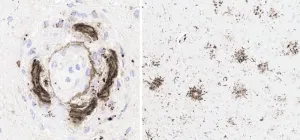
(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, May 24, 2023 – In a noteworthy case study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease investigators report autopsy findings in a 65-year-old woman with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) who received three open label infusions of the experimental anti-amyloid beta (Aβ) antibody drug lecanemab. Four days after the last infusion, she experienced stroke symptoms and died several days later due to multifocal intracerebral hemorrhage despite attempts at therapeutic intervention. Neuropathologic findings reflected therapy-induced Aβ phagocytosis involving fibrillar Aβ both in the parenchymal brain tissue and in the cerebral vasculature.
The most widely explored theory regarding AD pathogenesis is the amyloid cascade hypothesis, which states that Aβ excess in the form of neurotoxins drives the disease process in AD, with neurofibrillary degeneration, neuronal loss, and neurological deterioration occurring as downstream events. By extension, mitigation of Aβ would be a logical strategy for therapeutic intervention.
The patient participated in a phase III study of the efficacy and safety of experimental lecanemab, a humanized monoclonal therapeutic agent thought to target soluble Aβ protofibrils. The trial demonstrated a 27% reduction in the rate of cognitive decline at 18 months. The potential for adverse reactions to Aβ-targeting experimental therapies had been shown in previous clinical trials.
"It is of note that despite clinical trials targeting Aβ have been ongoing for more than 20 years and known adverse reactions clinically and on imaging (amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, or ARIA), we had essentially no insight into cellular reactions to these experimental antibodies or the mechanism of amyloid clearance prior to this case," explained lead investigator Rudolph J. Castellani, MD, Professor of Neuropathology, Department of Pathology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA.
In this case, the patient passed away after only three infusions with lecanemab, in the "subacute” phase of reaction to the drug. This finding at this point in the treatment regimen had not been previously reported. Although autopsy revealed no significant systemic cardiovascular comorbidities, examination of the brain confirmed that the anti-Aβ therapy resulted in a previously undescribed amyloid phagocytic syndrome that extended into the innumerable small blood vessels of the cerebral cortex that had abundant cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA). This appeared to have led to the onset of stroke symptoms and precipitated hemorrhage with the attempt at stroke intervention.
Dr. Castellani commented, "In this case it is, in my opinion, abundantly clear that the patient's response to the anti-Aβ therapeutic led to the clinical symptoms and provided a substrate for hemorrhage with therapeutic intervention, raising the issue of a potentially lethal drug interaction. The question then becomes whether patients receiving anti-Aβ therapeutics can be adequately evaluated for the extent of CAA (which is variable in Alzheimer’s disease, from little to no CAA, to abundant CAA, as in this case), and whether adverse and potentially lethal outcomes can be avoided. On the positive side, there appeared to be partial clearing of Aβ and possibly even phosphorylated tau, the latter not previously described. In short, improvement was achieved, but it came at the expense of collateral injury to small blood vessels involved by CAA."
Co-investigator Pouya Jamshidi, MD, Department of Pathology, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, cautioned, “Although this is the first reported case detailing the neuropathologic findings in response to lecanemab, the pattern and distribution of pathology are so striking it is inconceivable to believe this would be an isolated occurrence.”
According to M.-Marsel Mesulam, MD, Ruth Dunbar Davee Professor of Neuroscience and Chief of Behavioral Neurology, Department of Neurology, Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine, and namesake for the Mesulam Center for Cognitive Neurology and Alzheimer’s Disease at Northwestern, “The availability of lecanemab introduces a new phase in the treatment of AD. The benefits are modest at the group level and unknowable in individual patients. The side effects, even if rarely symptomatic, can be devastating as implied by this case report. Screening for cerebrovascular disease and apolipoprotein E status becomes essential for prescribing the drug. In addition, the patient may need to be told that anticoagulant treatment for stroke, should such an event occur, may become an option with even greater risk.”
"There is clearly a delicate and precarious balancing act going on between Aβ targeting culminating in a deleterious host response, especially as it relates to blood vessels involved by CAA. Better biomarkers that can accurately assess the extent of CAA are badly needed. Neuroimaging and APOE genotyping, while important for risk stratification, leave many cases of severe CAA undetected,” added Dr. Castellani.
“The results of this case call for intense and careful scrutiny of those suffering ill from these experimental drugs to minimize the risk of brain damage and death,” noted George Perry, PhD, Editor-in-Chief, Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, and Semmes Distinguished University Chair in Neurobiology at The University of Texas at San Antonio.
END
Case study reveals potentially lethal side effects of lecanemab for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
As reported in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, the study details previously unreported adverse and potentially lethal outcomes
2023-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How can universities better understand students’ experiences of violence and victimisation?
2023-05-24
Researchers from City, University of London, in collaboration with the University of Surrey, De Montfort University, Universities UK (UUK) and the National Centre (NatCen) for Social Research have conducted the first pilot study into students’ experiences of all forms of violence and victimisation at UK universities.
The Violence at University project, led by Dr Carrie-Anne Myers, Reader in the Department of Sociology and Criminology at City, aimed to investigate whether an effective tool could be developed for tracking when, where and how incidents take place.
Tackling violence and harassment has been high on universities’ agenda for several years. Hate crime has ...
Use of AI: Placebo effect increases risk-taking
2023-05-24
Human augmentation technologies refer to technological aids that enhance human abilities. They include things like exoskeletons, but also augmented reality headsets. A study at the Chair of Human-Centered Ubiquitous Media at LMU has now shown that users have high expectations of the effects of these technologies. As soon as they believe that AI is enhancing their cognitive abilities, they increase their risk-taking. And they do this independently of whether the AI is actually assisting them.
“The hype around AI applications affects the expectations of users. This can lead to riskier behavior,” says Steeven Villa, doctoral researcher ...
Mixing metals for improved performance
2023-05-24
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – A teenage fascination with metals has led to a prestigious early-career award for a superconducting radiofrequency (SRF) materials scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
Shreyas Balachandran has been chosen to receive the ICMC Cryogenic Materials Award for Excellence, presented annually to an individual under 40 who has demonstrated innovation, impact and international recognition for their work in advancing the knowledge of cryogenic materials.
“It’s ...
SwRI’s Dr. Peter Lee named STLE Fellow
2023-05-24
SAN ANTONIO — May 24, 2023 —Dr. Peter Lee of Southwest Research Institute’s Tribology Research and Evaluations Section has been named a Fellow of the Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers (STLE).
An STLE fellowship recognizes society members with significant contributions over 20 years of active practice in the field of tribology and lubrication engineering. These contributions must meet a standard considered by STLE above and beyond those typically expected of a scientist or engineer. Tribology is the study of lubrication, friction ...
Phytophthora “the plant destroyer” meets its match with a new identification tool
2023-05-24
Known as the “plant destroyer,” the genus Phytophthora is considered one of the most important groups of plant pathogens—causing significant economic and environmental losses throughout history and into today. There are over 200 identified species in the Phytophthora genus. These pathogens, and those yet to be identified, can spread quickly due to the increasing rate of global trade, e-commerce, and travel. Rapid identification is therefore critical for effective plant disease management.
While several international online resources for Phytophthora identification ...
Engineers at UMass Amherst harvest abundant clean energy from thin air, 24/7
2023-05-24
Researchers describe the “generic Air-gen effect”—nearly any material can be engineered with nanopores to harvest, cost effective, scalable, interruption-free electricity
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has recently shown that nearly any material can be turned into a device that continuously harvests electricity from humidity in the air. The secret lies in being able to pepper the material with nanopores less than 100 nanometers in diameter. The research appeared in the journal Advanced Materials.
“This is very exciting,” ...
Multifunctional interface enables manipulation of light waves in free space
2023-05-24
Recent technological advances have given us a remarkable ability to manipulate and control light waves, opening up numerous applications in various fields, such as optical communication, sensing, imaging, energy, and quantum computing. At the heart of this progress are photonic structures that can control light waves, either at the chip level in the form of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) or in free space as meta-optics. Combining these structures allows for the creation of compact optical systems. The PICs can be used to make subtle changes to the light wave, ...
Harvard professor and entrepreneur Tim Springer donates $210 million to the Institute for Protein Innovation
2023-05-24
BOSTON, March 29, 2023 — The Institute for Protein Innovation (IPI), a nonprofit research organization, announced today a $210 million gift from Tim Springer, Ph.D., veteran entrepreneur and professor at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, who founded IPI in 2017 with Andrew Kruse, Ph.D. The gift will advance protein science and accelerate research to improve human health.
The philanthropic gift—made by Springer, his wife Chafen Lu, Ph.D., and their children—adds ...
New research prizes will give $2.5 million to top scientists in Texas
2023-05-24
DALLAS – Texas scientists will receive $2.5 million in funding to advance their research thanks to a new prize program from Lyda Hill Philanthropies and TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology). The Hill Prizes, funded by Lyda Hill Philanthropies, will accelerate high-risk, high-reward research ideas with significant potential for real-world impact.
The Prizes will celebrate top Texas innovators and researchers whose work could significantly impact science and society in five categories: Medicine, Engineering, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences ...
Morressier joins the fight for science with federated integrity suite for authors and publishers
2023-05-24
Berlin and Washington DC, May 24, 2023 – Morressier announced today an integrity suite that will be offered as part of its end-to-end platform, designed to increase the quality of and trust in the outputs of scientific research.
Pre-flight checks for authors will flag potential quality issues, check for completeness of submissions, and provide recommendations for improvements in areas such as language.
Publishers using the Morressier platform now have access to a powerful suite of automated tools to help them identify integrity issues early and at scale. Plagiarism detection tools in the Morressier platform, for instance, indicate phrases in submissions that may ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
[Press-News.org] Case study reveals potentially lethal side effects of lecanemab for treatment of Alzheimer's diseaseAs reported in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, the study details previously unreported adverse and potentially lethal outcomes