(Press-News.org) Publishing in the journal Nature Sustainability, a team of conservationists led by the Wildlife Conservation Society say that providing a “Conservation Basic Income” (CBI) – of $5.50 per day to all residents of protected areas in low- and middle-income countries would cost less than annual subsidies given to fossil fuels and other environmentally harmful industries.
CBI is an unconditional cash payment to individuals, similar to universal basic income (UBI)10 but targeting residents of important conservation areas. A Conversation Basic Income would support stewardship of land and biodiversity by Indigenous Peoples and local communities.
The authors provided the first global estimates for the gross costs of CBI using spatial analyses of three plausible future conservation scenarios. Gross costs vary widely, depending on the areas and populations included as well as the payment amounts: from $351 billion to $6.73 trillion annually.
The authors say a CBI is a potentially powerful mechanism for facilitating a radical shift in conservation. They say that evidence from other poverty-alleviation cash transfer programs that are unconditional with respect to conservation outcomes suggest that a CBI could achieve conservation in many contexts. For example, Indonesia’s national program of anti-poverty cash transfers also reduced deforestation across Indonesia.
Said lead author Dr. Emiel de Lange of WCS’s Cambodia Program: “CBI more equitably distributes the costs and benefits of conservation because basic income schemes improve wellbeing, reduce poverty, and redress inequalities including gender inequity. Inequalities, including gender, are key drivers of biodiversity loss. CBI could enable communities to pursue their own visions of a good life and avoid exploitation by extractive industries. Moreover, through redistribution of wealth from affluent populations and/or harmful industries, CBI can reduce aggregate global consumption and environmental impact.”
These costs of a CBI are significant compared to current government conservation spending, (~$133 billion in 2020) but represent a potentially sensible investment in safeguarding incalculable social and natural values as well as the estimated $44 trillion in global economic production dependent on nature.
READ THE STUDY HERE.
END
Conservationists propose “global conservation basic income” to safeguard biodiversity
Analysis shows that paying a basic income of $5.50 per day to all residents of protected areas in low- and middle-income countries would cost less than subsidies given to fossil fuels
2023-05-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals key molecular interaction that sets the timing of our biological clocks
2023-05-18
Molecular clocks in our cells synchronize our bodies with the cycle of night and day, cue us for sleep and waking, and drive daily cycles in virtually every aspect of our physiology. Scientists studying the molecular mechanisms of our biological clocks have now identified a key event that controls the timing of the clock.
The new findings, published May 18 in Molecular Cell, reveal important details of the molecular interactions that are disrupted in people with an inherited sleep disorder called Familial Advanced Sleep Phase ...
Paleontology: Fossil fragments shed light on a new spinosaurid dinosaur in Spain
2023-05-18
A dinosaur specimen from Castellón, Spain represents a new proposed species of spinosaurid, reports a paper published in Scientific Reports. The identification of a potential new species suggests that the Iberian peninsula may have been a diverse area for medium-to-large bodied spinosaurid dinosaurs and sheds light on the origin and evolution of spinosaurids.
Spinosaurids comprise of different groups of dinosaurs that are often large, stand on two feet, and are carnivorous. Well-known examples of spinosaurids include Spinosaurus ...
Cost-related medication nonadherence and desire for medication cost information
2023-05-18
About The Study: In a national panel survey of 2,000 respondents in 2022, approximately 1 in 5 older adults reported cost-related medication nonadherence. Real-time benefit tools may support medication cost conversations and cost-conscious prescribing, and patients are enthusiastic about their use. However, if disclosed prices are inaccurate, there is potential for harm through loss of confidence in the physician and nonadherence to prescribed medications.
Authors: Stacie B. Dusetzina, Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
Potential clinical and economic outcomes of over-the-counter hearing aids
2023-05-18
About The Study: In this cost-effectiveness analysis, provision of over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids was associated with greater uptake of hearing intervention and was cost-effective over a range of prices so long as OTC hearing aids were greater than 55% as beneficial to patient quality of life as traditional hearing aids. Over-the-counter hearing aids may expand access to beneficial treatment for hearing loss and represent an efficient use of resources.
Authors: Gillian D. Sanders Schmidler, Ph.D., of the Duke University ...
Examining mental health, education, employment, and pain in sickle cell disease
2023-05-18
About The Study: The findings of this cross-sectional analysis of 2,200 individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) suggest that employment status, sex, age, and depression are associated with pain frequency. Depression screening for these patients is warranted, especially among those experiencing higher pain frequency and severity. Comprehensive treatment and pain reduction must consider the full experiences of patients with SCD, including impacts on mental health.
Authors: Kelly M. Harris, ...
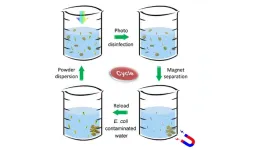
New non-toxic powder uses sunlight to quickly disinfect contaminated drinking water
2023-05-18
At least 2 billion people worldwide routinely drink water contaminated with disease-causing microbes.
Now Stanford University scientists have invented a low-cost, recyclable powder that kills thousands of waterborne bacteria per second when exposed to ordinary sunlight. The discovery of this ultrafast disinfectant could be a significant advance for nearly 30 percent of the world’s population with no access to safe drinking water, according to the Stanford team. Their results are published in a May 18 study in Nature Water.
“Waterborne diseases are responsible for 2 million deaths annually, the majority in children under the age of 5,” said study ...
Some climate-smart agricultural practices may not be so smart
2023-05-18
-Several practices being promoted as climate smart could lead to land use spillovers that change their net impact on climate
-Most evidence is that cover cropping with rye, as done in the US, causes a yield loss. We show that the land use spillovers can then negate most of the climate benefit of cover cropping.
-The method and data we used were made available (as an R package) so that others can apply the same approach to other questions related to land use spillovers END ...
Keeping California’s oil in the ground will improve health but affect jobs
2023-05-18
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — As society reckons with climate change, there’s a growing call to keep fossil fuels right where they are, in the ground. But the impact of curtailing oil production will depend on the policies we implement to achieve this.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers investigated the carbon emissions, labor and health implications of several policies to reduce oil extraction, with a special focus on how the effects vary across different communities in California. Their results, published in Nature Energy, ...
Biodiversity discovery: Unknown species ("dark taxa") drive insect diversity
2023-05-18
Biodiversity loss ranks among the top three risks to humanity, as stated in the 2023 World Economic Forum Global Risks Report. Understanding biodiversity's basic building blocks is essential to monitor changes, identify influencing factors, and implement appropriate policies. However, much of terrestrial animal diversity, including insects, remains unknown or "dark taxa."
For example, the global biodiversity information portal GBIF has nine times more information on birds than insects and arthropods, despite birds only accounting ...
Climate change to push species over abrupt tipping points
2023-05-18
Climate change is likely to abruptly push species over tipping points as their geographic ranges reach unforeseen temperatures, finds a new study led by a UCL researcher.
The new Nature Ecology & Evolution study predicts when and where climate change is likely to expose species across the globe to potentially dangerous temperatures.
The research team from UCL, University of Cape Town, University of Connecticut and University at Buffalo analysed data from over 35,000 species of animals (including mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds, corals, fish, cephalopods and plankton) and seagrasses from every continent and ocean basin, alongside climate projections running up to 2100.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
Lifestyle medicine experts call meaning, purpose, and spirituality foundational to evidence-based, whole-person lifestyle change
Significant acceleration of global warming since 2015
FAU awarded $2.4M NIH grant to study immune signaling and social behavior
Deep learning-enabled virtual multiplexed immunostaining of label-free tissue for vascular invasion assessment
New PET imaging study reveals how ketamine relieves treatment-resistant depression
New study reveals differences between anime bamboo muzzle and actual bamboo
The ‘Great Texas Freeze’ killed thousands of purple martins; biologists worry recovery could take decades
Cancer has a unique nuclear metabolic fingerprint
Tiny thermometers offer on-chip temperature monitoring for processors
New compound stops common complications after intestinal surgery
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
[Press-News.org] Conservationists propose “global conservation basic income” to safeguard biodiversityAnalysis shows that paying a basic income of $5.50 per day to all residents of protected areas in low- and middle-income countries would cost less than subsidies given to fossil fuels