New analysis of critical limb-ischemia patients places best-cli trial into context within real-world setting
Limited patient population and physician representation underscore need for tailored treatment options for older critical limb-ischemia patients
2023-05-19
(Press-News.org) Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- New analysis of chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) treatment outcomes was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. Following the initial results of the BEST-CLI (Best Endovascular vs. Best Surgical Therapy in Patients With Critical Limb Ischemia) trial in 2022 which found surgical intervention superior to endovascular revascularization, questions remained regarding how inclusive the enrolled patient population was, how reflective the specialty of the physicians who performed the procedures are compared to the broader breakdown of U.S. specialists performing peripheral procedures, and whether outcome rates are similarly observed in clinical practice among Medicare beneficiaries.
CLTI is associated with poor long-term outcomes and a reduction in quality of life. The BEST-CLI trial compared two CLTI treatment options, endovascular revascularization and surgical bypass to understand which approach leads to better outcomes. While the study found surgical revascularization to be superior, the generalizability of this study to the clinical population with CLTI has not been evaluated.
The new study sought to analyze a broader clinical population by identifying all Medicare beneficiaries between 2016-2019 and aged 65-85 years with a diagnosis of CLTI who underwent endovascular or surgical revascularization. Revascularization was stratified by endovascular, autologous graft, and nonautologous graft. The endpoint was a composite of major adverse limb events (MALE) and death.
66,153 patients were included in this study (10,125 autologous graft; 7,867 nonautologous graft; 48,161 endovascular). Compared to BEST-CLI Cohort 1, patients were older, more often female and had a greater burden of comorbidities. Endovascular operators for the study population versus BEST-CLI were less likely to be surgeons (55.9% vs 73.0%) and more likely to be interventional cardiologists (25.5% vs 13.0%). The risk of death or MALE in this cohort was higher with surgery (56.6% autologous grafts vs 42.6% BEST-CLI Cohort 1; 51.6% nonautologous grafts vs 42.8% BEST-CLI Cohort 2) but similar with endovascular (58.7% real-world vs 57.4% Cohort 1; 47.0% real-world vs 47.7%). Of those receiving endovascular treatment, major interventions occurred less frequently compared to the trial (10.0% real-world vs 23.5% Cohort 1; 8.6% real-world vs 25.6% Cohort 2).
“For critical limb ischemia, the key is ensuring timely access to vascular care. Although the BEST-CLI trial is important, it doesn’t fully capture the full range of CLI patients, including older patients with greater comorbidities,” said Eric A. Secemsky, MD, MSc, FSCAI, Director of Vascular Intervention, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Mass. and study lead. “The findings from our study point to the need to individually tailor revascularization strategies based on patient risks, benefits and preferences.”
Authors note that older CLI patients may not experience the same benefit with bypass surgery as observed in BEST-CLI where at the time, fewer Medicare patients were enrolled in the trial.
Session Details:
“Contextualizing the BEST-CLI Trial Results in Clinical Practice”” [Friday, May 19, 2023, 3:40-5:10 PM MST, West 103, First Floor, Phoenix Convention Center]
About SCAI:
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) is a non-profit professional association with over 4,500 members representing interventional cardiologists and cardiac catheterization teams in the United States. SCAI promotes excellence in interventional cardiovascular medicine for both adults and children through education, representation, and the advancement of quality standards to enhance patient care.
For more information about the SCAI 2023 Scientific Sessions, visit https://scai.org/scai-2023-scientific-sessions. Follow @SCAI on Twitter for the latest heart health news and use #SCAI2023 to follow the latest discussions.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- Data from a cohort of one million patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. Using data from Medicare, the cohort, Chronic Limb threatening Ischemia Process PERformance (CLIPPER), found one out of six patients with CLTI died within their first year of diagnosis and 50% survived at five years.
CLTI is a serious condition in ...
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- Results from the Evolut FX TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement) Clinical Survey were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The survey, comprised of feedback from physicians across the United States, reported improved deliverability, tracking, and deployment of the next-generation device compared to its predecessor.
Aortic stenosis (AS), is one of the most common valvular heart diseases and can potentially lead to heart failure. Once symptoms of AS begin, average ...
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- A new study examining the criteria proposed by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) to prescribe long-term treatment with more than one blood thinner after percutaneous coronary intervention was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The study confirmed that patients presenting the characteristics proposed in the ESC guidelines are more likely to experience complications due to blood clotting in the coronary arteries. These patients may therefore benefit from a long-term treatment with more ...
2023-05-19
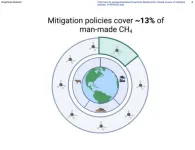
Methane, a greenhouse gas known to do about 80 times more damage to the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period, is often overlooked by policymakers and governments. In a review publishing in the journal One Earth on May 19, researchers analyzed the coverage, stringency, and real-world impact of current global methane emissions policies for the first time. They found that only 13% of emissions are currently covered by direct mitigation policies.
In order to limit climate warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius in accordance with the Paris Agreement, global methane emissions need to be cut by at least 40%–45%, according to the 2021 Global Methane Assessment—a feat that the ...
2023-05-19
New research from Queen Mary University of London shows that only around 13% of global methane emissions are regulated, despite methane emissions causing at least 25% of current global warming.
The global review, published on 19 May in One Earth, also found that little is known about the effectiveness of the policies that exist, with potentially unrepresentative methane emission estimations used rather than actual measurements. Inaccurate estimations can also mean the issue is taken less seriously by decision-makers by masking its severity.
The researchers argue that the lack ...
2023-05-19
(Philadelphia, PA) – Genetic alterations that give rise to a rare, fatal disorder known as MOGS-CDG paradoxically also protect cells against infection by viruses. Now, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have harnessed this unusual protective ability in a novel gene-editing strategy aimed at eliminating HIV-1 infection with no adverse effects on cell mortality.
The new approach, described online April 28 in the journal Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids, is based on a combination of two gene-editing constructs, one that ...
2023-05-19
About The Study: This survey study found that although there has been substantial policy attention around incentivizing COVID-19 vaccination, fewer than 1 in 10 vaccinated individuals in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults reported receiving an incentive. Most vaccinated respondents reported that an incentive did not make a difference in their decision-making to get the COVID-19 vaccine.
Authors: Laura J. Faherty, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.H.P., of the RAND Corporation in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
2023-05-19
About The Study: In this decision analytical model, increased uptake of bivalent booster vaccination among eligible age groups was associated with decreased hospitalizations and school absenteeism in the pediatric population. These findings suggest that although COVID-19 prevention strategies often focus on older populations, the benefits of booster campaigns for children may be substantial.
Authors: Alison P. Galvani, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
2023-05-19
About The Study: In this case-control surveillance study of more than 100,000 pregnancies, COVID-19 booster vaccination in pregnancy was not associated with spontaneous abortion. These findings support the safety of recommendations for COVID-19 booster vaccination, including in pregnant populations.
Authors: Elyse O. Kharbanda, M.D., M.P.H., of HealthPartners Institute in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.14350)
Editor’s ...
2023-05-19
HealthPartners Institute researchers have published new data in JAMA Network Open that shows monovalent COVID-19 booster vaccinations administered in early pregnancy (before 20 weeks’ gestation) were not associated with miscarriage. The research adds to the growing understanding about the safety of COVID-19 booster vaccinations among people who are pregnant.
The researchers analyzed data from more than 100,000 pregnancies between six and 19 weeks’ gestation from eight large health systems participating in the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD). The data was collected between Nov. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New analysis of critical limb-ischemia patients places best-cli trial into context within real-world setting
Limited patient population and physician representation underscore need for tailored treatment options for older critical limb-ischemia patients