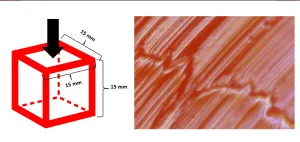
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 16, 2023 – For gummy candies, texture might be even more important than taste. Biting into a hard, stale treat is disappointing, even if it still carries a burst of sweetness. Keeping gummies in good condition depends on their formulation and storage, both of which alter how the molecules in the candies link together.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Ozyegin University and Middle East Technical University conducted a series of experiments that explore how changing key parts of the gummy-making process affects the final product, as well as how the candies behave in different storage temperatures. They used these results to identify the most shelf-stable combination for gummy candies.
To tackle these questions, the group adjusted a variety of inputs while making the gummies, from the glucose syrup-to-sucrose ratio to starch and gelatin concentrations. They wanted to understand how these changes affected features like candy texture, moisture content, and pH.
They then studied the resulting features of the candies before and after storage. Storage conditions varied from 10 to 30 degrees Celsius for 12 weeks or 15 to 22 C for a year.
Such extensive combinations of procedures presented their own hurdles during the study.
“A high number of parameters was the main challenge in our study,” author Suzan Tireki said. “We had eight different candy formulations, four different temperature conditions, and two different storage times. Another challenge was to try to find a common model for all these eight formulations, as each of them behaved differently.”
To account for such a variety of variables, the researchers used a statistical model to describe how each combination affected the quality parameters of the gummy. They specifically explored the chemical crosslink distances, or the length of bonds between molecules in the candy.
“The most innovative part of our study was investigating the texture of the gummy candies by estimating the average crosslink distances using the hardness data coming from texture profile analysis,” Tireki said.
The moisture content and pH, for example, were heavily dependent on the glucose syrup-to-sucrose ratio, whereas the gelatin content affected crosslink distances.
“Our most surprising finding was that hardness and average crosslink distance were not affected by the amount of starch,” Tireki said.
Identifying the most stable combinations for gummies can extend shelf life and improve candy quality in different climates and across the food industry.
The researchers next look to explore the role of plant-based formulations, mold shapes, and packaging types.
###
The article “Investigation of average crosslink distance and physicochemical properties of gummy candy during storage: Effect of formulation and storage temperature” is authored by Suzan Tireki, Gulum Sumnu, and Serpil Sahin. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on May 16, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0146761). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0146761.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
END
The physics of gummy candy
Dozens of ingredient and storage combinations reveal what factors make some gummies harder than others and how product formulation affects shelf life
2023-05-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The economic burden of racial, ethnic, and educational health inequities in the US
2023-05-16
About The Study: According to two data sources, in 2018, the economic burden of health inequities for racial and ethnic minority populations (American Indian and Alaska Native, Asian, Black, Latino, and Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander populations) was $421 billion or $451 billion and the economic burden of health inequities for adults without a 4-year college degree was $940 billion or $978 billion. The economic burden of health inequities is unacceptably high and warrants investments in policies and interventions to promote health equity for racial and ethnic minorities and adults with less than a 4-year college degree.
Authors: Darrell ...
Excess mortality and years of potential life lost among the black population in the US
2023-05-16
About The Study: Based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, from 1999 through 2020, the Black population in the U.S. experienced more than 1.63 million excess deaths and more than 80 million excess years of life lost when compared with the white population. After a period of progress in reducing disparities, improvements stalled, and differences between the Black population and the white population worsened in 2020.
Authors: Harlan M. Krumholz, M.D., S.M., of the Yale School of Medicine ...
Engineers design sutures that can deliver drugs or sense inflammation
2023-05-16
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Inspired by sutures developed thousands of years ago, MIT engineers have designed “smart” sutures that can not only hold tissue in place, but also detect inflammation and release drugs.
The new sutures are derived from animal tissue, similar to the “catgut” sutures first used by the ancient Romans. In a modern twist, the MIT team coated the sutures with hydrogels that can be embedded with sensors, drugs, or even cells that release therapeutic molecules.
“What we have is a suture that ...
Integration of AI decision aids to reduce workload and enhance efficiency in thyroid nodule management
2023-05-16
About The Study: The results of this diagnostic study involving 16 radiologists and 2,054 ultrasonographic images suggest that an optimized artificial intelligence (AI) strategy in thyroid nodule management may reduce diagnostic time-based costs without sacrificing diagnostic accuracy for senior radiologists, while the traditional all-AI strategy may still be more beneficial for junior radiologists.
Authors: Wei Wang, M.D., Ph.D., of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Use of immunization information systems in ascertainment of COVID-19 vaccinations for claims-based vaccine safety and effectiveness studies
2023-05-16
About The Study: The findings of this study of 5.1 million individuals suggested that supplementing COVID-19 claims records with Immunization Information Systems vaccination records substantially increased the number of individuals who were identified as vaccinated, yet potential under-recording remained. Improvements in reporting vaccination data to Immunization Information Systems infrastructures could allow frequent updates of vaccination status for all individuals and all vaccines.
Authors: Karen Schneider, Ph.D., of OptumServe Consulting in Falls ...
Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults
2023-05-16
About The Study: In this analysis of nationally representative survey data, the incidence of chronic pain was high compared with other chronic diseases and conditions for which the incidence in the U.S. adult population is known, including diabetes, depression, and hypertension. This comparison emphasizes the high disease burden of chronic pain in the U.S. adult population and the need for both prevention and early management of pain before it can become chronic, especially for groups at higher risk.
Authors: Richard L. Nahin, M.P.H., Ph.D., of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Moving from distressed areas to better-resourced neighborhoods improves kids’ asthma
2023-05-16
Children whose families participated in a program that helped them move from distressed neighborhoods to areas with lower rates of poverty and better public resources like schools and parks experienced significant improvements in severe asthma episodes, according to a new study led by a researcher at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin.
The study, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association, involved 123 children, ages 5 to 17, with persistent asthma whose families took part in a six-year housing mobility program in Baltimore.
Before ...
Researchers reveal DNA repair mechanism
2023-05-16
A new study adds to an emerging, radically new picture of how bacterial cells continually repair faulty sections of their DNA.
Published online May 16 in the journal Cell, the report describes the molecular mechanism behind a DNA repair pathway that counters the mistaken inclusion of a certain type of molecular building block, ribonucleotides, into genetic codes. Such mistakes are frequent in code-copying process in bacteria and other organisms. Given that ribonucleotide misincorporation can result in detrimental DNA code changes (mutations) and DNA breaks, all organisms have ...
Three professional societies unite on National Science Foundation grant in effort to increase access and inclusivity in ornithology
2023-05-16
CHICAGO — May 16, 2023 — The landscape of science is changing: People from increasingly varied backgrounds, identities, cultures, and genders are pursuing careers in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields. Support for this more diverse population of scientists needs to extend beyond “one size fits all” to better meet the needs of today’s scientists. Expanding support and strengthening the sense of community for individuals and groups who have not been historically welcomed in a discipline can foster a deeper sense of belonging and meaningfully broaden representation within that field. Researchers ...
NIH launches largest precision nutrition research effort of its kind
2023-05-16
The National Institutes of Health is now enrolling participants in a landmark initiative to advance nutrition research. Nutrition for Precision Health, powered by the All of Us Research Program, or NPH, is working with 14 sites across the United States – including Pennington Biomedical Research Center and LSU Health Sciences New Orleans in Louisiana – to engage 10,000 participants from diverse backgrounds and learn more about how our bodies respond differently to food.
“Nutrition for Precision Health brings us a step closer to precision medicine. The study will generate a massive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] The physics of gummy candyDozens of ingredient and storage combinations reveal what factors make some gummies harder than others and how product formulation affects shelf life