(Press-News.org) New research has revealed children’s physical activity in the UK has largely returned to pre-pandemic levels – but children are still more sedentary during the week.
The study, led by the University of Bristol, found that by summer last year 41% of children were meeting the national recommended physical activity guidelines of an hour on average of moderate to vigorous physical activity daily. Although this shows an improvement from the immediate aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, when little more than a third (37%) were meeting this target, it means the majority of children were still found to be falling short.
Children are more sedentary during the week since public lockdown restrictions lifted, spending an extra 13 minutes on average daily being inactive according to the findings.
Lead author Russ Jago, Professor of Physical Activity and Public Health, said: “It’s encouraging that on average children’s physical activity levels are back to where they were before the pandemic.
“But it’s taken nearly a year since the last public lockdown was lifted, and children’s increased sedentary time during the week has persisted, which is an area of concern for policy makers, schools, and parents.”
The study, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research, measured physical activity levels of 393 children aged 10 to 11 years old between June and December 2021 and a further 436 children of the same age between January and July last year. Children and a parent or carer wore an accelerometer to measure their physical activity and answered a questionnaire. Participants came from 28 schools in the Bristol area. This information was compared with data from nearly 1,300 children and their parents from 50 schools in the same area before the pandemic.
On average, parents were found to take part in eight minutes more moderate to vigorous physical activity at weekends than before the pandemic.
Physical activity is important for children’s health and well-being. The UK Chief Medical Officers recommend all children and young people should take part in an hour of moderate to vigorous physical activity each day. This is activity that gets children slightly hot, slightly sweaty, and out of breath. The Chief Medical Officers also advise children should limit the amount of time they spend being sedentary, which means sitting or lying down, except when sleeping, for extended periods.
Co-author Dr Ruth Salway, Senior Research Associate in Epidemiology and Statistics, said: “The findings suggest physical activity is susceptible to disruptions in provision and leisure opportunities, and highlight that still not enough 10 to 11-year- olds meet the guidelines. On the flipside, it’s great to see how the pandemic may have encouraged parents to be more active and it looks like these habits may be continuing.”
END
Study shows children’s inactivity remains an issue in wake of pandemic
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
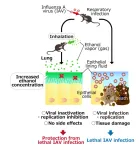
Inhaled ethanol may treat respiratory infections and stop pandemics
2023-04-27
Inhaling low concentrations of ethanol vapor can disable the influenza A virus in mice, without harmful side effects, says a new study by scientists at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST). The scientists believe it may also treat similar viruses such as the one that causes Covid-19.
Prof. Tsumoru Shintake, who leads the Quantum Wave Microscopy Unit at OIST, first proposed the idea to use ethanol vapor to treat respiratory tract infections. He set out to test the approach with his colleague, Prof. Hiroki Ishikawa, leader of the Immune Signal Unit at OIST, and their team members.
“Ethanol is an effective disinfectant ...
Air-breathing cathode enhances energy conversion efficiency and durability of alkaline nickel-zinc batteries
2023-04-27
Nickel-zinc (Ni-Zn) batteries are promising due to their high output voltage, high theoretical specific energy, high safety, and low cost. However, rechargeable alkaline Ni-Zn batteries are challenging, since the cathodic side reaction of oxygen evolution results in low energy efficiency and poor stability.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. ZHU Kaiyue from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed ...
Methanol biotransformation to efficiently produce fatty alcohols
2023-04-27
Methanol is a potential feedstock for biomanufacturing since it's easily obtained in an environment-friendly manner. But it is still challenging to construct a microbial cell factory for methanol-based bioproduction due to the toxicity of methanol and complex cellular metabolism.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHOU Yongjin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has engineered yeast Ogataea polymorpha for efficient ...
Duke-NUS, IMH: Cost of anxiety and depression in Singapore runs into the billions
2023-04-27
SINGAPORE, 26 April 2023 – Symptoms of anxiety and depression in the post-peak pandemic era could be costing Singapore 2.9 per cent of its gross domestic product (GDP)—or nearly S$16 billion—suggests a study conducted by Duke-NUS Medical School and the Institute of Mental Health (IMH).
Publishing in the journal BMC Psychiatry, the researchers estimated the total economic burden of lost productivity due to anxiety and depression in Singapore to be S$15.7 billion (US$11.72 billion) annually, based on survey data from 5,725 Singaporean adults collected via an online panel between April and June 2022.
Using ...
Maths unlocks molecular interactions that open window to how life evolved
2023-04-27
Dr Araujo, from the QUT School of Mathematical Sciences, said the research findings represented a blueprint for adaptation-capable signalling networks across all domains of life and for the design of synthetic biosystems.
“Our study considers a process called robust perfect adaptation (RPA) whereby biological systems, from individual cells to entire organisms, maintain important molecules within narrow concentration ranges despite continually being bombarded with disturbances to the system,” Dr Araujo ...
The conservation laws of a dynamical system are no mystery to artificial intelligence
2023-04-27
Osaka, Japan – Many real-world systems, from climate systems to the physical mechanisms of robots, are governed by the invariant quantities that arise from their underlying geometric structures. Modelling these systems using computer simulations is a key tool for understanding them (for weather forecasting, for instance, or developing robot locomotion). It’s often possible to collect data for these systems, but making sense of those data to build a model is a more challenging task.
Artificial intelligence ...
Infectious-diseases response initiative reduced staff burnout and helped prevent HAI increases at VA health care system during covid-19 pandemic
2023-04-27
Arlington, Va., April 27, 2023 – A serious infectious threat response initiative (SITRI) implemented by the Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) team at Veterans Affairs North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS) positively impacted IPC staff burnout and helped prevent an increase in healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings, published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC), suggest that pre-emptive investment in preparedness initiatives can enable healthcare facilities to retain routine prevention efforts and improve patient safety during infectious disease outbreaks.
“During ...
Former EPA and NIEHS directors urge overhaul of WHO’s draft PFAS drinking water guidance
2023-04-27
The World Health Organization’s draft drinking water guidance for the two most well-studied per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exhibit a “striking and inappropriate disregard of the best available science,” according to former directors of the U.S. EPA’s Office of Science and Technology and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). In a viewpoint for the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science & Technology, Betsy Southerland and Linda Birnbaum strongly recommend ...
Using microbes to get more out of mining waste
2023-04-27
Researchers have developed a new mining technique which uses microbes to recover metals and store carbon in the waste produced by mining. Adopting this technique of reusing mining waste, called tailings, could transform the mining industry and create a greener and more sustainable future.
Tailings are a by-product of mining. They are the fine-grained waste materials left after extracting the target ore mineral, which are then stacked and stored. This method is called dry-stack tailing.
Over time, mining practices have evolved and become more efficient. But the climate crisis and rising demand for critical minerals require the development of new ore removal and ...
Carnegie Mellon research aims to revive office chatter
2023-04-26
About one-third of our lives are spent at work, and the relationships we build there can have personal and professional benefits. But a majority of workers indicate difficulty connecting with co-workers socially, especially in the new landscape of remote and hybrid work arrangements.
To ease the friction caused by reduced in-person interaction, a team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Human-Computer Interaction Institute created a Slack application that helps to initiate casual conversations and create affinity groups in an online workspace.
"We were freshly out of the pandemic, and we realized that everyone around us was complaining ...