(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—Jeffery Kelly, PhD, the Lita Annenberg Hazen Professor of Chemistry at Scripps Research, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences for his work on understanding protein shapes and controlling the ensemble of shapes with small molecules in order to develop therapeutic strategies for a range of devastating diseases. The academy awards membership in recognition of “distinguished and continuing achievements in original research.”
The election of Kelly brings the total number of memberships held by Scripps Research faculty in the National Academies of Sciences, Medicine and Engineering to 31.
“This well-deserved honor is in recognition of Jeff's groundbreaking research in protein folding, misfolding, and aggregation,” says Scripps Research President and CEO Peter Schultz, PhD. “His work has opened new avenues for therapeutic intervention in protein-folding diseases.”
By unraveling the mechanisms by which protein misassembly-associated toxicity leads to diseases of the heart and brain, Kelly is at the forefront of designing and developing molecules that stabilize proteins, leading to much-needed new medications.
His research has resulted in a variety of treatments, including the FDA-approved drug tafamidis (Vyndaqel® and Vyndamax®): a treatment that slows the progression of familial amyloid polyneuropathy (a neurodegenerative disease), and familial and sporadic TTR cardiomyopathy disease (a condition that ultimately causes heart failure).
His work also holds promise for Alzheimer’s disease, in which patients often have abnormal protein assemblies called beta-amyloid plaques in the brain.
For this groundbreaking research, Kelly recently won the prestigious Wolf Prize in Chemistry in February, and the Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences last September. He is also the recipient of the 2019 E.B. Hershberg Award for Important Discoveries in Medicinally Active Substances, and the 2016 Jacob and Louise Gabbay Award in Biotechnology and Medicine.
Kelly earned his PhD in organic chemistry at the University of North Carolina before doing his postdoctoral work at Rockefeller University. He joined Scripps Research in 1997 and served as dean of the Skaggs Graduate School of Chemical and Biological Sciences from 2000 to 2008.
The National Academy of Sciences is a private, nonprofit institution that was established under a congressional charter signed by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863. It recognizes achievement in science by election to membership, and—with the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Medicine—provides science, engineering and health policy advice to the federal government and other organizations.
To view a full list of members elected in 2022, visit the National Academy of Sciences website.
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
END
Renowned Scripps Research professor Jeffery Kelly elected to National Academy of Sciences
Kelly’s groundbreaking work on protein misfolding has led to therapies for neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases
2023-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How the ancient messengers cAMP and cGMP deliver their messages
2023-05-09
Two highly similar molecules with essential, but often contrasting, signaling roles in most life forms exert their distinct effects through subtle differences in their bindings to their signaling partners, according to a new study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine.
In the study, published March 27 in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, the researchers used exquisitely sensitive measurement techniques to reveal at the single-molecule level how the signaling molecules cAMP and cGMP bind to an ion channel from the pacemaker channel family, one of the major types of proteins whose activities they regulate.
Ion channels are common features of cell membranes, ...
Researchers map the immunology of the gut in children with IBD
2023-05-09
Researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Sachs’ Children and Youth Hospital in Sweden have mapped the immune system in the gut of children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The results, which were published in Cell Reports Medicine, can be used to design more targeted therapies.
Today, we know relatively little about how the immune system functions in children with IBD and how this differs from adults. About 40 percent of patients, including both children and adults, do not respond to the treatments that are currently available. It is therefore very important to identify biomarkers that can both predict ...
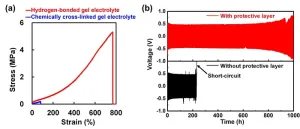
Extending the life of a lithium metal anode using a protective layer made of an extremely tough gel electrolyte
2023-05-09
A National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) research team has succeeded in substantially improving the cycling performance of a lithium metal battery by developing a mechanically very strong polymeric gel electrolyte and integrating it into the battery as a layer to protect the lithium metal anode. This achievement may greatly facilitate efforts to put lithium metal anodes—a potentially very high performance anode material—into practical use.
Today’s society is rapidly transforming through the widespread use of digital technologies, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the growing use of renewable energy. These ...
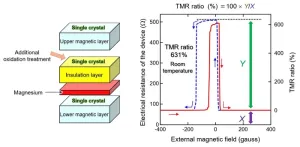
MTJ device with the world’s highest TMR performance developed through precision interfacial control
2023-05-09
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has achieved a tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio of 631% at room temperature, breaking the previous world record which had stood for 15 years. This was accomplished by fine-tuning the interfaces in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). This MTJ exhibited very large TMR ratio oscillation effect with a peak-to-valley (PV) difference of 141%. This phenomenon may be exploitable to significantly increase the sensitivity of magnetic sensors and the capacity of magnetoresistive random access ...
Scientists use gene-editing technology to produce first calf resistant to major viral disease
2023-05-09
CLAY CENTER, Neb., May 9, 2023 -Scientists have collaborated to produce the first gene-edited calf with resistance to bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), a virus that costs the U.S. cattle sector billions of dollars annually.
The recent study published in PNAS Nexus results from a collaboration between the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS), the University of Nebraska–Lincoln (UNL), the University of Kentucky, and industry partners, Acceligen and Recombinetics, Inc.
BVDV is one of the most significant viruses ...
Gene-edited calf may reduce reliance on antimicrobials against cattle disease
2023-05-09
Cattle worldwide face major health threats from a highly infectious viral disease that decades of vaccinations and other precautions have failed to contain. Federal, private-sector and Husker scientists are collaborating on a new line of defense, by producing a gene-edited calf resistant to the virus.
If follow-up research confirms its efficacy, the gene-editing approach offers long-term potential to reduce antimicrobial and antibiotic use in the cattle industry.
The bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) devastates the bovine immune system and can cause severe respiratory and intestinal harm to infected beef and dairy cattle, said veterinary epidemiologist Brian Vander ...
Scientists at uOttawa streamline a widely used chemical reaction, creating new manufacturing opportunities
2023-05-09
A team of scientists from the University of Ottawa has developed an innovative technique to manufacture complex chemical structures from easily accessible substrates, making it one of the simplest and most practical methods for converting alcohols into their arylated equivalents.
This innovative method for performing the reaction, namely the deoxygenative Suzuki-Miyaura arylation of aliphatic alcohols, uses two distinct metal catalysts. Their reaction operates under mild reaction conditions with minimal waste products and is expected to have a significant impact on the creation of new molecules. As a result, it will contribute to advances in pharmaceutical, agrochemical, ...
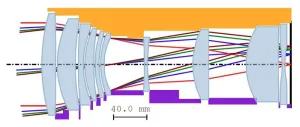
Designing cameras for harsh environments? Be sure to account for lens mount details
2023-05-09
Cameras used in harsh environments must be designed in a way that prevents temperature swings from influencing their optical performance. New research demonstrates that accounting for the exact lens mounting structure used is a critical step in ensuring that lens systems remain robust to temperature changes.
Eric M. Schiesser from Synopsys, Inc. will present the new research at the Optica Design and Fabrication Conference, which will take place 04 – 08 June 2023 in Quebec City, Canada.
“Most optical systems – from the camera in your smartphone to the eyes of the Mars rover - are used over a range of temperatures. To keep the image sharp ...
New study led by Brown researchers sheds light on incidental findings in lung cancer screening
2023-05-09
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University]—When patients receive a low-dose computed tomography screen for lung cancer, doctors can see more than just the lungs. The screening test often picks up abnormalities or potentially “significant incidental findings” (SIFS) not associated with lung cancer. A new study led by Ilana Gareen, an associate professor of epidemiology at the Brown University School of Public Health, and published in JAMA Internal Medicine, highlights the need for proper reporting and management of these findings to reduce mortality, health care costs and unnecessary ...
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic senescent cell populations
2023-05-09
“In summary, single-cell transcriptomic analysis has allowed us to identify the specific populations and the dynamic transition states during senescence initiation and progression.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 9, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic senescent cell populations.”
Senescence is a state of enduring growth arrest triggered by sublethal cell damage. Given that senescent cells actively ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
6 in 10 US women projected to have at least one type of cardiovascular disease by 2050
People’s gut bacteria worse in areas with higher social deprivation
Unique analysis shows air-con heat relief significantly worsens climate change
Keto diet may restore exercise benefits in people with high blood sugar
Manchester researchers challenge misleading language around plastic waste solutions
Vessel traffic alters behavior, stress and population trends of marine megafauna
Your car’s tire sensors could be used to track you
Research confirms that ocean warming causes an annual decline in fish biomass of up to 19.8%
Local water supply crucial to success of hydrogen initiative in Europe
New blood test score detects hidden alcohol-related liver disease
High risk of readmission and death among heart failure patients
Code for Earth launches 2026 climate and weather data challenges
Three women named Britain’s Brightest Young Scientists, each winning ‘unrestricted’ £100,000 Blavatnik Awards prize
Have abortion-related laws affected broader access to maternal health care?
Do muscles remember being weak?
Do certain circulating small non-coding RNAs affect longevity?
How well are international guidelines followed for certain medications for high-risk pregnancies?
New blood test signals who is most likely to live longer, study finds
Global gaps in use of two life-saving antenatal treatments for premature babies, reveals worldwide analysis
Bug beats: caterpillars use complex rhythms to communicate with ants
High-risk patients account for 80% of post-surgery deaths
Celebrity dolphin of Venice doesn’t need special protection – except from humans
Tulane study reveals key differences in long-term brain effects of COVID-19 and flu
The long standing commercialization challenge of lithium batteries, often called the dream battery, has been solved.
New method to remove toxic PFAS chemicals from water
The nanozymes hypothesis of the origin of life (on Earth) proposed
Microalgae-derived biochar enables fast, low-cost detection of hydrogen peroxide
Researchers highlight promise of biochar composites for sustainable 3D printing
Machine learning helps design low-cost biochar to fight phosphorus pollution in lakes
Urine tests confirm alcohol consumption in wild African chimpanzees
[Press-News.org] Renowned Scripps Research professor Jeffery Kelly elected to National Academy of SciencesKelly’s groundbreaking work on protein misfolding has led to therapies for neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases