(Press-News.org) East Hanover, NJ – April 25, 2023 – New data shows that Hispanics with disabilities in the United States rebounded to historic levels in the labor force following the first 12-month period of the COVID-19 pandemic. While the disparity between their non-Hispanic white counterparts remains, their recovery has narrowed this gap and surpassed that of their black/African American counterparts, according to experts speaking during last Friday’s nTIDE Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar. To further improve employment opportunities for Hispanics with disabilities, experts also reviewed measures that address social determinants of health, education, and language barriers that disproportionately impact Hispanic communities.
Using data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) for persons ages 16-64, the monthly employment-to-population ratio averaged over the 12-month period, April 2022-March 2023, was 35.5 percent for Hispanic civilians with disabilities, compared to 38.0 percent for non-Hispanic white civilians with disabilities. However, estimates of 27.2 percent for non-Hispanic black/African Americans with disabilities indicate that this group has not rebounded as strongly as Hispanic and non-Hispanic white civilians with disabilities.
In contrast, the average monthly employment-to-population ratio was 71.8 percent for Hispanic civilians without disabilities, compared to 77.0 percent for non-Hispanic white civilians without disabilities in the same period. The monthly employment-to-population ratio, a key indicator, reflects the number of people in a population who are working, relative to the total number of people in that population. A 12-month average of this indicator is used to boost statistical precision. The 12-month period of April in one year to March in the next year is used to help examine employment trends before and after the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown recession.
“Among people with disabilities, each group has recovered but not at the same rate. Breaking out segment estimates of Hispanic, non-Hispanic white, and non-Hispanic black/African Americans with disabilities shows a compelling story,” summarized nTIDE expert Andrew Houtenville, PhD, professor of economics at the University of Hampshire (UNH) and research director of the UNH Institute on Disability. “Overall, we have seen a strong rebound in the job market for Hispanics with disabilities, reaching historic highs since bouncing back from the pandemic lockdown. Yet, there is still a substantial gap between Hispanic and non-Hispanic white civilians,” he added. “Non-Hispanic black/African Americans with disabilities were slower to recover in April 2021-March 2022, but have since picked up ground over the past 12 months, he added.
Disparities Still Remain
Even with the latest employment-to-population ratio rally among Hispanics with disabilities, this group still faces barriers in accessing quality jobs due to language, cultural differences, and social determinants of health, according to Javier Robles, director of the Center for Disability Sports, Health and Wellness at Rutgers University and co-chair of the Rutgers University Disability Studies committee.
“We are talking about a varied population with many different cultures and languages,” said Robles. Additional focus on providing tailored support and resources for Hispanic individuals with disabilities can help them access the programs and systems designed to reduce employment barriers, he added. These measures should emphasize promoting access to Spanish-language materials, addressing health disparities, and challenging societal attitudes towards disabilities in the Hispanic community.
“In addition, businesses need to understand the cultural aspects of hiring individuals from Latino cultures, particularly in the context of respect. In our culture, there is a deep respect for authority. A Latino with disabilities may not ask for an accommodation because they feel such a request questions that authority,” Robles asserted. Addressing these underlying factors will help close the disability employment gap and create a more equitable workforce for all individuals.
Note on Data Collection and Language
When presenting information about race, nTIDE employs the terminology found in the survey that serves as the basis for BLS data, known as the Current Population Survey (CPS). Participants in the survey were asked to select one or multiple race categories from the following five options: White; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; Asian; and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander. Separately, participants are asked whether they are of Hispanic origin. The statistics presented in the nTIDE Deeper Dive represent participants who specifically indicated being of Hispanic origin; non-Hispanic origin and white only; and non-Hispanic origin and black/African American only. Respondents who chose more than one race category were not included in these calculations. Statistics for other categories are available upon request and may be the subject of future nTIDE Deeper Dives. The questionnaire may be found at the following link.
Live Webinar on Disability and Employment
In conjunction with each nTIDE report, experts host a 12:00 PM – 1:00 PM (ET) Lunch & Learn Webinar via Zoom featuring in-depth analyses, guest speakers, and news updates from the field. Webinars include invited panelists who discuss current disability-related findings and events. On May 5, 2023, a guest panelist joins Drs. O’Neill and Houtenville, and Denise Rozell, policy strategist from the Association of University Centers on Disabilities (AUCD). Register for our upcoming nTIDE webinars on May 5 and May 19, 2023, at ResearchonDisability.org/nTIDE, where you will also find the nTIDE archives.
About nTIDE Updates
National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) is a joint project of Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire Institute on Disability. The nTIDE team closely monitors the job numbers, issuing semi-monthly reports that track the impact of economic shifts on employment for people with and without disabilities. As the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic continues to wane and inflation persistently rises, the nTIDE team has superseded its mid-month COVID Update to a “Deeper Dive” into the BLS data for people with disabilities.
About the Institute on Disability at the University of New Hampshire
The Institute on Disability at the University of New Hampshire was established in 1987 to provide a university-based focus for the improvement of knowledge, policies, and practices related to the lives of persons with disabilities and their families. For information on the Institute’s NIDILRR-funded Rehabilitation Research and Training Center on Disability Statistics and Demographics (StatsRRTC), visit ResearchOnDisability.org.
About Kessler Foundation
Kessler Foundation, a major nonprofit organization in the field of disability, is a global leader in rehabilitation research. Our scientists seek to improve cognition, mobility, and long-term outcomes, including employment, for adults and children with neurological and developmental disabilities of the brain and spinal cord including traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and autism. Kessler Foundation also leads the nation in funding innovative programs that expand opportunities for employment for people with disabilities. We help people regain independence to lead full and productive lives.
For more information, contact:
Deb Hauss, DHauss@KesslerFoundation.org
Carolann Murphy, CMurphy@KesslerFoundation.org
Stay Connected with Kessler Foundation
Twitter | Facebook | YouTube | Instagram | iTunes & SoundCloud
nTIDE is funded by Kessler Foundation and was initially funded, in part, with grants from the National Institute on Disability, Independent Living and Rehabilitation Research (NIDILRR, 90RTGE0001).
END
nTIDE April 2023 Deeper Dive: Hispanics with disabilities making historic rebound in job market post-COVID-19 shutdown
National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) – issued semi-monthly by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
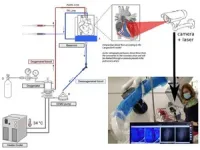
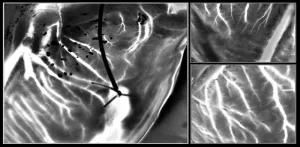
Laser speckle imaging can identify hearts suitable for transplantation
2023-04-25
In the majority of cases, graft failure after heart transplantation is attributable to abnormalities like severe coronary artery disease. As donors with extended criteria like advanced age and pre-existing heart conditions become eligible for heart transplantation, careful screening for congenital abnormalities has become crucial. Invasive coronary angiography is an essential screening tool that can detect coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition characterized by cholesterol deposits in the heart's arteries. However, logistical challenges limit utility so it’s used for fewer than a third of donors who are at risk of developing CAD.
To overcome this limitation, a new heart ...
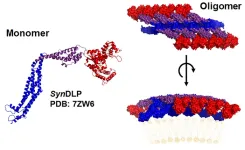
Relatives discovered: Membrane proteins of cyanobacteria and higher organisms are structurally highly similar
2023-04-25
-- JOINT PRESS RELEASE OF FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JÜLICH AND JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERSITY MAINZ --
SynDLP could be a bacterial ancestor of eukaryotic membrane proteins
The cells of living organisms are equipped with proteins that are involved in the shaping and remodeling of cellular membranes, thereby performing important tasks. The cell membrane encloses the cell interior, but is constantly remodeled, for example, due to membrane budding, invagination, or fusion processes. This also involves various proteins that were long assumed to be present exclusively or predominantly in higher organisms. ...
Medium-sized black holes eat stars like messy toddlers
2023-04-25
If they exist, intermediate-mass black holes likely devour wayward stars like a messy toddler — taking a few bites and then flinging the remains across the galaxy — a new Northwestern University-led study has found.
In new 3D computer simulations, astrophysicists modeled black holes of varying masses and then hurled stars (about the size of our sun) past them to see what might happen.
When a star approaches an intermediate-mass black hole, it initially gets caught in the black hole’s orbit, the researchers discovered. After that, the black hole begins its lengthy and violent meal. Every time the star makes a lap, the black hole takes a bite — ...
Fishermen-developed “banger bar” helps reduce risk of injury on crab boats, OSU study finds
2023-04-25
Dungeness crab fishermen are at high risk for on-the-job injury, but having a metal bar to bang crab pots against as they harvest can help them prevent injury, an Oregon State University study found.
The study sought to determine whether the fishermen-designed “banger bar” actually improves worker safety aboard crab vessels. The metal bar is installed atop the crab-sorting table and makes it easier for fishermen to empty the crab pots they haul up from the ocean floor, but there is no industry standard on whether crabbers install one or how they ...
New Parkinson's research could allow doctors to map brain of patients with neurodegenerative disorder
2023-04-25
1. Introduction
While the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is not fully understood, it has been traditionally linked to a reduction in the dopamine available to brain regions involved in motor control (Alexander, 2004, Brooks, 2010, Fahn, 2008, Meder et al., 2019, Obeso et al., 2017, Poewe et al., 2017). It is important to note that much of what is known about the neural bases of motor deficits in PD is based on task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showing abnormal motor-related blood oxygen ...
Researcher aims to create a sustainable protein source powered by hydrogen
2023-04-25
Lutz Grossmann is on a scientific mission to create tasty, animal-free protein that has a low carbon footprint and is produced without relying on agricultural land – a usual and progressively stressed source of the global food supply.
“The increasing global population and a changing climate increase the pressure on our food and protein supply coming from these natural habitats,” says Grossmann, an assistant professor of food science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
“By 2050, we need ...
A simple paper test could offer early cancer diagnosis
2023-04-25
CAMBRIDGE, MA — MIT engineers have designed a new nanoparticle sensor that could enable early diagnosis of cancer with a simple urine test. The sensors, which can detect many different cancerous proteins, could also be used to distinguish the type of a tumor or how it is responding to treatment.
The nanoparticles are designed so that when they encounter a tumor, they shed short sequences of DNA that are excreted in the urine. Analyzing these DNA “barcodes” can reveal distinguishing features of a particular patient’s tumor. The researchers designed their test so that it can be performed using a strip of paper, ...
BSC develops pioneering artificial intelligence method to fight urban air pollution
2023-04-25
99% of the world's population breathes air that exceeds the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). This scenario is exacerbated in urban areas where more than 50% of the world's population is concentrated. To mitigate the problem of air pollution, considered by the WHO to be the main environmental risk factor for health worldwide, it is crucial to have more reliable and accurate data on the concentration of air pollutants in our cities, especially nitrogen dioxide (NO2) because of its harmful effects on ...
How a horse whisperer can help engineers build better robots
2023-04-25
Humans and horses have enjoyed a strong working relationship for nearly 10,000 years — a partnership that transformed how food was produced, people were transported and even how wars were fought and won. Today, we look to horses for companionship, recreation and as teammates in competitive activities like racing, dressage and showing.
Can these age-old interactions between people and their horses teach us something about building robots designed to improve our lives? Researchers with the University of Florida say yes.
“There are no fundamental guiding principles ...
Say ‘ahhh’: This ecofriendly tongue depressor checks vitals
2023-04-25
Doctors often use tongue depressors when peering in a patient’s mouth and throat. But what if that flat wooden spatula could actively evaluate the patient’s health? That’s the premise of an ecofriendly disposable sensor, reported in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry, that can check levels of glucose and other biomarkers in saliva. Researchers say the easy-to-produce device could someday help doctors assess a range of conditions.
Wood is a renewable, biodegradable, natural material that is widely available at low cost, which makes it attractive for researchers who design electronics and sensors. However, this is challenging because the material isn’t good ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] nTIDE April 2023 Deeper Dive: Hispanics with disabilities making historic rebound in job market post-COVID-19 shutdownNational Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) – issued semi-monthly by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire