(Press-News.org) There is broad agreement that Homo sapiens originated in Africa. But there remain many uncertainties and competing theories about where, when, and how.
In a paper published today in Nature, an international research team led by McGill University and the University of California-Davis suggest that, based on contemporary genomic evidence from across the continent, there were humans living in different regions of Africa, migrating from one region to another and mixing with one another over a period of hundreds of thousands of years. This view runs counter to some of the dominant theories about human origins in Africa.
Competing theories about human origins in Africa
One theory holds that, about 150,000 years ago, there was a single central ancestral population in Africa from which other populations diverged. Another suggests that this central ancestral population was the result of the mixing of modern humans with a Neanderthal-like hominins (human-like beings), resulting in a leap forward in human evolution, as has been suggested took place in Eurasia.
“At different times, people who embraced the classic model of a single origin for Homo sapiens suggested that humans first emerged in either East or Southern Africa,” says Brenna Henn, a population geneticist in the Department of Anthropology and in the Genome Center at the University of California, Davis and co-lead author of the research. “But it has been difficult to reconcile these theories with the limited fossil and archaeological records of human occupation from sites as far afield as Morocco, Ethiopia, and South Africa which show that Homo sapiens were to be found living across the continent as far back as at least 300,000 years ago.”
So, the research team took a different approach.
Contemporary genomic evidence tells a different story
In the first systematic test of these competing anthropological models against genetic data, the team worked backwards from contemporary genomic material of 290 individuals from four geographically and genetically diverse African groups to trace the similarities and differences between the populations over the past million years and gain insight into the genetic interconnections and human evolution across the continent.
The groups were the Nama (Khoe-San from South Africa); the Mende (from Sierra Leone); the Gumuz (recent descendants of a hunter-gatherer group from Ethiopia); and the Amhara and Oromo (agriculturalists from eastern Africa). The researchers also included some Eurasian genetic material to include the traces of colonial incursions and mixing Africa.
“We used a new algorithm to rapidly test hundreds of possible scenarios. Those with gene flow back and forth between populations in various parts of the continent over the course of hundreds of thousands of years provided a much better explanation of the genetic variation we see today,” adds Simon Gravel, Associate Professor in the Department of Human Genetics at McGill University, and co-senior author on the paper. “We wrote this algorithm to understand how genetic disease risk varies across populations, and it led us to this deep dive into human origins. It’s been really fun to tie applied and fundamental research together in this way.”
About the study
“A weekly structured stem for human origins in Africa” by Aaron Ragsdale et al was published in Nature.
END
A new understanding of human origins in Africa
Contemporary DNA evidence suggests that humans emerged from the interaction of multiple populations living across the continent
2023-05-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
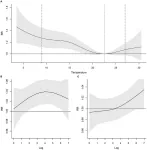
Low temperatures increase the risk of sickness absence, especially for women, young people and third sector professionals
2023-05-17
A retrospective study of temperatures in the province of Barcelona reveals that low temperatures increase the risk of going on a period of sick leave, due in particular to infectious and respiratory diseases. The study, carried out by researchers from Center for Research in Occupational Health (CISAL) and the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences at UPF (MELIS); the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation and CIBER of Epidemiology and Public Health (CIBERESP), shows that the sectors of the population most affected are women, young people and ...
Newcomers may change ecosystem functions – or not
2023-05-17
In a study tracking climate-induced changes in the distribution of animals and their effects on ecosystem functions, North Carolina State University researchers show that resident species can continue managing some important ecological processes despite the arrival of newcomers that are similar to them, but resident species’ role in ecosystem functioning changes when the newcomers are more different.
The findings could lead to predictive tools for understanding what might happen as climate change forces new species into communities, such as the movement of species from lower to higher latitudes or elevations.
“Species ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researcher contributes to the discovery of an Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone with volcanic activity
2023-05-17
Abu Dhabi, UAE: – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Montreal has recently discovered an Earth-sized exoplanet, a world beyond our solar system, that may be carpeted with volcanoes and potentially hospitable to life. Called LP 791-18 d, the planet could undergo volcanic outbursts as often as Jupiter’s moon Io, the most volcanically active body in our solar system. The team includes Mohamad Ali-Dib, a research scientist at the NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) Center for Astro, Particle, and Planetary Physics.
The planet was found and studied using data ...
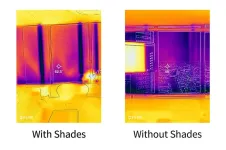
Automated window shades show potential for significant energy savings, Illinois Tech study finds
2023-05-17
CHICAGO—May 17, 2023—Automated insulating window shades can cut energy consumption by approximately one-quarter and may recoup the cost of installation within three to five years, according to a landmark study conducted by Illinois Institute of Technology researchers at Willis Tower. The study, funded by ComEd, showcases a promising path for sustainability and energy efficiency in architectural design.
Temperature regulation typically accounts for 30–40 percent of the energy used by buildings in climates similar to Chicago. The research team, led by Assistant Professor of Architectural Engineering Mohammad ...
Found: a likely volcano-covered terrestrial world outside the Solar System
2023-05-17
A large international team led by astronomers at the Trottier Institute for Research on Exoplanets at Université de Montréal (UdeM) today announced in the journal Nature the discovery of a new temperate world around a nearby small star.
This planet, named LP 791-18 d, has a radius and a mass consistent with those of Earth. Observations of this exoplanet and another one in the same system indicate that LP 791-18 d is likely covered with volcanoes similar to Jupiter’s moon Io, the most volcanically active body in our Solar System.
“The discovery of this exoplanet is an extraordinary ...
Odd cells found in lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
2023-05-17
A pair of internationally renowned stem cell cloning experts at the University of Houston is reporting their findings of variant cells in the lungs of patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) which likely represent key targets in any future therapy for the condition.
IPF is a progressive, irreversible and fatal lung disease in which the lungs become scarred and breathing becomes difficult. The rapid development and fatal progression of the disease occur by uncertain mechanisms, but the most pervasive school of thought is that IPF arises from recurrent, subclinical lung ...
What did the earliest animals look like?
2023-05-17
For more than a century, biologists have wondered what the earliest animals were like when they first arose in the ancient oceans over half a billion years ago.
Searching among today's most primitive-looking animals for the earliest branch of the animal tree of life, scientists gradually narrowed the possibilities down to two groups: sponges, which spend their entire adult lives in one spot, filtering food from seawater; and comb jellies, voracious predators that oar their way through the world's oceans in search of food.
In a new study published this week in the journal Nature, researchers use a novel approach based on chromosome structure to come up with ...
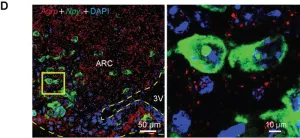
Researchers pinpoint brain cells that drive appetite in obesity
2023-05-17
A team at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research has discovered a group of brain cells that boosts appetite when there is a prolonged surplus of energy in the body, such as excess fat accumulation in obesity.
The researchers discovered that these cells not only produced the appetite-stimulating molecule NPY, but they in fact made the brain more sensitive to the molecule, boosting appetite even more.
“These cells kickstart changes in the brain that make it more sensitive to even low levels of NPY when there is a surplus of energy in the body in the form of excess fat – driving appetite during obesity,” explains Professor Herbert Herzog, senior ...
Receipt of medications for chronic disease during the first 2 years of COVID-19
2023-05-17
About The Study: This study of 18.1 million beneficiaries of fee-for service Medicare found that, in contrast to in-person health services, receipt of medications for chronic conditions was relatively stable in the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic overall, across racial and ethnic groups, and for community-dwelling patients with dementia. This finding of stability may hold lessons for other outpatient services during the next pandemic.
Authors: Nancy E. Morden, M.D., M.P.H., of the Geisel ...
Genetic associations between modifiable risk factors and Alzheimer disease
2023-05-17
About The Study: This genetic association study including 39,000 participants with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer disease (AD) and 401,000 control participants without AD found novel genetic associations between high high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol concentrations and high systolic blood pressure with higher risk of AD. These findings may inspire new drug targeting and improved prevention implementation.
Authors: Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, M.D., D.M.Sc., Ph.D., of Copenhagen University Hospital–Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13734)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] A new understanding of human origins in AfricaContemporary DNA evidence suggests that humans emerged from the interaction of multiple populations living across the continent