(Press-News.org) A new study in the journal PLOS ONE examines how individuals coped with stressors during the COVID-19 pandemic and which strategies were associated with higher quality of life.
The study’s findings provide important insights for both individuals and institutions as they prepare for and respond to future large-scale traumatic events. It was based on responses from more than 1,000 Americans on their experiences and behaviors during the pandemic.
The research found that problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies were associated with higher quality of life, while avoidant coping had a negative correlation.
Problem-focused coping involves tactics such as problem-solving, obtaining instrumental support, and planning. Emotion-focused coping strategies include the use of emotional support, humor, religion, and positive reframing. Avoidant coping includes tactics such as distraction, behavioral disengagement, and substance abuse.
“People use different types of coping to deal with different stressors, and people may use all three strategies at different times,” said the study’s author Dr. Fathima Wakeel, associate professor in the Department of Community and Population Health at Lehigh University. “What this study demonstrates is how those strategies work during a large-scale traumatic event.”
The study’s findings echoed existing research conducted in other contexts that demonstrate positive associations with problem-focused coping. However, this study demonstrated a distinctive positive correlation between emotion-focused coping and quality of life.
Researchers say emotion-focused coping strategies may be most helpful when stressors are unpredictable or outside of individuals’ control, like many of those faced during the pandemic.
In addition, the study found that avoidant coping correlated with worse physical and psychological well-being. Avoidant tactics such as substance abuse can exacerbate problems over the long run.
According to Wakeel, the findings can be valuable to individuals in dealing with stressful life events as well as to societal institutions. Both problem-focused and emotion-focused coping require strong social supports and available resources within communities, and the discouragement of avoidant coping will require cooperation among all levels of wellness providers.
END
Coping Under COVID: Study provides lessons from the pandemic on how to cope with large-scale traumatic events
2023-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson research highlights for May 10, 2023
2023-05-10
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include a combination therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, new insights into the evolution of anaplastic thyroid cancer, a promising new treatment approach for PTEN/p53-deficient pancreatic cancer, a novel pan-species artificial intelligence model to detect cancer cells, a ...
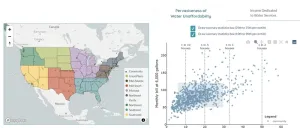
Millions of U.S. households may struggle to afford basic water services
2023-05-10
A new analysis suggests that about one in seven households across the U.S. may face financial hardship in paying for access to water and wastewater services. Lauren Patterson and colleagues at Duke University, North Carolina, present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Water.
U.S. households pay utilities for access to water for drinking, cooking, cleaning, and sanitation, as well as for wastewater services. However, in recent years, the cost of these services has increased alongside a widening income gap, fueling affordability concerns. ...
Data from Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source provides foundation for first US approved RSV vaccine
2023-05-10
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a highly contagious disease that affects millions of people each year around the world, resulting in an estimated 160,000 deaths. In the United States, severe RSV causes 6,000 to 10,000 deaths among people 65 years of age or older.
On May 3, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Arexvy, an RSV vaccine developed by pharmaceutical company GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc. It is the first RSV vaccine to be approved in the United States, and according to GSK’s press release, the first for older adults to be approved anywhere in the world. This is a ...
New procedure allows micro-printing inside existing materials with greater accuracy
2023-05-10
3D printers form objects by layering melted plastic or metal, but this only works on large scales. What you need to fabricate microdevices for which the layering step is not feasible? What if it were possible to print directly into the bulk of an existing three-dimensional material?
The research groups of Lynford Goddard and Paul Braun, professors at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, have been collaborating to develop such a process. They use the technique of multiphoton lithography to print inside an existing ...
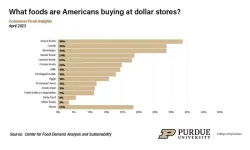
Purdue April Consumer Food Insights report explores role of dollar stores in food landscape
2023-05-10
Purdue April Consumer Food Insights report explores role of dollar stores in food landscape
A market for an expanded grocery selection at dollar stores potentially exists, especially with consumers who live less than 10 minutes away, according to data reported in the April Consumer Food Insights report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies, and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated ...
Using reflections to see the world from new points of view
2023-05-10
As a car travels along a narrow city street, reflections off the glossy paint or side mirrors of parked vehicles can help the driver glimpse things that would otherwise be hidden from view, like a child playing on the sidewalk behind the parked cars.
Drawing on this idea, researchers from MIT and Rice University have created a computer vision technique that leverages reflections to image the world. Their method uses reflections to turn glossy objects into “cameras,” enabling a user to see the world as if they were looking through the “lenses” of everyday objects like a ceramic coffee mug or a metallic ...
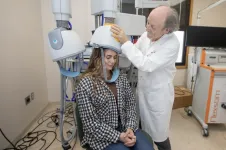
Stimulating hope: Personalizing treatment options for depression
2023-05-10
Artificial intelligence. Gene editing. mRNA vaccines. It’s safe to say the past few decades have felt like the next big wave of medicine. However, what continues to be needed in virtually every field is a personalized approach to care.
That’s certainly needed when it comes to using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to treat depression, said Medical University of South Carolina Distinguished University Professor Mark George, M.D.
TMS uses a magnet to increase brain activity in ...
Gene p16 drives colorectal cancer emerging as a target for potential therapies
2023-05-10
Colorectal cancer is the fourth most common and second deadliest cancer. How colorectal cancer develops is not well understood, but a team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine reports in the Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research that silencing the gene p16, even though the DNA itself does not change, can drive colorectal cancer progression in animal models. The researchers also revealed a strategy that reduced tumor growth and improved survival in tumor-bearing mice, opening new possibilities for future targeted therapies in patients with gene p16 alterations.
“Years of research have shown ...
New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
2023-05-10
New database offers insight into consequences of language loss
Languages, like animal species, can go extinct. More than half of the world’s approximately 7,000 signed and spoken languages are currently endangered. And without intervention they are likely to become extinct, meaning nobody will speak or sign them any longer.
While language loss is happening across the world, the costs vary strikingly in different places, according to a new study co-authored by Yale linguist Claire Bowern. Regions where all Indigenous language are endangered — including parts of South America and the United States — ...
Bigger isn’t always better: Size of research teams does not equate to better research outcomes, finds new study
2023-05-10
Having a large research team isn’t linked to producing higher quality research, finds a new study from the University of Surrey which analysed data from 1.4 million academic papers.
Professor Sorin Krammer, lead author of the study and Professor of Strategy and International Business at the University of Surrey, said:
“Despite the prevalence of large teams in research, there is still a lack of a good understanding of how their size and diversity affects their performance.”
“Our ...