(Press-News.org) Managing cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors may play a role in preserving physical function during the aging process, according to new research published today by The Journals of Gerontology, Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences.
“Approximately 10% of older adults have muscle weakness and diminished physical function that leads to adverse health outcomes and physical disability,” said lead author Dr. Shivani Sahni. “Since loss of physical function contributes to reduced mobility, disability, institutionalization, and mortality, management of CVD risk factors can help preserve physical function with age,” said Dr. Sahni.
This study showed that vascular measures are associated with grip strength in cross-sectional analyses and change in gait speed (a measure of physical function) in longitudinal analyses.
This is one of the first community-based studies to comprehensively examine relations of aortic stiffness and vascular function with age-related decline in physical function. Higher aortic stiffness was associated with loss of physical function over ~11 years, said Dr. Sahni, who is an Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and an Associate Scientist at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife. She directs the Nutrition Program at the Marcus Institute.
Blood flow declines with aging, in part due to arterial stiffening. Consequent dysfunction in blood vessel dynamics may contribute to organ pathology and declines in muscle mass, explains Dr. Sahni. Yet, few studies have specifically assessed the role of vascular function, and changes in functional muscle measures such as mobility and muscle strength.
The current study utilized data from a large cohort of relatively healthy men and women and extends previous investigations by utilizing a longitudinal study design.
The majority of previously published studies have utilized cross-sectional study designs with modest sample sizes. The authors believe that future studies should evaluate whether interventions that target vascular health may reduce age-related declines in physical function. This is important because one third of older adults experience physical limitations contributing to reduced mobility, disability, institutionalization, and mortality. Hence, there is a need for development of novel interventions that target prevention of physical limitations in older adults.
This Paper
“Association of Vascular Health Measures and Physical Function: A Prospective Analysis in the Framingham Heart Study,” was written by lead author Dr. Sahni and coauthors Alyssa B. Dufour, PhD,1 Na Wang, PhD,2 Douglas P. Kiel, MD, MPH,1 Marian T. Hannan, DSc, MPH,1 Paul F. Jacques, DSc,3 Emelia J. Benjamin, MD, ScM,4,5 Ramachandran S. Vasan, MD,4,5 Joanne M. Murabito, MD,4,5 Anne B. Newman, MD, MPH,6 Roger A. Fielding, PhD,3 Gary F. Mitchell, MD,7 Naomi M. Hamburg, MD4.
Collaborating Institutions
1Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute of Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife, Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2Biostatistics and Epidemiology Data Analytics Center, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, MA; 3Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging, Tufts University, Boston, MA; 4Boston Medical Center and Boston University Schools of Medicine and Public Health, Boston, MA; 5Framingham Heart Study, Framingham, MA; 6Graduate School of Public Health, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA; 7Cardiovascular Engineering, Inc., Norwood, MA.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (grant numbers R01 AG051728; R01 AR53205; and R01 AR41398); the Heart, Lung and Blood Institute's Framingham Heart Study (contract number HHSN268201500001I; N01-HC-25195; 75N92019D00031; and 1R01 HL60040); the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) Grants in Aid Program (GAP) Award.
Dr. Sahni is supported partly by the Boston Claude D. Pepper Center Older American Independence Centers (OAIC; 1P30AG031679) and Peter and Barbara Sidel Fund. Drs. Fielding and Jacques are supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA; agreement No. 58-1950-4-00). Dr. Fielding is also supported by the Boston Claude D. Pepper Center Older American Independence Centers (OAIC; 1P30AG031679). Dr. Newman is supported by National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging (grant number U01 HL130114); CHS Research Resources for the Cardiovascular Health of Adults; and Pittsburgh Older Americans Independence Center (grant number P30 AG024827). Vascular measures were supported by grant numbers 1R01HL60040 and 1R01HL70100. Dr. Benjamin is supported by R01HL128914; 2R01 HL092577; 1R01 HL141434 01A1; 2U54HL120163; 1R01AG066010; and American Heart Association 18SFRN34110082. Dr. Vasan is supported in part by research grants R01HL142983; R01HL126136; R01HL070279 from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, the Evans Medical Foundation and the Jay and Louis Coffman Endowment from the Department of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine.
Conflict of Interest Statement
Dr. Sahni has institutional grants from Dairy Management Inc. (ended 2022) and Solarea Bio Inc., has reviewed grants for American Egg Board’s Egg Nutrition Center, and was a scientific advisor to Institute for the Advancement of Food and Nutrition Sciences (position ended 2022). Dr. Mitchell is the president of Cardiovascular Engineering, Inc., a company that designs and manufactures devices that measure vascular stiffness. He serves as a consultant to and receives honoraria and grant support from Novartis, Servier, Merck, Bayer and deCODE genetics. Dr. Kiel serves as a consultant to Solarea Bio, Reneo, and Pfizer, and receives grant support from Amgen, Solarea Bio Inc., and Radius Health, and royalties for publication in UpToDate by Wolters Kluwer. Dr. Hannan receives institutional grant funds from Amgen. Dr. Murabito served as a guest lecturer/consultant for Merck unrelated to this work.
About Hebrew SeniorLife
Hebrew SeniorLife, an affiliate of Harvard Medical School, is a national senior services leader uniquely dedicated to rethinking, researching, and redefining the possibilities of aging. Hebrew SeniorLife cares for more than 3,000 seniors a day across six campuses throughout Greater Boston. Locations include: Hebrew Rehabilitation Center-Boston and Hebrew Rehabilitation Center-NewBridge in Dedham; NewBridge on the Charles, Dedham; Orchard Cove, Canton; Simon C. Fireman Community, Randolph; Center Communities of Brookline, Brookline; and Jack Satter House, Revere. Founded in 1903, Hebrew SeniorLife also conducts influential research into aging at the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, which has a portfolio of more than $85 million, making it one of the largest gerontological research facilities in the U.S. in a clinical setting. It also trains more than 1,000 geriatric care providers each year. For more information about Hebrew SeniorLife, visit our website or follow us on our blog, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
About the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research
Scientists at the Marcus Institute seek to transform the human experience of aging by conducting research that will ensure a life of health, dignity, and productivity into advanced age. The Marcus Institute carries out rigorous studies that discover the mechanisms of age-related disease and disability; lead to the prevention, treatment, and cure of disease; advance the standard of care for older people; and inform public decision-making.
END
Managing cardiovascular disease risk factors may help preserve physical function as we age
Study examines relationship of aortic stiffness, vascular function with age-related physical decline
2023-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Endocrine community joins forces on European Hormone Day to raise awareness of vital role of hormones in preventing and treating rare and chronic diseases
2023-05-15
PRESS RELEASE
EMBARGOED TO 15 MAY 2023
Contact: Victoria Withy
Head of Marketing, Communications and Membership
E: victoria.withy@ese-hormones.org
M: +44 (0) 7761 800855
Today, 15 May 2023, the European Society of Endocrinology (ESE), the European Hormone and Metabolism Foundation (ESE Foundation) and other partners are marking the second European Hormone Day.
European Hormone Day brings together all those with an interest in endocrine health and disease to promote a better understanding of the role of hormones and encourage a collective call for change about ...
How old is that microplastic? A new way to estimate the age of microplastics in the upper ocean
2023-05-15
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University and Asahi Kasei Corporation have developed a new way to estimate the age of microplastics found in the upper oceans. The method involves a combination of analyzing plastic oxidation levels with environmental factors such as UV exposure and ambient temperature.
The team applied their new method to estimate the age of microplastics found in nearshore and offshore sites in the North Pacific Ocean. They found that the age of microplastics in nearshore regions ranged from 0 to 5 years old, whereas microplastics from offshore regions ranged from 1 to 3 years old. Their ...
New deal inked to space test meta-optical surfaces
2023-05-15
A new engineering study has been commissioned by the European Space Agency (under PECS, the Program for European Cooperating States), to prove the reliability of meta-optical elements for space use in a collaboration between the ESA, Bulgarian start-up company LaboraXpert and TMOS, the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems.
In the first study of its kind, it will determine whether meta-optical components can withstand the pressures of space launch and prolonged exposure to the space environment.
TMOS Centre Director Prof. Dragomir Neshev says, “The demand for Earth observation data is growing, yet the industry still faces the ...
Scientists create first humanised mouse model for rare genetic disease
2023-05-15
Mice with a defected human gene responsible for a rare genetic disease, called congenital adrenal hyperplasia, have been developed for the first time. The achievement, presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology, may help to develop new therapies for people with the most common type of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of inherited conditions, which affects about 1 in 15,000 births. In the most common form, called 21-hydroxylase deficiency, mutations in the CYP21A2 gene cause the adrenal glands ...
Novel sustainable electrochemical method converts carbon dioxide into carbonaceous materials
2023-05-15
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major greenhouse gas emitted through various types of human activities. In an effort to decrease humanity’s carbon footprint, scientists and policymakers across the globe are continuously trying to explore new methods for reducing atmospheric CO2 emissions and converting them into useful forms. In this regard, the electrochemical method of reducing CO2 to other carbonaceous forms like carbon monoxide, alcohols and hydrocarbon has gained considerable attention.
Against this ...
Managing menopause: Hormone therapy is back
2023-05-15
Hot flashes, night sweats and sleep disturbances are common symptoms of menopause that can affect health, quality of life and work productivity. A new review published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221438 recommends menopausal hormone therapy, historically known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), as first-line treatment in people without risk factors.
Menopausal symptoms may occur up to 10 years before the last menstrual period and can last more than 10 years, with negative effects for many people.
"Menopause and perimenopause can be associated with distressing ...
Can’t find your phone? There’s a robot for that
2023-05-15
Engineers at the University of Waterloo have discovered a new way to program robots to help people with dementia locate medicine, glasses, phones and other objects they need but have lost.
And while the initial focus is on assisting a specific group of people, the technology could someday be used by anyone who has searched high and low for something they’ve misplaced.
“The long-term impact of this is really exciting,” said Dr. Ali Ayub, a post-doctoral fellow in electrical and computer engineering. “A user can be involved not just with a companion robot but a personalized ...
Study shows how both metabolically healthy and unhealthy ‘forms’ of obesity increase risk of various obesity-related cancers
2023-05-14
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO, Dublin, 17-20 May). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
New research to be presented at this coming week’s European Congress on Obesity in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May) and published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute shows that both the metabolically healthy and unhealthy ‘forms’ of obesity are associated with an increased risk of various obesity-related cancers, with the relationship stronger in metabolically unhealthy obesity. The study is by Dr Ming Sun, Lund University, Malmö, ...
Clinically relevant deficiency of the “bonding hormone” oxytocin demonstrated
2023-05-14
The hormone oxytocin is important for social interaction and to control emotions. A deficiency of this hormone has previously been assumed in various diseases such as autism, but has never been proven. Now, for the first time, researchers from the University of Basel and the University Hospital of Basel have succeeded in demonstrating a deficiency of oxytocin in patients with a deficiency of vasopressin caused by a disease of the pituitary gland. This finding could be key to developing new therapeutic approaches.
The hormones oxytocin and vasopressin are produced in the same area of the brain ...
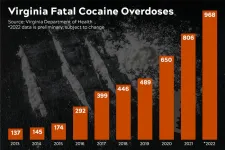
Addiction scientists seek to better understand cocaine use disorder: ‘Stimulants are coming back’
2023-05-14
Nearly 2 percent of the U.S. population reported cocaine use in 2020, and the highly addictive substance was involved in nearly one in five overdose deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
In Virginia, the number of cocaine-related overdoses has been increasing since 2013, with 968 fatal overdoses in 2022, according to preliminary data from the Virginia Department of Health, a 20 percent increase over 2021. Of those, four in five included fentanyl — prescription, illicit or analog — a driving force behind the fatalities.
Researchers at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
[Press-News.org] Managing cardiovascular disease risk factors may help preserve physical function as we ageStudy examines relationship of aortic stiffness, vascular function with age-related physical decline