(Press-News.org) Woods Hole, Mass. (Monday, May 8, 2023) -- New research provides clear evidence of a human “fingerprint” on climate change and shows that specific signals from human activities have altered the temperature structure of Earth’s atmosphere.
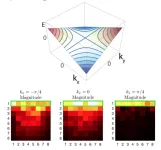
Differences between tropospheric and lower stratospheric temperature trends have long been recognized as a fingerprint of human effects on climate. This fingerprint, however, neglected information from the mid to upper stratosphere, 25 to 50 kilometers above the Earth’s surface.
“Including this information improves the detectability of a human fingerprint by a factor of five. Enhanced detectability occurs because the mid to upper stratosphere has a large cooling signal from human-caused CO2 increases, small noise levels of natural internal variability, and differing signal and noise patterns,” according to the journal article, “Exceptional stratospheric contribution to human fingerprints on atmospheric temperature,” published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). Noise in the troposphere can include day-to-day weather, interannual variability arising from El Niños and La Niñas, and longer-term natural fluctuations in climate. In the upper stratosphere, the noise of variability is smaller, and the human-caused climate change signal is larger, so the signal can be much more easily distinguished.
“Extending fingerprinting to the upper stratosphere with long temperature records and improved climate models means that it is now virtually impossible for natural causes to explain satellite-measured trends in the thermal structure of the Earth’s atmosphere,” the paper states.
“This is the clearest evidence there is of a human-caused climate change signal associated with CO2 increases,” according to lead author Benjamin Santer, an adjunct scientist in the Physical Oceanography Department at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (WHOI) in Massachusetts.
“This research undercuts and rebuts claims that recent atmospheric and surface temperature changes are natural, whether due to the Sun or due to internal cycles in the climate system. A natural explanation is virtually impossible in terms of what we are looking at here: changes in the temperature structure of the atmosphere,” added Santer, who has worked on climate fingerprinting for more than 30 years. “This research puts to rest incorrect claims that we don’t need to treat climate change seriously because it is all natural.”
The research was motivated by earlier work by Suki Manabe and Richard Wetherald, who in 1967 used a simple climate model to study how CO2 from fossil fuel burning might change atmospheric temperature. Their modeling found a very distinctive feature: an increase in CO2 levels led to more trapping of heat in the troposphere (the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere) and less heat escaping higher up into the stratosphere (the layer above the troposphere), thus warming the troposphere and cooling the stratosphere. This prediction of tropospheric warming and stratospheric cooling in response to increasing CO2 has been confirmed many times by more complex models and verified by comparing model results with global-mean atmospheric temperature observations from weather balloons and satellites.
Although these earlier studies considered global-mean temperature changes in the middle and upper stratosphere, roughly 25 to 50 kilometers above Earth’s surface, they did not look at detailed patterns of climate change in this layer. This region can be better studied now because of improved simulations and satellite data. The new research is the first to search for human-caused climate change patterns – also called “fingerprints” – in the middle and upper stratosphere.
“The human fingerprints in temperature changes in the mid to upper stratosphere due to CO2 increases are truly exceptional because they are so large and so different from temperature changes there due to internal variability and natural external forcing. These unique fingerprints make it possible to detect the human impact on climate change due to CO2 in a short period of time (~10 – 15 years) with high confidence,” stated co-author Qiang Fu, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric Sciences at the University of Washington.
“The world has been reeling under climate change, so being as confident as possible of the role of carbon dioxide is critical,” said co-author Susan Solomon, Martin Professor of Environmental Studies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. “The fact that observations show not only a warming troposphere but also a strongly cooling upper stratosphere is unique tell-tale evidence that nails the dominant role of carbon dioxide in climate change and greatly increases confidence.”
Santer said that although it is intellectually gratifying to be able to extend fingerprinting higher up into the atmosphere to test the prediction by Manabe and Wetherald, it is also deeply concerning.
“As someone who tries to understand the kind of world that future generations are going to inhabit, these results make me very worried. We are fundamentally changing the thermal structure of Earth’s atmosphere, and there is no joy in recognizing that,” Santer said.
“This study shows that the real world has changed in a way that simply cannot be explained by natural causes,” Santer added. “We now face important decisions, in the United States and globally, on what to do about climate change. I hope those decisions are based on our best scientific understanding of the reality and seriousness of human effects on climate.”
Funding for the study was provided by National Science Foundation, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, U.S. Department of Energy, and the Francis E. Fowler IV Center for Ocean and Climate at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
Authors :
Benjamin D. Santera, b, Stephen Po-Chedleyc, Lilong Zhaod, Cheng-Zhi Zoue, Qiang Fuf, Susan Solomong, David W. J. Thompsonh,i, Carl Mearsj, and Karl E. Taylorc
Affiliations :
aPhysical Oceanography Department, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA
bJoint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering, University of California at Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
cProgram for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA
dNanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China
eCenter for Satellite Applications and Research, NOAA/NESDIS, College Park, MD, USA
fDepartment of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA
gEarth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
hDepartment of Atmospheric Sciences, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA
iSchool of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK
jRemote Sensing Systems, Santa Rosa, CA, USA
About Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Massachusetts, dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate an understanding of the ocean’s role in the changing global environment. WHOI’s pioneering discoveries stem from an ideal combination of science and engineering—one that has made it one of the most trusted and technically advanced leaders in basic and applied ocean research and exploration anywhere. WHOI is known for its multidisciplinary approach, superior ship operations, and unparalleled deep-sea robotics capabilities. We play a leading role in ocean observation and operate the most extensive suite of data-gathering platforms in the world. Top scientists, engineers, and students collaborate on more than 800 concurrent projects worldwide—both above and below the waves—pushing the boundaries of knowledge and possibility. For more information, please visit www.whoi.edu
Key takeaways:
• New research provides clear evidence of a human “fingerprint” on climate change and shows that specific signals from human activities have altered the temperature structure of Earth’s atmosphere.
• Differences between tropospheric and lower stratospheric temperature trends have long been recognized as a fingerprint of human effects on climate. This fingerprint, however, neglected information from the mid to upper stratosphere, 25 to 50 kilometers above the Earth’s surface.
• “Including this information improves the detectability of a human fingerprint by a factor of five. Enhanced detectability occurs because the mid to upper stratosphere has a large cooling signal from human-caused CO2 increases, small noise levels of natural internal variability, and differing signal and noise patterns.”
• “Extending fingerprinting to the upper stratosphere with long temperature records and improved climate models means that it is now virtually impossible for natural causes to explain satellite-measured trends in the thermal structure of the Earth’s atmosphere.”
• “This is the clearest evidence there is of a human-caused climate change signal associated with CO2 increases.”
• “This research undercuts and rebuts claims that climate change is natural, whether due to the Sun or due to internal cycles in the climate system. A natural explanation is virtually impossible in terms of what we are looking at here: changes in the temperature structure of the atmosphere.”
END
Atmospheric research provides clear evidence of human-caused climate change signal associated with CO2 increases
Claims that climate change is natural are inconsistent with atmospheric temperature trends
2023-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UC Irvine, NASA JPL researchers discover a cause of rapid ice melting in Greenland
2023-05-08
Irvine, Calif., May 8, 2023 – While conducting a study of Petermann Glacier in northwest Greenland, researchers at the University of California, Irvine and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory uncovered a previously unseen way in which the ice and ocean interact. The glaciologists said their findings could mean that the climate community has been vastly underestimating the magnitude of future sea level rise caused by polar ice deterioration.
Using satellite radar data from three European missions, the UCI/NASA team learned that Petermann Glacier’s grounding line – where ice detaches from the land bed and begins floating in the ocean – shifts substantially ...
A new twist on chirality: researchers extend the concept of directionality and propose a new class of materials
2023-05-08
It is often desirable to restrict flows—whether of sound, electricity, or heat—to one direction, but naturally occurring systems almost never allow this. However, unidirectional flow can indeed be engineered under certain conditions, and the resulting systems are said to exhibit chiral behavior.
The concept of chirality is traditionally limited to single direction flows in one dimension. In 2021, however, researchers working with Taylor Hughes, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, ...
New York’s fertility rate drops, average age of mothers rises
2023-05-08
ITHACA, NY – A decline in New York’s childbirth rate is showing no sign of reversing and many women are waiting longer to have children, according to newly compiled data from the Program in Applied Demographics (PAD) in the Cornell Jeb E. Brooks School of Public Policy.
In 2011, about 241,312 were born in New York. In 2021, that number was 210,742 – a 13% decline.
New York state’s total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of births a woman would have in her lifetime if current patterns continue – dropped from ...
Department of Energy announces $45 million for Inertial Fusion Energy (IFE)
2023-05-08
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Today, at the celebration ceremony of the historic achievement of fusion ignition at the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm announced a plan to provide up to $45 million to support Inertial Fusion Energy (IFE) research and development.
Fusion, the process that powers the sun and stars, has the potential to provide clean, safe, and reliable carbon-free energy on earth. Harnessing fusion energy is one of the greatest scientific and technological challenges of the 21st century. Fusion requires the fuel to ...
The ability to chew properly may improve blood sugar levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes
2023-05-08
For release: May 8, 2023
Contact: Mary Durlak, durlak@buffalo.edu
University at Buffalo
716-645-4595
The ability to chew properly may improve blood sugar levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes
BUFFALO, N.Y. – If you’re a health care provider treating people with Type 2 diabetes (T2D), University at Buffalo researcher Mehmet A. Eskan has this suggestion for you: check your patients’ teeth.
In a study published in PLOS ONE on April 14, Eskan demonstrates that patients with T2D who have full chewing function have a blood glucose level that is significantly lower ...
Drug industry’s carbon impact could be cut by half
2023-05-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – In a first-of-its-kind analysis, Cornell University researchers and partners found that pharmaceutical producers could reduce their environmental impact by roughly half by optimizing manufacturing processes and supply chain networks and by switching to renewable energy sources.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, similar in magnitude to the automotive industry, though it has not received anywhere near the level of academic or regulatory ...
Clearing the runway: Modeling a realistic supply chain for bio-based jet fuel
2023-05-08
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists led the development of a supply chain model revealing the optimal places to site farms, biorefineries, pipelines and other infrastructure for sustainable aviation fuel production.
The project focused on carinata, a hardy, oil-rich plant targeted as a winter bioenergy crop in Georgia. Scientists used geographical data to model facilities to grow, harvest, store, process and deliver carinata-based fuel at the lowest cost and carbon intensity.
“Our model is unique in capturing the fuel’s life-cycle carbon footprint,” said ...
DRI aims to increase scientific access to earth monitoring data with re-launch of ClimateEngine.org
2023-05-08
The combined use of satellite and climate data has rapidly become critical for scientists and resource managers seeking to accurately assess changes in land cover and land use over time and across space. Unfortunately, processing such vast amounts of data can be time and cost-prohibitive, which is why researchers teamed up with Google and federal agencies to create ClimateEngine.org. Climate Engine’s innovative web application allows scientists, natural resource agencies, and other users to create maps and time series plots that integrate satellite and climate data, providing an indispensable ...
Fame-seeking mass shooters more likely to plan ‘surprise’ attacks, and the novelty of their locations and targets brings added fame
2023-05-08
Mass shooters pursuing fame often plan their attacks as “surprises," carefully crafting them in ways that set them apart from previous incidents, which makes them uniquely challenging to prevent.
That is a key finding in a groundbreaking new study from NYU Tandon School of Engineering, about the subset of mass shooters in the U.S. for whom notoriety is a primary objective. The study is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Led by Maurizio Porfiri, NYU Tandon Institute Professor and Director of the Center for Urban Science and ...
UC Irvine scientists develop gene silencing DNA enzyme that can target a single molecule
2023-05-08
NOTE TO EDITORS: PHOTO AVAILABLE AT
https://news.uci.edu/2023/05/08/uc-irvine-scientists-develop-gene-silencing-dna-enzyme-that-can-target-a-single-molecule/
Irvine, Calif., May 8, 2023 — Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have developed a DNA enzyme – or DNAzyme – that can distinguish between two RNA strands inside a cell and cut the disease-associated strand while leaving the healthy strand intact. This breakthrough “gene silencing” technology could revolutionize the development of DNAzymes for treating cancer, infectious diseases and neurological disorders.
DNAzymes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
Lower music volume levels in fitness class and perceived exercise intensity
Of crocodiles, counting and conferences
AERA announces 2026 award winners in education research
Saving two lives with one fruit drop
Photonic chips advance real-time learning in spiking neural systems
[Press-News.org] Atmospheric research provides clear evidence of human-caused climate change signal associated with CO2 increasesClaims that climate change is natural are inconsistent with atmospheric temperature trends