Workplace accidents are most likely to occur in moderately dangerous settings
2023-05-10
(Press-News.org)
Although some people might expect very dangerous jobs to be associated with the highest incidence of workplace accidents, a new study finds that accidents are actually most likely to occur within moderately dangerous work environments.
“In highly dangerous environments, individuals engage in a high degree of safety behaviours, which offsets the chance of an accident,” said Dr. James Beck, lead author and a professor of psychology. “On the other hand, in moderately dangerous environments, people usually engage in some safety behaviours, yet most people do not engage in enough safety behaviours to avoid accidents.”
Safety behaviours are often viewed as cumbersome and inefficient, which can mean workers do not practice these behaviours consistently.
According to Beck, under moderately dangerous conditions, people tend to underestimate the degree of safety behaviour that is needed. As a result, they tend to respond to danger in a more-or-less proportional manner so that moderately dangerous situations are met with a moderate degree of safety behaviour. However, the researchers found this response insufficient as “minimizing accidents requires a very sharp increase in safety behaviours, even in response to a small increase in danger.”
The authors conducted four studies. In two of the studies, historical workplace injury data were used to demonstrate that moderately dangerous environments were associated with the most accidents. The remaining two studies were experiments that had individuals complete work simulations in which they knew the level of danger and how to engage with it safely.
The experiments demonstrated that individuals under-allocate time and effort to work safely within moderately dangerous environments despite knowing about the dangers.
“It appears that the level of safety behaviours needed to offset moderate dangers is simply not very obvious or intuitive,” Beck said.
The findings provide insights into how workplace safety training programs may be designed to emphasize moderately hazardous work environments to help individuals avoid accidents.
The paper Moderation in all things, except when it comes to workplace safety: Accidents are most likely to occur under moderately hazardous work conditions, by Beck, Midori Nishioka, Abigail A. Scholer, and Jeremy M. Beus, was published in the journal Personnel Psychology.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-09
Imagine sitting on a park bench, watching someone stroll by. While the scene may constantly change as the person walks, the human brain can transform that dynamic visual information into a more stable representation over time. This ability, known as perceptual straightening, helps us predict the walking person’s trajectory.
Unlike humans, computer vision models don’t typically exhibit perceptual straightness, so they learn to represent visual information in a highly unpredictable way. But if machine-learning models had this ability, it might enable them to better estimate how objects or people will move.
MIT researchers have discovered that a specific training ...
2023-05-09
ORLANDO, May 9, 2023 – A University of Central Florida College of Medicine researcher has developed a new, more precise treatment for a major cause of illness around the world each year — acute respiratory viral infections.
Acute respiratory viral infections include sicknesses such as the flu, pneumonia, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and coronavirus. These infections cause millions of illnesses worldwide, with the flu alone responsible for 3 million to 5 million cases of severe illness and up to 650,000 respiratory deaths each year, ...
2023-05-09
Hamilton, ON (March 9, 2023) – McMaster University researchers Dena Zeraatkar and Tyler Pitre have found that the drug solriamfetol is the most effective treatment for excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) for people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
The standard treatment for OSA is a positive airway pressure (PAP) mask that uses compressed air to support lung airways during sleep. However, some people with OSA still experience EDS and may benefit from anti-fatigue medication.
Zeraatkar ...
2023-05-09
The study, published April 7 in Nature Communications, analyzed electronic health records as part of the National Institutes of Health’s Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative to better understand the persistence of symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection, also known as long COVID, among broad, diverse populations. Led by Dr. Rainu Kaushal, chair of the Department of Population Health Sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine and physician-in-chief of population health sciences at New York-Presbyterian ...
2023-05-09
LA JOLLA, CA—Jeffery Kelly, PhD, the Lita Annenberg Hazen Professor of Chemistry at Scripps Research, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences for his work on understanding protein shapes and controlling the ensemble of shapes with small molecules in order to develop therapeutic strategies for a range of devastating diseases. The academy awards membership in recognition of “distinguished and continuing achievements in original research.”
The election of Kelly brings the total number of memberships held by Scripps Research faculty in the National Academies of Sciences, Medicine and Engineering to 31.
“This ...
2023-05-09
Two highly similar molecules with essential, but often contrasting, signaling roles in most life forms exert their distinct effects through subtle differences in their bindings to their signaling partners, according to a new study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine.
In the study, published March 27 in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, the researchers used exquisitely sensitive measurement techniques to reveal at the single-molecule level how the signaling molecules cAMP and cGMP bind to an ion channel from the pacemaker channel family, one of the major types of proteins whose activities they regulate.
Ion channels are common features of cell membranes, ...
2023-05-09
Researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Sachs’ Children and Youth Hospital in Sweden have mapped the immune system in the gut of children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The results, which were published in Cell Reports Medicine, can be used to design more targeted therapies.
Today, we know relatively little about how the immune system functions in children with IBD and how this differs from adults. About 40 percent of patients, including both children and adults, do not respond to the treatments that are currently available. It is therefore very important to identify biomarkers that can both predict ...
2023-05-09
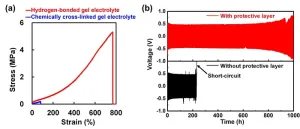
A National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) research team has succeeded in substantially improving the cycling performance of a lithium metal battery by developing a mechanically very strong polymeric gel electrolyte and integrating it into the battery as a layer to protect the lithium metal anode. This achievement may greatly facilitate efforts to put lithium metal anodes—a potentially very high performance anode material—into practical use.
Today’s society is rapidly transforming through the widespread use of digital technologies, the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the growing use of renewable energy. These ...
2023-05-09
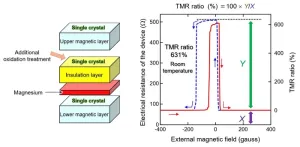
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) has achieved a tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio of 631% at room temperature, breaking the previous world record which had stood for 15 years. This was accomplished by fine-tuning the interfaces in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). This MTJ exhibited very large TMR ratio oscillation effect with a peak-to-valley (PV) difference of 141%. This phenomenon may be exploitable to significantly increase the sensitivity of magnetic sensors and the capacity of magnetoresistive random access ...
2023-05-09
CLAY CENTER, Neb., May 9, 2023 -Scientists have collaborated to produce the first gene-edited calf with resistance to bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), a virus that costs the U.S. cattle sector billions of dollars annually.
The recent study published in PNAS Nexus results from a collaboration between the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS), the University of Nebraska–Lincoln (UNL), the University of Kentucky, and industry partners, Acceligen and Recombinetics, Inc.
BVDV is one of the most significant viruses ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Workplace accidents are most likely to occur in moderately dangerous settings