(Press-News.org) SINGAPORE, 26 April 2023 – Symptoms of anxiety and depression in the post-peak pandemic era could be costing Singapore 2.9 per cent of its gross domestic product (GDP)—or nearly S$16 billion—suggests a study conducted by Duke-NUS Medical School and the Institute of Mental Health (IMH).
Publishing in the journal BMC Psychiatry, the researchers estimated the total economic burden of lost productivity due to anxiety and depression in Singapore to be S$15.7 billion (US$11.72 billion) annually, based on survey data from 5,725 Singaporean adults collected via an online panel between April and June 2022.
Using a short questionnaire to identify the subset with current symptoms of anxiety or depression, they found 14 per cent of respondents had symptoms consistent with depression and 15 per cent, including many of the same individuals, had symptoms consistent with anxiety. Results further revealed that, among those who were identified as having these conditions, only 32 per cent reported seeking healthcare to treat their mental health conditions and only 24 per cent consulted a mental health provider.
“This is concerning is it suggests these individuals are not benefitting from effective treatments,” said senior author Professor Eric Finkelstein, a health economist with Duke-NUS’ Health Services & Systems Research Programme.
To this point, 13 per cent of those suffering from these conditions made at least one visit to the Emergency Department and 9 per cent were admitted into the hospital. This increased healthcare costs by an average of S$1,050 per year for these individuals.
Further results revealed the affected respondents reported missing an extra 17.7 days of work per year and being 40 per cent less productive while at work, bringing the total value of lost productivity attributable to anxiety and depression in Singapore to S$15.7 billion. Prof Finkelstein said, “These findings reveal that successful efforts to improve mental health will have both health and productivity benefits.”
These estimates are consistent with global findings. The World Health Organization estimates that COVID-19 has directly or indirectly contributed to an increased prevalence of depression and anxiety of 28 per cent and 26 per cent, respectively. Other estimates put the global economic burden of mental health conditions at $1 trillion per year.
Recognising the growing mental health crisis, the Singapore government has created a multiagency task force to address the growing mental health pandemic. However, more can be done.
“Greater efforts to encourage undiagnosed cases to seek treatment, expanded access to peer support programmes, increased efforts to improve mental health literacy and reduce stigma, and greater training among community resources such as general practitioners (GPs) and allied health professionals to diagnose and treat mental health symptoms are all part of a successful recovery strategy for the whole population,” said Associate Professor Daniel Fung, Chief Executive Officer, Institute of Mental Health, and a co-author of the study.
The research was conducted using an internal grant from Duke-NUS. The research team is conducting a similar study focusing on Singapore’s youth and also looking at strategies to increase access to peer support programmes.
END
Duke-NUS, IMH: Cost of anxiety and depression in Singapore runs into the billions
Singapore scientists find use of healthcare resources, absenteeism and reduced productivity due to mental health issues place a significant burden on Singapore’s economy.
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Maths unlocks molecular interactions that open window to how life evolved
2023-04-27
Dr Araujo, from the QUT School of Mathematical Sciences, said the research findings represented a blueprint for adaptation-capable signalling networks across all domains of life and for the design of synthetic biosystems.
“Our study considers a process called robust perfect adaptation (RPA) whereby biological systems, from individual cells to entire organisms, maintain important molecules within narrow concentration ranges despite continually being bombarded with disturbances to the system,” Dr Araujo ...
The conservation laws of a dynamical system are no mystery to artificial intelligence
2023-04-27
Osaka, Japan – Many real-world systems, from climate systems to the physical mechanisms of robots, are governed by the invariant quantities that arise from their underlying geometric structures. Modelling these systems using computer simulations is a key tool for understanding them (for weather forecasting, for instance, or developing robot locomotion). It’s often possible to collect data for these systems, but making sense of those data to build a model is a more challenging task.
Artificial intelligence ...
Infectious-diseases response initiative reduced staff burnout and helped prevent HAI increases at VA health care system during covid-19 pandemic
2023-04-27
Arlington, Va., April 27, 2023 – A serious infectious threat response initiative (SITRI) implemented by the Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) team at Veterans Affairs North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS) positively impacted IPC staff burnout and helped prevent an increase in healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), suggest that pre-emptive investment in preparedness initiatives can enable healthcare facilities to retain routine prevention efforts and improve patient safety during infectious disease outbreaks.
“During ...
Former EPA and NIEHS directors urge overhaul of WHO’s draft PFAS drinking water guidance
2023-04-27
The World Health Organization’s draft drinking water guidance for the two most well-studied per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exhibit a “striking and inappropriate disregard of the best available science,” according to former directors of the U.S. EPA’s Office of Science and Technology and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). In a viewpoint for the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science & Technology, Betsy Southerland and Linda Birnbaum strongly recommend ...
Using microbes to get more out of mining waste
2023-04-27
Researchers have developed a new mining technique which uses microbes to recover metals and store carbon in the waste produced by mining. Adopting this technique of reusing mining waste, called tailings, could transform the mining industry and create a greener and more sustainable future.
Tailings are a by-product of mining. They are the fine-grained waste materials left after extracting the target ore mineral, which are then stacked and stored. This method is called dry-stack tailing.
Over time, mining practices have evolved and become more efficient. But the climate crisis and rising demand for critical minerals require the development of new ore removal and ...
Carnegie Mellon research aims to revive office chatter
2023-04-26
About one-third of our lives are spent at work, and the relationships we build there can have personal and professional benefits. But a majority of workers indicate difficulty connecting with co-workers socially, especially in the new landscape of remote and hybrid work arrangements.
To ease the friction caused by reduced in-person interaction, a team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Human-Computer Interaction Institute created a Slack application that helps to initiate casual conversations and create affinity groups in an online workspace.
"We were freshly out of the pandemic, and we realized that everyone around us was complaining ...
Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation
2023-04-26
“Our study emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between STAT3α and STAT3β proteins and their active forms when discussing STAT3-related cancer diagnosis and therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 24, 2023, entitled, “Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation.”
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor involved in ...
Terasaki Institute to celebrate grand opening of Woodland Hills Research Center with ribbon-cutting
2023-04-26
WOODLAND HILLS, Calif. – April 26, 2023 – The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, a nonprofit dedicated to rapidly translating scientific knowledge into real-world solutions, will celebrate the grand opening of its latest biomedical research center with a ribbon-cutting ceremony on Saturday, April 29.
When: Saturday, April 29 at 11:30 a.m.
Where: 21100[ML1] Erwin St., Woodland Hills, Calif., 91367
What: ...
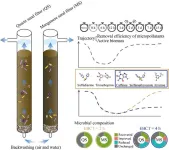
Backwashing affects the removal of micropollutants and the dynamic changes in the microbial community in sand filters
2023-04-26
Sand filters are commonly applied in drinking water treatment and can efficiently remove suspended solids, organic matter, and microorganisms from source water. During the process, particulate matter and microbes can attach to filter sands and develop a thick biofilm in both rapid and slow sand filters. To prevent clogging and restore pollutant removal efficiency, backwashing using air, water, or a combination of both is usually required for sand filters. However, backwashing can induce a loss in biomass, thus decreasing the pollutant ...
Researchers create antimicrobial ‘superfoam’
2023-04-26
A versatile new foam material developed by researchers at the University of Georgia could significantly reduce health care-related infections caused by implanted medical devices—or drastically improve cleanup efforts following environmental disasters like oil spills.
Like a spongy Swiss Army knife, the porous three-dimensional foam is water repellent—meaning it resists blood, microbes and proteins, while also exhibiting antimicrobial and oil-water separation properties. Its versatility, functionality and relatively inexpensive production costs could make it a valuable resource for future clinicians and environmental remediation professionals ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] Duke-NUS, IMH: Cost of anxiety and depression in Singapore runs into the billionsSingapore scientists find use of healthcare resources, absenteeism and reduced productivity due to mental health issues place a significant burden on Singapore’s economy.