(Press-News.org)
Researchers at Tokyo Tech have discovered hidden chemical order of the Mo and Nb atoms in disordered Ba7Nb4MoO20, by combining state-of-the-art techniques, including resonant X-ray diffraction and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. This study provides valuable insights into how a material’s properties, such as ionic conduction, can be heavily influenced by its hidden chemical order. These results would stimulate significant advances in materials science and engineering.
Determining the precise structure of a crystalline solid is a challenging endeavor. Materials properties such as ion conduction and chemical stability, are heavily influenced by the chemical (occupational) order and disorder. However, the techniques that scientists typically use to elucidate unknown crystal structures suffer from serious limitations.
For instance, X-ray and neutron diffraction methods are powerful techniques to reveal the atomic positions and arrangement in the crystal lattice. However, they may not be adequate for distinguishing different atomic species with similar X-ray scattering factors and similar neutron scattering lengths.
To tackle this issue, a research team led by Professor Masatomo Yashima of Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) in Japan sought to develop a novel and more powerful approach to analyze the order and disorder in crystals. They combined four different techniques to analyze the crystal structure of an important ionic conductor, Ba7Nb4MoO20. “We chose Ba7Nb4MoO20 as Ba7Nb4MoO20-based oxides and related compounds are a class of emerging materials with interesting properties such as high ionic conduction and high chemical stability,” explains Prof. Yashima. “However, given that both the Mo6+ and Nb5+ cations have similar scattering powers, all structural analyses of Ba7Nb4MoO20 until now have been performed assuming complete Mo/Nb disorder.”
As described in their recent paper published in Nature Communications, the researchers used an approach that combined two experimental techniques, resonant X-ray diffraction (RXRD) and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) aided by computational calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). The NMR provided direct experimental evidence that the Mo atoms occupy only the crystallographic M2 site in Ba7Nb4MoO20, indicating the chemical order of Mo atoms.
Next, the researchers used RXRD to quantify the occupancy factors of Mo and Nb atoms. They found that the occupancy factor of Mo atoms was 0.5 at the M2 site but zero at all other sites. Interestingly, the M2 site is close to the oxide-ion conducting, oxygen-deficient layer of Ba7Nb4MoO20. This suggests that the Mo atoms at the M2 site have key role in the high ion conduction of Ba7Nb4MoO20. Furthermore, DFT calculations indicated that the Mo ordering stabilizes Mo excess composition exhibiting high ionic conductivity. Positions, occupancy, and atomic displacements of protons and oxide ions were also determined by neutron diffraction.
“Our results demonstrate that the Mo order affects the material properties of Ba7Nb4MoO20,” highlights Prof. Yashima. “In this regard, our work represents a major advance in our understanding of the correlation between the crystal structure and the material properties of ionic conductors.” Further, in contrast to single-crystal X-ray and neutron diffraction, the proposed approach can even be extended to other polycrystalline and powdered samples.
Overall, the methodology presented in this study can open up new avenues for an in-depth analysis of chemical order/disorder in materials. In turn, this could lead to the development of physics, chemistry, and materials science and technology.
Only time will tell what other hidden orders and disorders we will stumble upon!
###
Yashima Research Group
Novel Oxychloride Shows High Stability and Oxide-Ion Conduction through Interstitial Oxygen Site | Tokyo Tech News
Fueling the Future with New Perovskite-related Oxide-ion Conductors | Tokyo Tech News
New Ba7Nb4MoO20-Based Materials with High Oxygen-Ion Conductivity Could Open Sustainable Future | Tokyo Tech News
New High Proton Conductors with Inherently Oxygen Deficient Layers Open Sustainable Future | Tokyo Tech News
Getting through the bottleneck—A new class of layered perovskite with high oxygen-ion conductivity | Tokyo Tech News
Apatite-Type Materials without Interstitial Oxygens Show High Oxide-Ion Conductivity by Overbonding | Tokyo Tech News
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tokyo Tech stands at the forefront of research and higher education as the leading university for science and technology in Japan. Tokyo Tech researchers excel in fields ranging from materials science to biology, computer science, and physics. Founded in 1881, Tokyo Tech hosts over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students per year, who develop into scientific leaders and some of the most sought-after engineers in industry. Embodying the Japanese philosophy of “monotsukuri,” meaning “technical ingenuity and innovation,” the Tokyo Tech community strives to contribute to society through high-impact research.
https://www.titech.ac.jp/english/
END
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has named Claus Daniel as Associate Laboratory Director for Advanced Energy Technologies (AET). He will begin his new role on Monday, May 1.
Daniel will join Argonne from Carrier Corporation, where he leads engineering partnerships and sustainability as part of Carrier’s strategy and innovation team. He manages the effort to decarbonize the product portfolio, with activities spanning 16 time zones in the U.S., Europe and Asia. Prior to joining Carrier, Daniel spent 16 years with DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in a number of roles.
“It is an exciting ...
The vast majority of AI models used in medicine today are “narrow specialists,” trained to perform one or two tasks, such as scanning mammograms for signs of breast cancer or detecting lung disease on chest X-rays.
But the everyday practice of medicine involves an endless array of clinical scenarios, symptom presentations, possible diagnoses, and treatment conundrums. So, if AI is to deliver on its promise to reshape clinical care, it must reflect that complexity of medicine and do so with high fidelity, says Pranav ...
New research has revealed children’s physical activity in the UK has largely returned to pre-pandemic levels – but children are still more sedentary during the week.
The study, led by the University of Bristol, found that by summer last year 41% of children were meeting the national recommended physical activity guidelines of an hour on average of moderate to vigorous physical activity daily. Although this shows an improvement from the immediate aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, when little more than a third (37%) were meeting this target, it means the majority of children were still ...
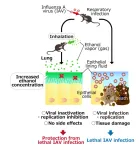
Inhaling low concentrations of ethanol vapor can disable the influenza A virus in mice, without harmful side effects, says a new study by scientists at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST). The scientists believe it may also treat similar viruses such as the one that causes Covid-19.
Prof. Tsumoru Shintake, who leads the Quantum Wave Microscopy Unit at OIST, first proposed the idea to use ethanol vapor to treat respiratory tract infections. He set out to test the approach with his colleague, Prof. Hiroki Ishikawa, leader of the Immune Signal Unit at OIST, and their team members.
“Ethanol is an effective disinfectant ...
Nickel-zinc (Ni-Zn) batteries are promising due to their high output voltage, high theoretical specific energy, high safety, and low cost. However, rechargeable alkaline Ni-Zn batteries are challenging, since the cathodic side reaction of oxygen evolution results in low energy efficiency and poor stability.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. ZHU Kaiyue from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed ...
Methanol is a potential feedstock for biomanufacturing since it's easily obtained in an environment-friendly manner. But it is still challenging to construct a microbial cell factory for methanol-based bioproduction due to the toxicity of methanol and complex cellular metabolism.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHOU Yongjin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has engineered yeast Ogataea polymorpha for efficient ...
SINGAPORE, 26 April 2023 – Symptoms of anxiety and depression in the post-peak pandemic era could be costing Singapore 2.9 per cent of its gross domestic product (GDP)—or nearly S$16 billion—suggests a study conducted by Duke-NUS Medical School and the Institute of Mental Health (IMH).
Publishing in the journal BMC Psychiatry, the researchers estimated the total economic burden of lost productivity due to anxiety and depression in Singapore to be S$15.7 billion (US$11.72 billion) annually, based on survey data from 5,725 Singaporean adults collected via an online panel between April and June 2022.
Using ...
Dr Araujo, from the QUT School of Mathematical Sciences, said the research findings represented a blueprint for adaptation-capable signalling networks across all domains of life and for the design of synthetic biosystems.
“Our study considers a process called robust perfect adaptation (RPA) whereby biological systems, from individual cells to entire organisms, maintain important molecules within narrow concentration ranges despite continually being bombarded with disturbances to the system,” Dr Araujo ...
Osaka, Japan – Many real-world systems, from climate systems to the physical mechanisms of robots, are governed by the invariant quantities that arise from their underlying geometric structures. Modelling these systems using computer simulations is a key tool for understanding them (for weather forecasting, for instance, or developing robot locomotion). It’s often possible to collect data for these systems, but making sense of those data to build a model is a more challenging task.
Artificial intelligence ...
Arlington, Va., April 27, 2023 – A serious infectious threat response initiative (SITRI) implemented by the Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) team at Veterans Affairs North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS) positively impacted IPC staff burnout and helped prevent an increase in healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), suggest that pre-emptive investment in preparedness initiatives can enable healthcare facilities to retain routine prevention efforts and improve patient safety during infectious disease outbreaks.
“During ...