a.m. PT will offer a 15-minute synchronous broadcast to help students learn how to add movement to their day leading up to the live Draft coverage from Kansas City.
Rooted in American Heart Association science, the Fitness Break broadcast helps students learn more about how physical activity supports ...
2023-04-24
The Haber-Bosch process is the industrial approach for NH3 production today, which must be operated at energy-intensive high temperatures and pressures. The reduction of dinitrogen (N2) by electrocatalysis offers an alternative way for NH3 production at ambient conditions and a variety of electrocatalysts have been studied over the past few years. However, even the best catalytic system reported could only get unsatisfied performance (such as the selectivity and production rate of NH3) due to the ...
2023-04-24
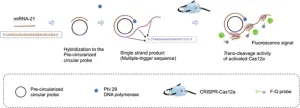
In the early 1990s, scientists who were studying the development of a roundworm identified a small RNA molecule that regulated the expression of specific genes. This marked the discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs), which are now known to be present across all forms of life. As it turns out, these molecules play essential roles in many biological processes.
A few years later, researchers realized that diseases could dysregulate the expression of miRNAs, highlighting their potential as biomarkers. In fact, abnormal miRNA expression is a hallmark of all tumor-related diseases. Thus, miRNA detection techniques ...
2023-04-24
Brain tumors located in regions that control speech, vision and motor function present additional challenges to neurosurgeons, as damaging the surrounding tissue can cause severe loss of those abilities.. Because of this, these regions are known as “eloquent brain areas” and require special attention and approaches to limit damage and deficits.
The University of Cincinnati’s Paolo Palmisciano, MD, was part of a research team that examined how well a minimally invasive approach worked to limit vision and hearing loss in patients following brain tumor surgery.
The research was published in the journal Brain Sciences, and the ...
2023-04-24
The report, “Wrestling with Social and Behavioral Genomics: Risks, Potential Benefits, and Ethical Responsibility,” produced by The Hastings Center, a bioethics institute, provides direction for research and communications in this area of study with both significant social risks and potential benefits. It is accompanied by an article that describes a fledgling effort to integrate community perspectives on the ethics of this research.
A webinar to launch the consensus report will take place today at 3 PM EST. Register here.
Research on genetic variants and human social and behavioral characteristics, or phenotypes, including anxiety, subjective well-being, ...
2023-04-24
The objective of this study is to identify these loci and decipher the polygenic architecture of malic acid content in tomato fruit. The authors carried out a GWAS using six milestone models with two-environment repeats. A series of associated SNP variations were identified from GWAS, and 15 high-confidence annotated genes were obtained based on the lead SNPs and the malic acid accumulation. The optimal allelic combination of the 15 loci was presented for tastier tomato. ...
2023-04-24
A severe windstorm that battered the UK more than a century ago produced some of the strongest winds[OS1] that Britain has ever seen, a team of scientists have found after recovering old weather records.
Old weather measurements, first recorded on paper after Storm Ulysses hit the UK in February 1903, have shed new light on what was one of the most severe storms to have hit the British Isles.
By turning hand-written weather data into digital records, the research team has laid the way to better understand other historical storms, ...
2023-04-24
The steady decline in cultivable land owing to the rapidly increasing global population has necessitated the use of efficient plant breeding methods that could be used to improve agricultural yields. However, in addition to genetic methods, we need approaches to control and improve complex crop traits. To this end, plant scientists make use of various cutting-edge imaging techniques that quantify crop traits (height, leaf shape, leaf color, etc.). Traditional imaging methods, however, are tedious, destructive, and non-sustainable. ...
2023-04-24
Lehigh University materials science and engineering (MSE) professor Masashi Watanabe is the 2023 recipient of the Microanalysis Society Presidential Science Award, which recognizes a senior scientist for “outstanding technical contributions to the field of microanalysis over a sustained period of time.”
Watanabe is a Fellow of the Microanalysis Society and a former MAS president. The career achievement honor highlights his work in advancing quantitative analysis in scanning transmission ...
2023-04-24
WASHINGTON, April 24, 2023 – Superconductors can conduct electricity without any resistance or power loss, and they can effortlessly cause magnets to levitate above them. These properties would make superconductors useful for high-speed trains or long-distance power transmission, except for one glaring problem: superconductors only work at low temperatures, more than a hundred degrees below zero.
This one requirement makes building a hyperefficient electrical grid or high-speed rail network very expensive. Unless, that is, a superconductor network could accomplish ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Maternal and early-life high-fat diets result in a taste for salty food