(Press-News.org)
The United States is in the midst of a mental health crisis with rising rates of hospitalization for suicide and self-harm events among children and adolescents.
A study, “Characteristics Associated with Serious Self-Harm Events in Children and Adolescents,” set to be published in the June issue of Pediatrics, looked at how best to determine which children are at elevated risk for self-harm.
Researchers identified four separate profiles to help medical professionals better assess children at elevated risk for a self-harm event.
“Predicting which children are at risk for serious self-harm events, such as suicide attempts or self-injurious behaviors, in the emergency department is extremely challenging,” said senior author, James Antoon, MD, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Hospital Medicine at Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt. “Our study provides an important step in evaluating the whole child in relation to self-harm risk assessment. These profiles can be used to better inform clinical decision making by providing a better assessment of overall risk of self-harm.”
Four distinct profiles of psychiatric comorbidity in children and adolescents with varying levels of risk for a serious self-harm event were identified — low risk, moderate risk, high risk and very high risk. The clinical profiles are based on a more comprehensive and flexible framework that complements previous assessments and can help identify children at elevated risk for a self-harm event, according to the study.
The findings also showed unique and distinct patterns of comorbidity that are also distinguishable between age and sex.
The study identified 1,098 children 5-18 years of age hospitalized with a neuropsychiatric event at Monroe Carell and Children’s Hospital of Colorado in Aurora, Colorado between April 2016 and March 2020. Of those hospitalized, 406 (37%) were diagnosed with a self-harm event.
A breakdown of findings:
Very high-risk profile consisted of males ages 10-13 with ADHD, bipolar disorder, autism spectrum disorder and other developmental disorders.
Low-risk profile consisted of children ages 5-9 who had a non-mental health diagnosis and an absence of mood disorders, behavioral disorders, psychotic disorders, developmental disorders, and trauma or substance-related disorders.
High-risk profile included females ages 14-17 with depression and anxiety in conjunction with substance- and trauma-related disorders. Personality and eating disorders were also significant for this profile.
Moderate risk had a significant absence of depressive disorders, suggesting that these disorders play a major role in driving the risk of suicidality.
The profiles considered demographic factors like age and sex, as well as overall underlying psychiatric and medical conditions.
“There are many interacting factors in children with self-harm events, ranging from individual, family, social support and specific life events,” said lead author Mert Sekmen, a research assistant with the Division of Hospital Medicine at Monroe Carell. “We know that psychiatric diagnoses are a well-established risk factor for self-harm. For example, 70% of children who die by suicide have more than two psychiatric diagnoses.”
According to study authors, previous studies focused on the independent risk of psychiatric diagnoses, such as depression or bipolar disorder, on self-harm events.
“Meaning after taking everything else into account, what are the odds of self-harm in someone with bipolar disorder? Or with a child with autism? This approach fails to consider the holistic and complex interactions that make up risk for self-harm,” said Sekmen. “We cannot evaluate these events without considering the whole child. For example, taking into account the interplay between age, sex, autism and ADHD at the same time.”
“Our study provides a novel approach that takes the child’s entire medical and psychiatric profile into account and assesses what overall constellations of factors are associated with imminent self-harm,” said Antoon.
The study authors agree that further study is needed to validate these risk profiles in larger populations and develop prognostic and clinical decision support applications that provide real-time risk assessments for providers.
END
The way our senses adjust while playing high-intensity virtual reality games plays a critical role in understanding why some people experience severe cybersickness and others don’t.
Cybersickness is a form of motion sickness that occurs from exposure to immersive VR and augmented reality applications.
A new study, led by researchers at the University of Waterloo, found that the subjective visual vertical – a measure of how individuals perceive the orientation of vertical lines – shifted considerably after participants played a high-intensity ...
In the race to make the world more livable for people and nature, progress on land outpaced successes in the seas, raising red flags that wealthier countries’ advantages may be upsetting a balance, a Michigan State University study shows.
Progress in oceans actually slowed after the United Nations member states adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. That action aims to facilitate global partnerships among developed and developing countries in sustainable development.
So far, though, a new study in the open-access journal iScience reveals evidence that ...
About The Study: The intervention examined in this randomized clinical trial resulted in improvements in the receipt of preventive care services versus usual care for children insured by Medicaid by incorporating community health workers in a team-based approach to early childhood well-child care.
Authors: Tumaini R. Coker, M.D., M.B.A., of Seattle Children’s Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.7197)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: This case series demonstrated that prostate cancer occurs in transgender women and is not as rare as published case reports might suggest. However, rates were lower than expected based on prior prostate cancer incidence estimates in cisgender male veterans.
Authors: Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.6028)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Transgender women keep their prostates even after gender-affirming surgery, but the extent to which they remain at risk of prostate cancer has been unclear.
Now a first of its kind study led by UC San Francisco has estimated the risk at about 14 cases per 10,000 people.
The study drew on 22 years of data from the Veterans Affairs Health System. Although the sample size was necessarily small, it is still the largest study of its kind. It publishes Saturday, April 29, 2023 in the Journal ...
At least 3,700 out-of-state mental health providers utilized New Jersey’s COVID-19 Temporary Emergency Reciprocity Licensure program to provide mental health services to more than 30,000 New Jersey patients during the first year of the pandemic, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in The Journal of Medical Regulation, surveyed health care practitioners who received a temporary license in New Jersey to examine the impact of the temporary licensure program on access to mental health care.
“The New Jersey program enabled patients with ...
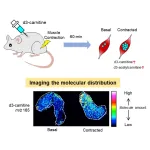
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way of mapping the distribution of carnitine in skeletal muscle cells. Carnitine is a small compound that helps transport fatty acids and reduce metabolic byproducts. They discovered that slow-type muscle fibers contained the most, and that activity promptly led to rises in acetylcarnitine, a product of the immediate response of carnitine contained in the cell. Their technique promises new insights into how muscle cells work.
Our muscles require ...
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical ...
Astronomers from McGill University are part of an international team that has discovered 25 new sources of repeating fast radio bursts (FRBs), these explosions in the sky that come from far beyond the Milky Way. This discovery brings the total number of confirmed FRB sources to 50. Based on data gathered by the CHIME/FRB collaboration, the new study, published this week in The Astrophysical Journal, may also bring scientists closer to understanding the origins of these mysterious phenomena.
A new way of identifying FRBs
Thanks to the radio telescopes such as those at CHIME, which scan the entire northern sky every day, the number of detected FRBs has grown exponentially in recent years. ...
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical charges can exist between microdroplets of water ...